Long Description: Acute myeloblastic leukemia, in remission. Version 2019 of the ICD-10-CM diagnosis code C92.01. Valid for Submission. The code C92.01 is valid for submission for HIPAA-covered transactions.
How do we diagnose acute myeloid leukemia?
Acute myeloid leukemia M6 (a) (b); Erythroleukemia ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C95.02 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Acute leukemia of unspecified cell type, in relapse Acute leukemia in relapse ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C94.21 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia, in remission
How to pronounce acute myeloid leukemia?
· Acute myeloid leukemia with multilineage dysplasia, not having achieved remission 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code C92.A0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Acute myeloid leuk w multilin dysplasia, not achieve remis
What is the ICD 10 code for history of lupus?
· Acute myeloblastic leukemia. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code. C92.0 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C92.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the symptoms of end stage leukemia?
2022 ICD-10-CM Codes C92*: Myeloid leukemia ICD-10-CM Codes › C00-D49 Neoplasms › C81-C96 Malignant neoplasms of lymphoid, hematopoietic and related tissue › Myeloid leukemia C92 Myeloid leukemia C92- Type 1 Excludes personal history of leukemia ( Z85.6) Includes granulocytic leukemia myelogenous leukemia Clinical Information
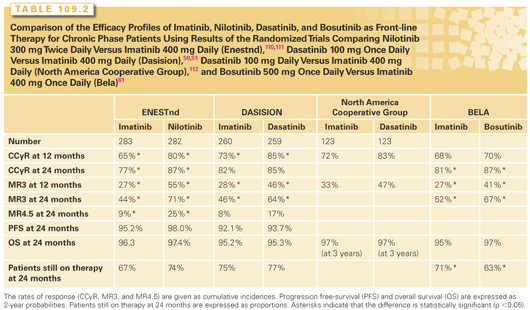
Is acute myeloid leukemia the same as acute myelogenous leukemia?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. It is the most common type of acute leukemia in adults. This type of cancer usually gets worse quickly if it is not treated. AML is also called acute myelogenous leukemia and acute nonlymphocytic leukemia.
How do you code acute myeloid leukemia?
ICD-10 Code for Acute myeloblastic leukemia, not having achieved remission- C92. 00- Codify by AAPC.
What is the difference between acute lymphocytic leukemia and acute myelogenous leukemia?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is cancer that affects the myeloid cells, which are cells that give rise to certain types of white blood cells. Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) is cancer that affects the lymphocytes, which are one of the primary white blood cells in the immune response.
What are the different types of acute myelogenous leukemia?
The types of acute myelogenous leukemia include:Myeloblastic (M0) - on special analysis.Myeloblastic (M1) - without maturation.Myeloblastic (M2) - with maturation.Promyeloctic (M3)Myelomonocytic (M4)Monocytic (M5)Erythroleukemia (M6)Megakaryocytic (M7)
What is diagnosis code C90 00?
ICD-10 code: C90. 00 Multiple myeloma Without mention of complete remission.
What is the code for acute leukemia myeloid unspecified in remission?
Valid for SubmissionICD-10:C92.90Short Description:Myeloid leukemia, unspecified, not having achieved remissionLong Description:Myeloid leukemia, unspecified, not having achieved remission
Is myeloid and myelogenous the same?
Myeloid leukemia (also known as myelogenous leukemia) may also start in white blood cells other than lymphocytes, as well as red blood cells and platelets.
What is the difference between myeloid and myelogenous leukemia?
In leukemia, the cancerous cells are discovered circulating in the blood and bone marrow, while in lymphoma, the cells tend to aggregate and form masses, or tumors, in lymphatic tissues. Myeloma is a tumor of the bone marrow, and involves a specific subset of white blood cells that produce a distinctive protein.
What's the difference between lymphocytic and myelogenous?
Lymphocytic or myelogenous leukemia Cancer can occur in either the lymphoid or myeloid white blood cells. When the cancer develops in the lymphocytes (lymphoid cells), it is called lymphocytic leukemia. When the cancer develops in the granulocytes or monocytes (myeloid cells), it is called myelogenous leukemia.
Who acute myeloid leukemia classification?
The French-American-British (FAB) classification of AMLFAB subtypeNameM0Undifferentiated acute myeloblastic leukemiaM1Acute myeloblastic leukemia with minimal maturationM2Acute myeloblastic leukemia with maturationM3Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL)5 more rows•Aug 21, 2018
What are the 4 main types of leukemia?
There are 4 main types of leukemia, based on whether they are acute or chronic, and myeloid or lymphocytic:Acute myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (AML)Chronic myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (CML)Acute lymphocytic (or lymphoblastic) leukemia (ALL)Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
What is the difference between chronic and acute leukemia?
Acute leukemia develops quickly and needs prompt treatment. Chronic leukemia develops slowly and may need management over many years. Leukemia is a cancer of the blood. It happens when blood cells in the bone marrow malfunction and form cancerous cells.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
When will the ICd 10 C92.A0 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C92.A0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is cytopenia in leukemia?
Patients often present with severe cytopenia. An acute myeloid leukemia, characterized by the presence of myelodysplastic features in at least 50% of the cells of at least two hematopoietic cell lines, arising de novo and not as a result of treatment .
What is the diagnosis for 838?
838 Chemotherapy with acute leukemia as secondary diagnosis with cc or high dose chemotherapy agent
What is acute leukemia?
