Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) of non-infectious origin without acute organ dysfunction. R65.10 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM R65.10 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What are the signs and symptoms of acute organ dysfunction?
Acute organ dysfunction can manifest in any organ, and frequently manifests clinically as shock, respiratory failure, acute kidney injury, hematologic or metabolic disturbances, or neurologic decline. When coding sepsis and severe sepsis which code should be sequenced first?
What is the ICD 10 code for acute kidney failure?
They must be used in conjunction with an underlying condition code and they must be listed following the underlying condition. code to identify specific acute organ dysfunction, such as: acute kidney failure ( ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N17. N17 Acute kidney failure N17.0 Acute kidney failure with tubular necrosis.
What is the CPT code for sepsis with acute organ dysfunction?
The coding of severe sepsis requires a minimum of two codes: first a code for the underlying systemic infection, followed by a code from subcategory R65. 2, Severe sepsis. If the causal organism is not documented, assign code A41. 9, Sepsis, unspecified organism, for the infection. Furthermore, what is severe sepsis with acute organ dysfunction?
Which ICD 10 code should not be used for reimbursement purposes?
R65.2 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R65.2 became effective on October 1, 2021.

What is the ICD-10 code for organ failure?
Hence, A41 should always be reported with the R65. 20 code and a specific organ dysfunction (or organ failure) code.
What is A41 89?
ICD-10 code A41. 89 for Other specified sepsis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases .
What is the ICD-10 code for multiple organ failure?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R65. 11 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of R65.
Do you code A41 9 R65 21?
Chapter-specific guidelines state, “First code for the underlying systemic infection, followed by R65. 21, septic shock. If the causal organism is not documented, assign code A41. 9, sepsis, unspecified organism, for the infection.
What is diagnosis code u071?
What is diagnosis code U07. 1? Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) due to the COVID-19 virus has been identified by testing or asymptomatic patients who have tested positive for coronavirus.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is an acute organ dysfunction?
Presence of altered organ function in an acutely ill patient such that homeostasis cannot be maintained without intervention. abbreviation: SIRS, systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
What is multiple organ dysfunction syndrome?
The Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS) can be defined as the development of potentially reversible physiologic derangement involving two or more organ systems not involved in the disorder that resulted in ICU admission, and arising in the wake of a potentially life-threatening physiologic insult.
Is acute respiratory failure and organ dysfunction?
Mortality in ARDS primarily results from progressive multiple organ failure rather than refractory hypoxemia. As such, ARDS is perceived as signifying the pulmonary manifestation of multiple organ dysfunction.
Can R65 21 be a primary diagnosis?
The code for septic shock cannot be assigned as a principal diagnosis. For septic shock, the code for the underlying infection should be sequenced first, followed by code R65. 21, Severe sepsis with septic shock or code T81.
