What is the ICD 10 code for alkalosis?
Alkalosis. E87.3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM E87.3 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E87.3 - other international versions of ICD-10 E87.3 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for acidosis?
Acidosis. E87.2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM E87.2 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E87.2 - other international versions of ICD-10 E87.2 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 for acute respiratory failure?
Acute respiratory failure, unspecified whether with hypoxia or hypercapnia. Short description: Acute respiratory failure, unsp w hypoxia or hypercapnia The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM J96.00 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J96.00 - other international versions of ICD-10 J96.00 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for excluded note?
E87.2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E87.2 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E87.2 - other international versions of ICD-10 E87.2 may differ. A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes.
See more
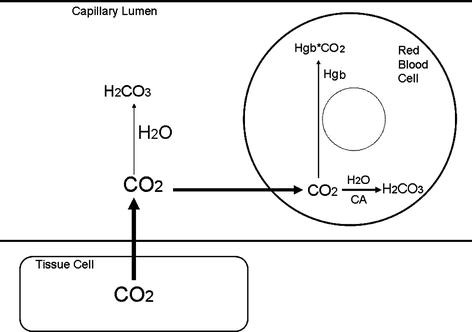
What is the ICD 10 code for Acute respiratory acidosis?
E87. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E87.
Is Acute respiratory failure respiratory alkalosis?
A study by Park et al indicated that in patients with high-risk acute heart failure, respiratory alkalosis is the most frequent acid-base imbalance. However, while acidosis was found to be a significant risk factor for mortality in acute heart failure patients, this was not true for alkalosis.
Why does respiratory alkalosis occur?
Respiratory alkalosis occurs when you breathe too fast or too deep and carbon dioxide levels drop too low. This causes the pH of the blood to rise and become too alkaline.
What is the ICD 10 code for acidosis?
Lactic acidosis shares the ICD-10-CM code, E87. 2, Acidosis, with other causes of acidosis, respiratory or metabolic. Mixed acid-base disorders are coded at E87. 4.
What is respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory alkalosis is a condition marked by a low level of carbon dioxide in the blood due to breathing excessively.
What is chronic respiratory alkalosis?
CHRONIC respiratory alkalosis is a common acid–base disturbance characterized by a primary and sustained decrease in arterial carbon dioxide tension (PaCO2) — that is, by primary hypocapnia. A decrease in PaCO2 occurs when the effective alveolar ventilation increases to a supernormal level.
How is respiratory alkalosis diagnosis?
Diagnosis. A doctor can diagnose respiratory alkalosis using a blood test called an arterial blood gas test. They will take blood from an artery, and a special machine will then interpret the acid-alkaline content of the blood.
What are the two types of respiratory alkalosis?
Classification. There are two types of respiratory alkalosis: chronic and acute as a result of the 3–5 day delay in kidney compensation of the abnormality. Acute respiratory alkalosis occurs rapidly, have a high pH because the response of the kidneys is slow.
How do you detect respiratory alkalosis?
Use pH to determine Acidosis or Alkalosis. ph. < 7.35. 7.35-7.45. ... Use PaCO2 to determine respiratory effect. PaCO2. < 35. ... Assume metabolic cause when respiratory is ruled out. You'll be right most of the time if you remember this simple table: High pH. ... Use HC03 to verify metabolic effect. Normal HCO3- is 22-26. Please note:
What is the ICD 10 code for Acute respiratory failure?
00 for Acute respiratory failure, unspecified whether with hypoxia or hypercapnia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
What is the respiratory acidosis?
Respiratory acidosis is a condition that occurs when the lungs cannot remove all of the carbon dioxide the body produces. This causes body fluids, especially the blood, to become too acidic.
Is metabolic acidosis the same as ketoacidosis?
There are several types of metabolic acidosis: Diabetic acidosis (also called diabetic ketoacidosis and DKA) develops when substances called ketone bodies (which are acidic) build up during uncontrolled diabetes (usually type 1 diabetes).
The ICD code E873 is used to code Acid-base imbalance
Acid–base imbalance is an abnormality of the human body's normal balance of acids and bases that causes the plasma pH to deviate out of the normal range (7.35 to 7.45). In the fetus, the normal range differs based on which umbilical vessel is sampled (umbilical vein pH is normally 7.25 to 7.45; umbilical artery pH is normally 7.18 to 7.38).
Coding Notes for E87.3 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #640-641 - Misc disorders of nutrition, metabolism, fluids or electrolytes with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'E87.3 - Alkalosis'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code E87.3. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 276.3 was previously used, E87.3 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
What is metabolic acidosis?
A disorder characterized by abnormally high acidity (high hydrogen-ion concentration) of the blood and other body tissues. A pathologic condition of acid accumulation or depletion of base in the body. The two main types are respiratory acidosis and metabolic acidosis, due to metabolic acid build up.
What are the two main types of acidosis?
The two main types are respiratory acidosis and metabolic acidosis, due to metabolic acid build up. A state due to excess retention of carbon dioxide in the body. Acid base imbalance resulting from an accumulation of carbon dioxide secondary to hypoventilation.
Can acidosis be caused by lactic acid?
It may occur spontaneously or in association with diseases such as diabetes mellitus, leukemia, or liver failure. Acidosis caused by accumulation of lactic acid more rapidly than it can be metabolized; may occur spontaneously or in association with diseases such as diabetes mellitus, leukemia, or liver failure.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for asdh
- 2. icd 10 code for history of cerebral aneurysm clipping
- 3. icd 10 code for benign neoplasm of pituitary gland
- 4. icd 9 code for spastic triplegia cerebral palsy
- 5. icd 10 code for megnessium
- 6. icd 10 code for insect bite on head
- 7. icd 9 code for urine retention
- 8. icd 9 code for traumatic intracranial bleed
- 9. icd 10 code for drug test
- 10. what is the icd 10 code for intraosseous hemangioma