Acute leukemia arising from myeloid tissue in which the granular, polymorphonuclear leukocytes and their precursors predominate.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
Where are myeloblasts found?
An aggressive (fast-growing) disease in which too many myeloblasts (immature white blood cells that are not lymphoblasts) are found in the bone marrow and blood.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as C92.0. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
Is Raeb-T a subcategory of myelodysplastic syndrome?
Raeb-t used to be a subcategory of myelodysplastic syndromes in the past. Recently, the term has been eliminated from the who based classification of myelodysplastic syndromes. The reason is that the percentage of peripheral blood blasts required for the diagnosis of acute myeloid leukemia has been reduced to 20%.
Is raeb-t a leukemia?
Currently, according to who classification, the vast majority of raeb-t cases are best classified as acute leukemias (acute leukemias with multilineage dysplasia following myelodysplastic syndrome). A minority of cases are part of raeb-2.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
When will the ICd 10 C92.51 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C92.51 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the diagnosis for 838?
838 Chemotherapy with acute leukemia as secondary diagnosis with cc or high dose chemotherapy agent
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What type of leukemia is characterized by no differentiation?
Leukemia in which the involved cell shows little or no differentiation, usually consisting of blast cells; two types are distinguished, acute lymphocytic and acute myelogenous leukemia.
What is a malignant neoplasm?
secondary and unspecified neoplasm of lymph nodes ( C77.-) A clonal (malignant) hematopoietic disorder affecting the bone marrow and the peripheral blood.
When will the ICd 10 C95.00 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C95.00 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the diagnosis for 838?
838 Chemotherapy with acute leukemia as secondary diagnosis with cc or high dose chemotherapy agent
What is the approximate match between ICd9 and ICd10?
This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code C92.A0 and a single ICD9 code, 205.00 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What are the lymphatic and hematopoietic tumors?
Tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues or haematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies are tumors that affect the blood, bone marrow, lymph, and lymphatic system. As those elements are all intimately connected through both the circulatory system and the immune system, a disease affecting one will often affect the others as well, making myeloproliferation and lymphoproliferation (and thus the leukemias and the lymphomas) closely related and often overlapping problems.
What is acute leukemia?
An acute leukemia of ambiguous lineage in which there is a dual population of blasts with each population expressing markers of a distinct lineage (myeloid and lymphoid or b-and t-lymphocyte). (who, 2001)
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What type of leukemia is characterized by no differentiation?
Leukemia in which the involved cell shows little or no differentiation, usually consisting of blast cells; two types are distinguished, acute lymphocytic and acute myelogenous leukemia.
What is a malignant neoplasm?
secondary and unspecified neoplasm of lymph nodes ( C77.-) A clonal (malignant) hematopoietic disorder affecting the bone marrow and the peripheral blood.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as C95.0. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
What is the ICD-10 code for acute myeloid leukemia?
C92.6 is a non-billable ICD-10 code for Acute myeloid leukemia with 11q23-abnormality. It should not be used for HIPAA-covered transactions as a more specific code is available to choose from below.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 Excludes note is a pure excludes. It means 'NOT CODED HERE!' An Excludes1 note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as the code above the Excludes1 note. An Excludes1 is used when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
What is a code also note?
A “code also” note instructs that two codes may be required to fully describe a condition, but this note does not provide sequencing direction. The sequencing depends on the circumstances of the encounter.
What is the most common type of acute myeloid leukemia?
In acute myeloid leukemia (AML ), there are too many of a specific type of white blood cell called a myeloblast. AML is the most common type of acute leukemia in adults. This type of cancer usually gets worse quickly if it is not treated.
What is the meaning of AML?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of acute leukemia. "Acute" means that the leukemia usually gets worse quickly if it's not treated. In AML, the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets. When the abnormal cells crowd out the healthy cells, it can lead to infection, anemia, and easy bleeding. The abnormal cells can also spread outside the blood to other parts of the body.
When was the ICd 10 code implemented?
FY 2016 - New Code, effective from 10/1/2015 through 9/30/2016 (First year ICD-10-CM implemented into the HIPAA code set)
What tests are needed for AML?
If you are diagnosed with AML, you may have additional tests to see whether the cancer has spread. These include imaging tests and a lumbar puncture , which is a procedure to collect and test cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
What causes AML?
AML happens when there are changes in the genetic material (DNA) in bone marrow cells. The cause of these genetic changes is unknown. However, there are certain factors that raise your risk of AML.
Is leukemia a cancer?
Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. White blood cells help your body fight infection. Your blood cells form in your bone marrow. In leukemia, however, the bone marrow produces abnormal white blood cells. These cells crowd out the healthy blood cells, making it hard for blood to do its work. In acute myeloid leukemia (AML), there are too many of a specific type of white blood cell called a myeloblast.

Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the icd 10 diagnosis code for bleeding from frenulum of penis
- 2. icd 10 code for left ischium contusion
- 3. icd-10 code for ana
- 4. icd 10 code for suspcious skin lesion
- 5. icd 10 code for history of cardiac stents
- 6. icd-10 code for hemodynamic instability
- 7. icd-10-cm code for exceptionally large newborn baby
- 8. what icd-10-cm code is reported for personal history of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder?
- 9. icd 10 code for infected insect bite right cald\f
- 10. icd 10 code for traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage with unspecified loss of consciouness