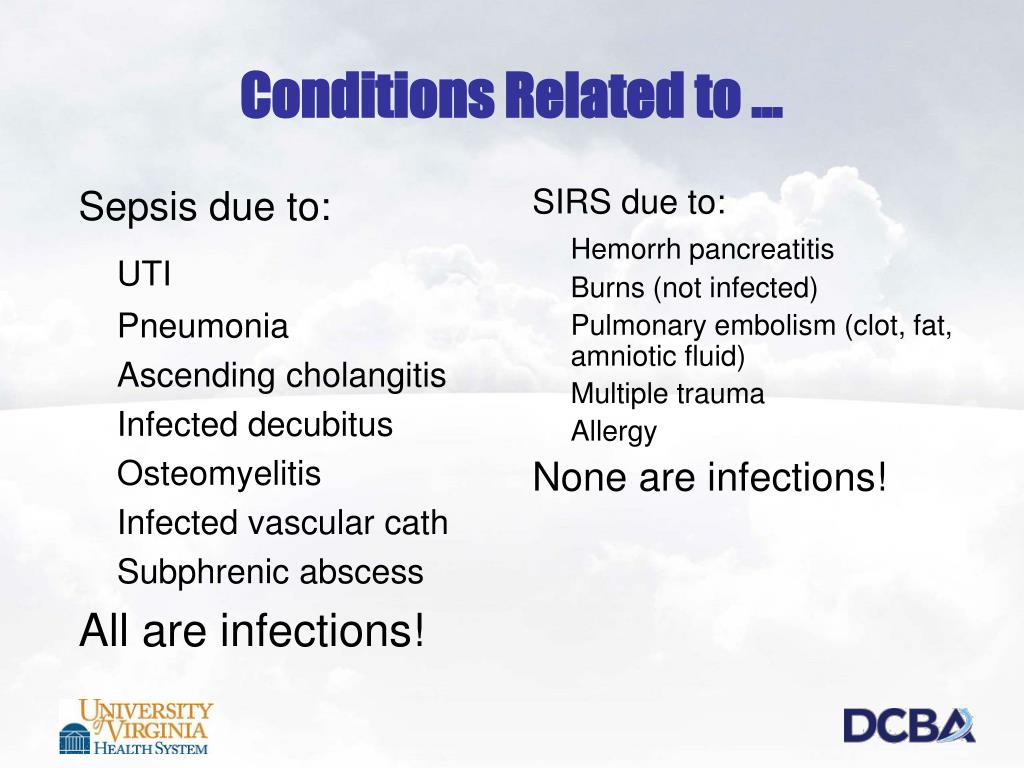
What's the difference between SIRS and sepsis?
Sepsis is a systemic response to infection. It is identical to SIRS, except that it must result specifically from infection rather than from any of the noninfectious insults that may also cause SIRS (see the image below).
Which of the following Z codes can only be used for a principal diagnosis?
A code from categories Z03-Z04 can be assigned only as the principal diagnosis or reason for encounter, never as a secondary diagnosis.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
What is a code title?
Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code. "In diseases classified elsewhere" codes are never permitted to be used as first listed or principle diagnosis codes.
What is Sepsis associated with?
Sepsis associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection.
When will the ICD-10-CM R65.2 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R65.2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the code for sepsis without organ dysfunction?
There are codes for sepsis without organ dysfunction (A41); and if organ dysfunction is present, additional codes are needed (A41. plus R65.20, plus specific organ dysfunction or failure codes). But the current sepsis definition indicates that life-threatening organ dysfunction should be present. This is what confuses most folks because it implies that with sepsis, there is already organ dysfunction. Hence, A41 should always be reported with the R65.20 code and a specific organ dysfunction (or organ failure) code.
What is a life threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection?
Sepsis is defined as a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection. Now, what would be considered "life-threatening?" Let's use a non-medical situation. A bomb would be considered life-threatening because it could detonate at any time. What about a dagger? A gun? Does it have to depend on the circumstances? In medicine, there is a wide range of life-threatening situations. Sepsis in itself is life-threatening, but so is acute blood loss, acute asthma, and/or acute heart failure (systolic/diastolic).
What is the code for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction?
Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and heart failure with reduced systolic function now can be coded to systolic heart failure. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) or heart failure with preserved systolic function now can be coded to diastolic heart failure.
What is organ failure?
Organ failure is defined as dysfunction to such a degree that normal homeostasis cannot be maintained without external clinical intervention. Think of dysfunction as a continuum going from mild to extreme, of which failure would be the extreme outcome.
What is organ dysfunction?
But are they? Organ dysfunction is defined as an abnormality or impairment in the function of a specified bodily organ or system.
What is the third definition of sepsis?
The third definition of sepsis was a reaction to the overuse of the term brought about by the 1992 systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) criteria in the first definition , which the second definition , issued in 2001, was unable to curb. Thus the term "life-threatening.".
How long does it take for a doctor to rule out sepsis?
