What is the ICD 10 code for renal insufficiency?
Type 1 Excludes. chronic renal insufficiency ( N18.9) unspecified nephritic syndrome ( N05.-) ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code O03.32 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Renal failure following incomplete spontaneous abortion. Incomplete miscarriage with renal failure; Incomplete pregnancy loss with kidney disease; Incomplete spontaneous abortion with renal failure;
What is the NU code for acute kidney failure?
Acute kidney failure, unspecified 1 N00-N99 Diseases of the genitourinary system. 2 N17-N19 Acute kidney failure and chronic kidney disease. 3 N17 Acute kidney failure.
What is the CPT code for chronic kidney disease?
code for any associated acute kidney failure and chronic kidney disease ( N17.-, N18.-)
What is the ICD 10 code for calcification of the kidney?
Diagnosis Index entries containing back-references to N28.89: Abscess (connective tissue) (embolic) (fistulous) (infective) (metastatic) (multiple) (pernicious) (pyogenic) (septic) L02.91 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code L02.91 Adhesions, adhesive (postinfective) K66.0 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K66.0 Calcification kidney N28.89 Calicectasis N28.89
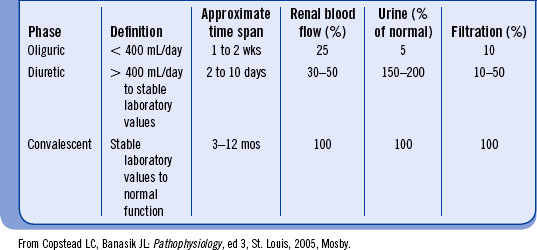
How do you code acute on chronic renal insufficiency?
Chronic Renal Insufficiency codes out the same as Chronic Renal Failure or Chronic Kidney Disease, so code 585.9 (unless the physician indicates which stage it is in, then code to the stage) and 593.9 for the Acute Renal Insufficiency, the ARI should be sequenced first.
What is meant by renal insufficiency?
Renal insufficiency is poor function of the kidneys that may be due to a reduction in blood-flow to the kidneys caused by renal artery disease. Normally, the kidneys regulate body fluid and blood pressure, as well as regulate blood chemistry and remove organic waste.
Is renal insufficiency the same as Chronic kidney disease?
Chronic renal insufficiency causes a slow loss of renal function. It is basically the end stage of chronic renal disease, which means the patient often requires dialysis treatment.
Is renal insufficiency the same as acute kidney injury?
Today the term acute kidney injury has replaced the term acute renal failure, with an understanding that such injury is a common clinical problem in critically ill patients and typically is predictive of an increase in morbidity and mortality.
What causes acute renal insufficiency?
Acute kidney failure can occur when: You have a condition that slows blood flow to your kidneys. You experience direct damage to your kidneys. Your kidneys' urine drainage tubes (ureters) become blocked and wastes can't leave your body through your urine.
What are the requirements for renal insufficiency?
CKD is defined as abnormalities of kidney structure or function, present for >3 months, with implications for health....What is the Criteria for CKD.Criteria for CKD: Either of the following present for > 3 monthsDecreased GFRGFR <60 ml/min/1.73 m2Abbreviations: CKD, chronic kidney disease; GFR, glomerular filtration rate.1 more row
What is progressive renal insufficiency?
Chronic renal insufficiency is associated with a progressive inability to excrete normal endogenously produced nonvolatile acid and usually results in systemic acidosis when the GFR is reduced to 0.42 mL/s or less.
What are the 3 types of acute renal failure?
Acute renal failure (ARF) can be divided into three main types: perennial, renal, and postrenal.
How do you classify acute kidney injury?
KDIGO defines AKI as any of the following:Increase in serum creatinine by 0.3mg/dL or more within 48 hours or.Increase in serum creatinine to 1.5 times baseline or more within the last 7 days or.Urine output less than 0.5 mL/kg/h for 6 hours.
What is a kidney disease?
A term referring to any disease affecting the kidneys. Conditions in which the function of kidneys deteriorates suddenly in a matter of days or even hours. It is characterized by the sudden drop in glomerular filtration rate. Impairment of health or a condition of abnormal functioning of the kidney.
Why is my kidney unable to remove waste?
This damage may leave kidneys unable to remove wastes. Causes can include genetic problems, injuries, or medicines. You are at greater risk for kidney disease if you have diabetes, high blood pressure, or a close family member with kidney disease. chronic kidney disease damages the nephrons slowly over several years.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for chronic regional pain syndrome
- 2. icd 10 code for food allergies in infants
- 3. icd 10 code for food sensitivity
- 4. icd 10 code for non surgical l spine stenosis
- 5. icd 10 cm code for hydrocortisone suppository
- 6. icd 10 code for type 1 diabetes mellitus with ketoacidosis
- 7. icd 10 code for enlarged liver with abdominal adenopathy
- 8. icd-9 code for ra
- 9. icd-10 code for leukopenia
- 10. what is the icd 10 code for pneumovax injection?