How do you diagnose osteomyelitis?
Oct 01, 2021 · Other acute osteomyelitis, left ankle and foot 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code M86.172 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M86.172 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the diagnosis code for left foot pain?
ICD-10 code M86.072 for Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis, left ankle and foot is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Osteopathies and chondropathies . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
What are the differential diagnoses for osteomyelitis?
Oct 01, 2021 · M86.171 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M86.171 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M86.171 - other international versions of ICD-10 M86.171 may differ.
How is osteomyelitis diagnosed?
Oct 01, 2021 · Osteomyelitis, unspecified. M86.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M86.9 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M86.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 M86.9 may differ.
What is the ICD-10 code for right calcaneal osteomyelitis?
M86. 171 - Other acute osteomyelitis, right ankle and foot. ICD-10-CM.
What is osteomyelitis of the foot?
Osteomyelitis is inflammation or swelling that occurs in the bone. It can result from an infection somewhere else in the body that has spread to the bone, or it can start in the bone — often as a result of an injury. Osteomyelitis is more common in younger children (five and under) but can happen at any age.
What is the ICD-10 code M86 172?
ICD-10 | Other acute osteomyelitis, left ankle and foot (M86. 172)
What is acute osteomyelitis?
Acute osteomyelitis is the clinical term for a new infection in bone. This infection occurs predominantly in children and is often seeded hematogenously. In adults, osteomyelitis is usually a subacute or chronic infection that develops secondary to an open injury to bone and surrounding soft tissue.Jun 15, 2001
How do you get osteomyelitis of the foot?
Osteomyelitis occurs when bacteria from nearby infected tissue or an open wound circulate in your blood and settle in bone, where they multiply. Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (staph infection) typically cause osteomyelitis. Sometimes, a fungus or other germ causes a bone infection.Dec 1, 2021
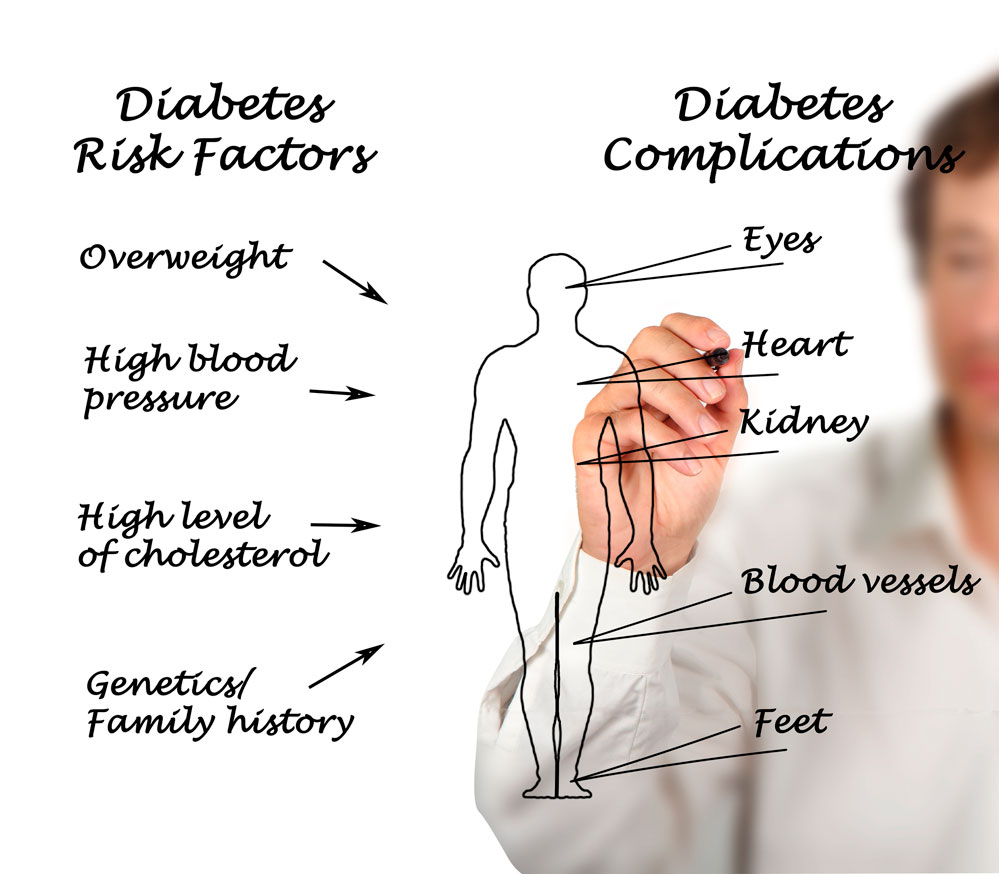
What is diabetic foot osteomyelitis?
Diabetic foot osteomyelitis (DFO) is mostly the consequence of a soft tissue infection that spreads into the bone, involving the cortex first and then the marrow. The possible bone involvement should be suspected in all DFUs patients with infection clinical findings, in chronic wounds and in case of ulcer recurrence.
What is ICD-10 code for left toe osteomyelitis?
M86. 172 - Other acute osteomyelitis, left ankle and foot. ICD-10-CM.
What is ICD-10 code for Left foot Pain?
ICD-10 | Pain in left foot (M79. 672)
What is hematogenous osteomyelitis?
In children, hematogenous osteomyelitis is an infection that primarily affects the most vascularized regions of the growing skeleton. The disease has increased in frequency, virulence, and degree of soft-tissue involvement.May 17, 2017
What are types of osteomyelitis?
Traditionally, osteomyelitis is a bone infection that has been classified into three categories: (1) a bone infection that has spread through the blood stream (Hematogenous osteomyelitis) (2) osteomyelitis caused by bacteria that gain access to bone directly from an adjacent focus of infection (seen with trauma or ...
What is the difference between acute and chronic osteomyelitis?
Acute osteomyelitis typically presents two weeks after bone infection, characterised by inflammatory bone changes. By contrast, chronic osteomyelitis typically presents six or more weeks after bone infection and is characterised by the presence of bone destruction and formation of sequestra.May 31, 2016
How do you classify osteomyelitis?
Osteomyelitis can be classified by duration (acute or chronic), pathogenesis (trauma, contiguous spread, hematogenous, surgical), site, extent, or type of patient.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for lumbar deg
- 2. icd 10 pcs code for mechanical gait training
- 3. screening for vitamin d deficiency icd 10 code
- 4. icd 9 code for stage 4 pressure ulcer
- 5. icd 10 code for hiv screening medicare
- 6. icd 10 code for lasik post op
- 7. icd 10 code for oxygen therapy dependent
- 8. icd 10 code for bilateral greater trochanteric bursitis
- 9. icd 10 code for bilateral leg contractures
- 10. icd 10 code for trouble breathing