A discerning provider will see the change with the patient's return to baseline (within four to six hours) and rule out sepsis ("sepsis ruled out" needs to be documented in next day's progress note). This is why medicine is called an art and a science.
What is the ICd 10 code for inflammatory response syndrome?
R65.10 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) of non-infectious origin without acute organ dysfunction . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 .
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also: Syndrome see also Disease.
What is systemic disease?
Systemic disease associated with the presence of pathogenic microorganisms or their toxins in the blood. The presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the blood stream causing a rapidly progressing systemic reaction that may lead to shock. Symptoms include fever, chills, tachycardia, and increased respiratory rate.
What is the term for the presence of bacteria or their toxins in the blood or tissues?
Urosepsis . Clinical Information. (sep-sis) the presence of bacteria or their toxins in the blood or tissues. A disorder characterized by the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the blood stream that cause a rapidly progressing systemic reaction that may lead to shock.
When will the ICD-10 A41.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM A41.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the life threatening condition that occurs when the body’s response to an infection damages its own tissues?
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when the body’s response to an infection damages its own tissues. Without timely treatment, sepsis can progress rapidly and lead to tissue damage, organ failure, and then death. Proper coding of sepsis and SIRS requires the coder to understand the stages of sepsis and common documentation issues.
How does sepsis affect the body?
Sepsis is an extreme response to infection that develops when the chemicals the immune system releases into the bloodstream to fight infection cause widespread inflammation. This inflammation can lead to blood clots and leaky blood vessels, and without timely treatment, may result in organ dysfunction and then death. Severe cases of sepsis often result from a body-wide infection that spreads through the bloodstream, but sepsis can also be triggered by an infection in the lungs, stomach, kidneys, or bladder. Thus, it is not necessary for blood cultures to be positive to code sepsis (guideline I.C.1.d.1.a.i).
How many codes are needed for sepsis?
Coding tips: Only one code is needed to report sepsis without organ dysfunction. Most sepsis codes are listed in A40.- through A41.9. If a causal organism is specified, then use the code for sepsis naming the specific organism. Per AHA Coding Clinic® (Vol. 5, No. 1, p. 16), when sepsis is linked to an infection with an organism, assign the combination code for sepsis including the organism. For example, sepsis due to E. coli UTI can be coded as A41.51 and N39.0.
Why is severe sepsis not assigned?
For instance, if sepsis, pneumonia, and acute renal failure due to dehydration are documented, the code for severe sepsis may not be assigned because the acute renal failure is not stated as due to or associated with sepsis. If the documentation is unclear, query the physician.
What is severe sepsis?
Severe sepsis is sepsis with acute organ dysfunction. It occurs when one or more of the body’s organs is damaged from the inflammatory response. Any organ can be affected.
What is the code for candida sepsis?
Sepsis can be caused by fungi, candida, or viruses, as well. It is important to use the Alphabetic Index to select the appropriate code for the systemic infection. For example, if a patient is diagnosed with candidal sepsis due to a candida UTI, you would report B37.7 Candidal sepsis for the principal diagnosis and B37.49 Other urogenital candidiasis for the secondary diagnosis. Do not select a code from A40.- through A41.9.
What is SIRS in the body?
SIRS is an inflammatory state affecting the whole body. It is an exaggerated defense response of the body to a noxious stressor, such as infection or trauma, that triggers an acute inflammatory reaction, which may progress and result in the formation of blood clots, impaired fibrinolysis, and organ failure.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for electrolyte imbalance
- 2. icd 9 code for new office visit
- 3. icd 10 code for colonic polyp
- 4. icd 10 code for right shoulder bicipital tendinitis
- 5. icd 10 code for generalized muscle pain
- 6. icd-10 code for colon resection
- 7. icd 10 code for right thumb contusion
- 8. icd 10 code for possible pneumonia
- 9. icd 10 code for right knee replacement
- 10. icd 10 code for bladder outlet obstruction due to bph