What are common ICD 10 codes?
ICD-10-CM Common Codes for Gynecology and Obstetrics ICD-10 Code Diagnoses Menstrual Abnormalities N91.2 Amenorrhea N91.5 Oligomenorrhea N92.0 Menorrhagia N92.1 Metrorrhagia N92.6 Irregular Menses N93.8 Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding N94.3 Premenstrual Syndrome N94.6 Dysmenorrhea Disorders Of Genital Area L29.3 Vaginal Itch N73.9 N75.0 Bartholin’s Cyst N76.0
Should antibiotics be prescribed for acute otitis media?
Management of acute otitis media should begin with adequate analgesia. Antibiotic therapy can be deferred in children two years or older with mild symptoms. High-dose amoxicillin (80 to 90 mg per kg per day) is the antibiotic of choice for treating acute otitis media in patients who are not allergic to penicillin.
When did ICD 10 effective?
Work on ICD-10 began in 1983, became endorsed by the Forty-third World Health Assembly in 1990, and was first used by member states in 1994. It was replaced by ICD-11 on January 1, 2022.
What are the risk factors for acute otitis media (AOM)?
- Hearing loss (conductive and sensorineural)
- TM perforation (acute and chronic)
- Chronic suppurative otitis media (with or without cholesteatoma)
- Cholesteatoma
- Tympanosclerosis
- Mastoiditis
- Petrositis
- Labyrinthitis
- Facial paralysis
- Cholesterol granuloma
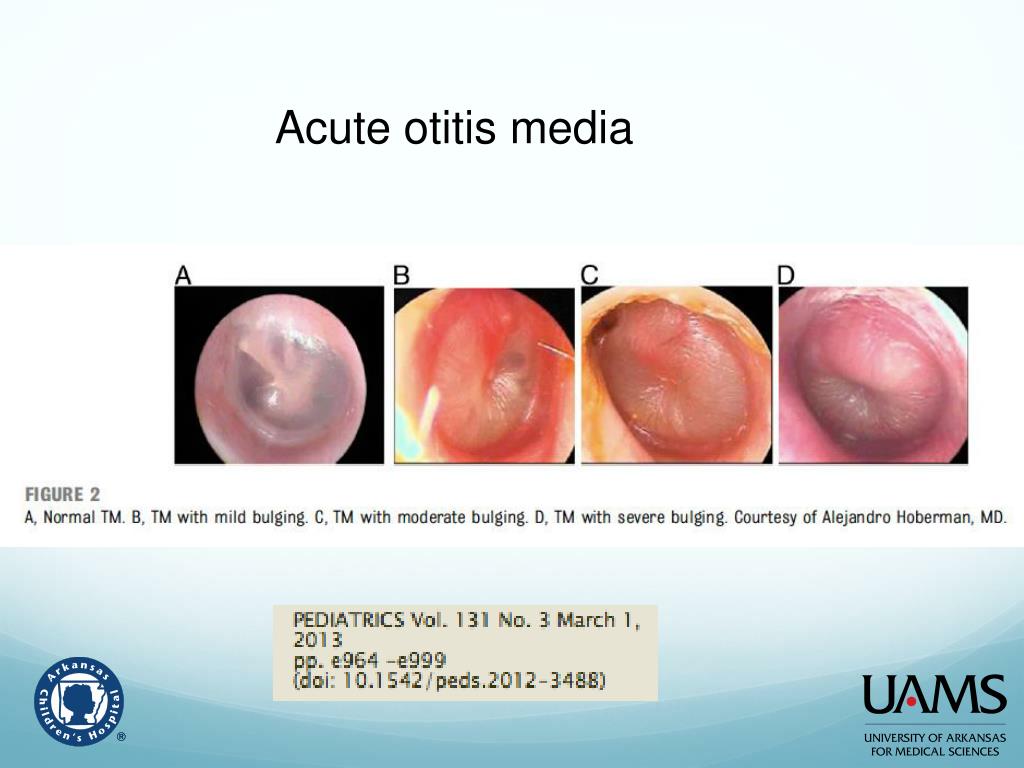
What is the ICD-10 code for bilateral otitis media?
ICD-10 code H66. 93 for Otitis media, unspecified, bilateral is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the ear and mastoid process .
What is the ICD-10 code for left acute otitis media?
ICD-10 Code for Otitis media, unspecified, left ear- H66. 92- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for right acute otitis media?
ICD-10 Code for Otitis media, unspecified, right ear- H66. 91- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for bilateral chronic and acute serous otitis media?
23: Chronic serous otitis media, bilateral.
What is acute serous otitis media?
Acute Serous Otitis Media Acute otitis media (AOM) is the most common ear infection, causing pain and swelling in the ear. A doctor can diagnose AOM simply by looking into your child's ears with an otoscope.
What is the diagnosis for ICD 10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is the CPT code for otitis media?
ICD-10-CM: H66. 001 (acute suppurative otitis media without spontaneous rupture of eardrum, right ear) CPT: 99203.
Which of the following is the correct code for Acute reactive otitis externa bilateral?
ICD-10-CM Code for Acute reactive otitis externa, bilateral H60. 553.
What is the ICD 10 code for otitis media?
ICD-10-CM Code for Otitis media, unspecified H66. 9.
What is the ICD 10 code for chronic otitis media?
Chronic serous otitis media, unspecified ear H65. 20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H65. 20 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is bilateral chronic serous otitis media?
Chronic otitis media- This is a middle ear infection that does not go away, or happens repeatedly, over months to years. The ear may drain (have liquid coming out of the ear canal). It can often be accompanied by a tympanic membrane perforation and hearing loss. Usually chronic otitis media is not painful.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for myopia unspecified
- 2. icd 10 cm code for tortuous colon
- 3. what is the correct icd 10 code for acute left hand cellulitis
- 4. icd-10 code for lithium level
- 5. icd 10 code for ethylene glycol poisoning
- 6. icd 10 cm code for allergic exacerbation af asthma
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for leg swelling
- 8. icd 10 code for rpr uric acid
- 9. icd 10 code for activity fall and twist
- 10. icd 10 code for cervical radciulopathy