What is the diagnosis code for renal failure?
Malignant hypertensive heart and chronic renal disease with congestive heart failure; code to identify. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I13.0. Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease with heart failure and stage 1 through stage 4 chronic kidney disease, or …
What is the ICD 10 code for kidney injury?
Icd 10 Code For Acute Renal Failure On Chronic Kidney Disease. Millions of Americans are estimated to have Chronic Kidney Disease. Most of the time dialysis or kidney transplants are the only options for those in the advanced stage of the disease. Take a look at to the Kidney Disease Solution, an all-in-one guide for improving kidney health and ...
What is the ICD 9 code for chronic renal disease?
What is the Kidney Disease Solution? Icd 10 Diagnosis Code For Acute On Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Disease Solution Kidney Disease Solution is an all-in-one program designed to enhance renal health as well as reverse the effects of kidney disease. It teaches you everything you need to learn about kidneys and the natural cure for kidney disease.
What is the CPT code for acute kidney injury?
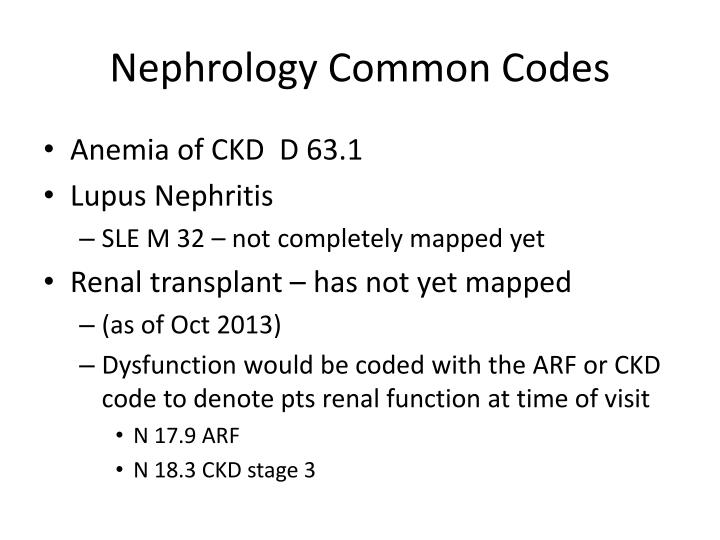
Oct 01, 2021 · Acute kidney failure, unspecified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code N17.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N17.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.

What is the ICD 10 code for acute kidney disease?
Acute kidney failure, unspecified N17. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N17. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is acute on chronic renal failure?
Acute kidney injury is a medical emergency characterised by a rapid (hours to days) fall in glomerular filtration rate. Most people who experience acute kidney injury have some degree of pre-existing chronic kidney disease (CKD).
What is the ICD 10 code for AKI on CKD 3?
Chronic kidney disease, stage 3 unspecified The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N18. 30 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can renal failure be both acute and chronic?
Kidney problems can develop suddenly (acute) or over the long term (chronic). Many conditions, diseases, and medicines can create situations that lead to acute and chronic kidney problems. Acute kidney injury, which used to be called acute renal failure, is more commonly reversible than chronic kidney failure.
What is the difference between acute and chronic renal failure?
Chronic kidney failure is a condition where the kidneys' ability to filter waste from the bloodstream becomes worse over time, generally over a period of years. Acute kidney failure is the sudden loss of this important ability. If your kidneys have experienced a direct injury or an obstruction, you are at risk.
What are the three types of acute renal failure?
Based upon the cause, acute renal failure or ARF (also called acute kidney injury) can be divided into three main types: prerenal, renal, and postrenal.Jan 5, 2022
How do you code acute kidney injury?
The most common code reported for the diagnosis of AKI is N17. 9 (Acute kidney failure, unspecified).May 12, 2020
Is renal insufficiency the same as CKD?
Chronic renal insufficiency causes a slow loss of renal function. It is basically the end stage of chronic renal disease, which means the patient often requires dialysis treatment.
What is the difference between ICD 10 N18 31 and N18 32?
N18. 31- Chronic Kidney Disease- stage 3a. N18. 32- Chronic Kidney Disease- stage 3b.Oct 9, 2020
What is the difference between CKD and AKD?
Relationships between AKI, CKD, and AKD. AKD encompasses a spectrum that includes both AKI and CKD. AKI may contribute to the development or progression of CKD, while CKD is a strong risk factor for AKI.Nov 11, 2015
What causes renal failure?
Gradual and usually permanent loss of kidney function resulting in renal failure. Causes include diabetes, hypertension, and glomerulonephritis. Impairment of health or a condition of abnormal functioning of the kidney. Impairment of the renal function due to chronic kidney damage.
What are the risks of kidney disease?
You are at greater risk for kidney disease if you have diabetes, high blood pressure, or a close family member with kidney disease. chronic kidney disease damages the nephrons slowly over several years. Other kidney problems include: cancer. cysts.
What is the function of kidneys?
Their main job is to filter wastes and excess water out of your blood to make urine. They also keep the body's chemical balance, help control blood pressure, and make hormones.chronic kidney disease (ckd) means that your kidneys are damaged and can't filter blood as they should.
What are the stages of kidney disease?
Chronic kidney disease and its severity are categorized in five stages: 1 Stage I (code 585.1), kidney damage with normal or increased GFR (greater than or equal to 90) 2 Stage II (code 585.2), kidney damage with mild decreased GFR (60–89) 3 Stage III (code 585.3), moderate with decreased GFR (30–59)
What is AKI in medical terms?
Acute kidney injury ( AKI) is a common disorder, with a population incidence of about 2,000 per million population (pmp). Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), as evidenced by a low eGFR or presence of proteinuria, are at higher risk for developing AKI, a condition known as acute on chronic renal failure (ACRF).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for aftercare following knee replacement
- 2. icd 10 code for nonketotic hyperglycinemia
- 3. icd 10 code for initial office visit
- 4. icd 10 code for cast complication
- 5. icd 10 code for syncope r55.9
- 6. icd-10 code for abrasion of foot
- 7. icd 10 code for associated chronic pain nos
- 8. what is the icd 10 code for non-progressive leukoencephalopathy of unknown etiology
- 9. icd 10 code for multiple compression fractures of thoracic vertebrae
- 10. icd 10 code for feeding tube obstruction