Acute and subacute hepatic failure without coma. K72.00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM K72.00 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What are the signs and symptoms of acute liver failure?
· Acute necrosis of liver Hepatic necrosis, subacute Subacute hepatic necrosis Subacute liver failure ICD-10-CM K72.00 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 441 Disorders of liver except malignancy, cirrhosis or alcoholic hepatitis with mcc 442 Disorders of liver except malignancy, cirrhosis or alcoholic hepatitis with cc
Can acute liver failure be cured?
· Chronic hepatic failure without coma. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. K72.10 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K72.10 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What does acute liver failure stand for?
Acute and subacute hepatic failure; Acute hepatic failure; Acute hepatic necrosis; Acute liver failure; Acute necrosis of liver; Hepatic necrosis, subacute; Subacute hepatic necrosis; Subacute liver failure. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K72.00. Acute …
What causes sudden liver failure?
K71.0 Toxic liver disease with cholestasis; K71.1 Toxic liver disease with hepatic necrosis. K71.10 Toxic liver disease with hepatic necrosis, wi... K71.11 Toxic liver disease with hepatic necrosis, wi... K71.2 Toxic liver disease with acute hepatitis; K71.3 Toxic liver disease with chronic persistent h... K71.4 Toxic liver disease with chronic lobular hepa...
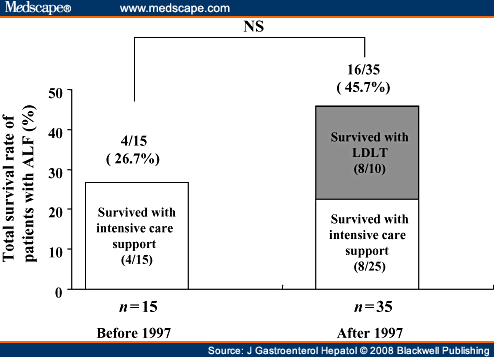
What is the difference between acute liver failure and chronic liver failure?
Acute liver failure is a rare condition. It happens when your liver suddenly begins to lose its ability to function. This often happens right after an overdose of medicine or poisoning. Chronic liver failure happens over a long stretch of time.
What is acute-on-chronic liver disease?
Acute-on-chronic liver failure is a syndrome that affects patients with chronic liver disease; is characterized by intense systemic inflammation, organ failure, and a poor prognosis; and frequently develops in close association with precipitating events.
What is the ICD 10 code for chronic liver disease?
ICD-10-CM Code for Liver disease, unspecified K76. 9.
What is acute-on-chronic liver failure Aclf?
Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is a serious condition which develops in patients with chronic liver disease (CLD) with compensated and decompensated cirrhosis. ACLF is defined as acute hepatic decompensation, development of multiorgan failure, and high risk of short-term mortality (1–3).
Can chronic liver failure become acute?
Acute on chronic liver failure is a clinical syndrome of sudden hepatic decompensation observed in patients with pre-existing chronic liver disease. Acute on chronic liver failure is a serious condition with very high morbidity and mortality.
What is acute decompensated liver failure?
Decompensated cirrhosis is defined as an acute deterioration in liver function in a patient with cirrhosis and is characterised by jaundice, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, hepatorenal syndrome or variceal haemorrhage.
What is the ICD-10 code for acute hepatic encephalopathy?
572.2 - Hepatic encephalopathy | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for end stage liver disease?
A diagnosis of just “end-stage liver disease” or ESLD is captured with K72. 90 (Hepatic failure, unspecified without coma).
What is ICD-10 code for cirrhosis of liver?
K74. 60 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K74.
What is the difference between acute liver failure and cirrhosis?
Acute liver failure is a true emergency, requiring intensive care and oftentimes transfer of the patient to a liver transplant center. Patients with decompensated cirrhosis have complications of portal hypertension, including variceal hemorrhage, ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, and hepatic encephalopathy.
Is acute liver failure cirrhosis?
The causes of acute liver failure, when the liver fails rapidly, include: Acetaminophen overdose: Large doses can damage your liver or lead to failure. Viruses including hepatitis A, B, and E, the Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, and herpes simplex virus: They lead to liver damage or cirrhosis.
Is cirrhosis chronic or acute?
Key points about cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a long-term (chronic) liver disease. The most common causes are hepatitis and other viruses, and alcohol abuse. Other medical problems can also cause it. The damage to the liver usually can't be reversed.
Is heart failure a chronic disease?
Heart failure can also be acute, chronic, or acute on chronic. In this case, acute heart failure is heart failure that happens when there has been sudden damage to the heart—for example, due to an MI, thrombus in the heart, or severe infection. Acute heart failure is life threatening.
Is heart failure life threatening?
Acute heart failure is life threatening. Chronic heart failure happens slowly and is typically due to an underlying condition, such as hypertension or heart disease. Acute on chronic is seen when a patient has chronic heart failure and suffers an acute exacerbation.
What are the different types of asthma?
Asthma is categorized by severity: 1 Mild intermittent: The patient is symptomatic two or fewer days per week, awakens at night two times or fewer per month, uses a rescue inhaler two or fewer days per week, has no interference with normal activity, and has greater than 80 percent predicted lung functions and normal lung function between exacerbations. 2 Mild persistent: The patient is symptomatic more than two days per week; awakens at night three to four times per month; uses a rescue inhaler more than two days per week, but not daily; has minor limitation with normal activity; and has greater than 80 percent predicted lung function. 3 Moderate persistent: The patient is symptomatic daily; awakens at night more than once per week, but not nightly; uses a rescue inhaler daily; has some limitation with normal activity; and has 60-80 percent predicted lung functions. 4 Severe persistent: The patient is symptomatic throughout the day; awakens nightly; uses a rescue inhaler several times per day; has extreme limitations with normal activity; and has less than 60 percent predicted lung functions.
What does acute mean in medical terms?
To help clear up any coding confusion you may have, first consider Merriam-Webster’s definition of acute: (1): characterized by sharpness or severity, “acute pain” (2): having a sudden onset, sharp rise, and short course, “acute disease” (3): being, providing, or requiring short-term medical care (as for serious illness or traumatic injury) ...
What is ST elevation?
ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) occurs when there is a transmural infarction of the myocardium, which means the entire thickness of the myocardium (endocardium, myocardium, and pericardium) has undergone necrosis. This results in ST elevation on an electrocardiogram (ECG).
Is heart failure systolic or diastolic?
Heart failure can be systolic, diastolic, or combined systo lic and diastolic: When the left ventricle can’t contract enough, it’s systolic heart failure. When the left ventricle can’t fill with enough blood, it’s diastolic heart failure. Heart failure can also be acute, chronic, or acute on chronic.
How many children have asthma?
According to the American Lung Association, asthma is one of the most common chronic disorders in childhood, with an estimated 7.1 million children under 18 years of age affected.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for hyperpigmented keloid
- 2. icd 10 code for atn
- 3. icd 10 dx code for history of nstemi
- 4. icd 10 code for passenger injured in collision with unspecified motor vehicles in traffic accident
- 5. icd 10 code for arm weaknesss
- 6. icd 10 diagnosis code for psvt
- 7. icd 9 code for tailbone pain
- 8. icd 10 code for acute lateral wall myocardial infarction, initial episode
- 9. icd 10 code for exploratory laparoscopy
- 10. icd 9 code for pneumonia nos