What are the guidelines for acute respiratory failure?
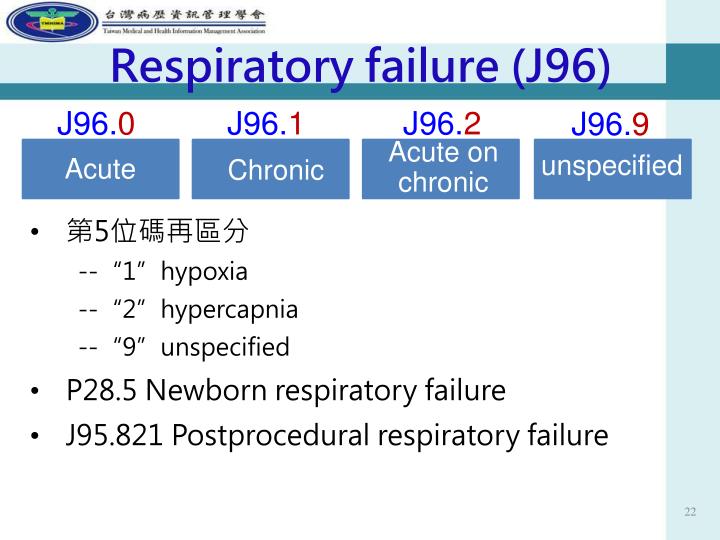
Oct 01, 2021 · Acute respiratory failure with hypoxia. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. J96.01 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J96.01 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the signs and symptoms of acute respiratory failure?
Oct 01, 2021 · J96.00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Acute respiratory failure, unsp w hypoxia or hypercapnia. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM …
What are the clinical indicators of acute respiratory failure?
ICD-10 code J96.01 for Acute respiratory failure with hypoxia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
What is the ICD 10 code for acute respiratory insufficiency?
Oct 01, 2021 · Acute and chronic respiratory failure with hypoxia. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. J96.21 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J96.21 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is hypoxia Acute respiratory failure?
Doctors call this hypoxemic respiratory failure. It means that a person is not exchanging oxygen properly in their lungs. This may be due to swelling or damage to the lungs. A person with type 1 acute respiratory failure has very low oxygen levels.Feb 22, 2019
What is the CPT code for Acute respiratory failure with hypoxia?
01.
How do you code Acute respiratory failure?
ICD-10-CM Code for Acute respiratory failure, unspecified whether with hypoxia or hypercapnia J96. 00.
What is chronic respiratory failure with hypoxia?
Chronic respiratory failure can also be classified as hypoxemic or hypercapnic respiratory failure. Low blood oxygen levels cause hypoxemic respiratory failure. High carbon dioxide levels cause hypercapnic respiratory failure.
Are hypoxia and hypoxemia the same?
Hypoxemia (low oxygen in your blood) can cause hypoxia (low oxygen in your tissues) when your blood doesn't carry enough oxygen to your tissues to meet your body's needs. The word hypoxia is sometimes used to describe both problems.Jun 14, 2020
What is acute respiratory failure with hypoxia and hypercapnia?
Hypoxemic respiratory failure means that you don't have enough oxygen in your blood, but your levels of carbon dioxide are close to normal. Hypercapnic respiratory failure means that there's too much carbon dioxide in your blood, and near normal or not enough oxygen in your blood.
What is the ICD-10 code for hypokalemia?
ICD-10 | Hypokalemia (E87. 6)
What is the ICD-10 code for hyperkalemia?
ICD-10 | Hyperkalemia (E87. 5)
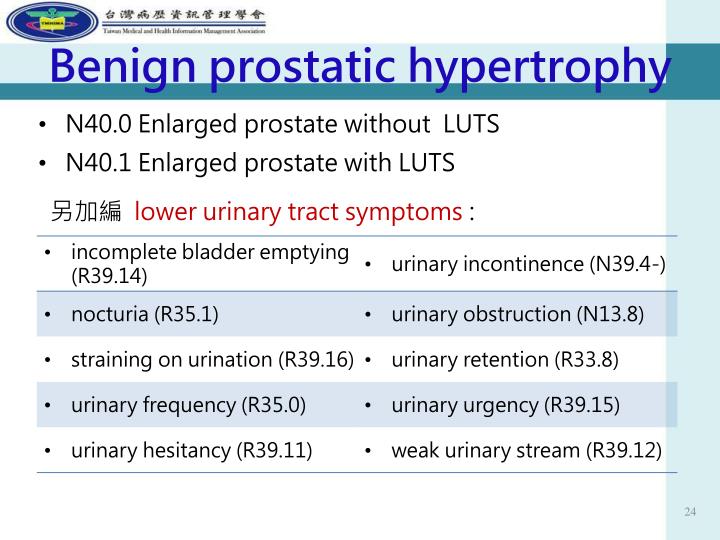
What is the ICD-10 code for acute on chronic respiratory failure with hypercapnia?
ICD-10-CM Code for Acute and chronic respiratory failure, unspecified whether with hypoxia or hypercapnia J96. 20.
What is the definition of acute respiratory failure?
Acute respiratory failure is defined as the inability of the respiratory system to meet the oxygenation, ventilation, or metabolic requirements of the patient.
What does a acute on chronic respiratory failure?
Key Points. Acute-on-chronic respiratory failure (ACRF) occurs when relatively minor, although often multiple, insults cause acute deterioration in a patient with chronic respiratory insufficiency.
How do you differentiate acute and chronic respiratory acidosis?
Respiratory acidosisAcute: Expected decrease in pH = 0.08 x (measured PaCO2 - 40)Chronic: Expected drop in pH = 0.03 x (measured PaCO2 - 40)
What is the ICd code for hypoxia?
The ICD code J96 is used to code Hypoxia (medical) Hypoxia (also known as hypoxiation) is a condition in which the body or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Hypoxia may be classified as either generalized, affecting the whole body, or local, affecting a region of the body. Although hypoxia is often a pathological ...
What is the ICd 9 code for arterial oxygen concentration?
Specialty: Pulmonology, Toxicology. MeSH Code: D000860. ICD 9 Code: 799.02.
What is the ICd 10 code for respiratory failure?
J96.01 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Acute respiratory failure with hypoxia . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also: Failure, failed. respiration, respiratory J96.90.
What is the ICd 10 code for acute respiratory failure?
J96.01 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of acute respiratory failure with hypoxia. The code J96.01 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code J96.01 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like acute hypercapnic respiratory failure, acute hypoxemic and hypercapnic respiratory failure, acute hypoxemic respiratory failure, acute hypoxemic respiratory failure, acute hypoxemic respiratory failure due to disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 , hypercapnic respiratory failure, etc.
What is respiratory failure?
Respiratory failure is a condition in which your blood doesn't have enough oxygen or has too much carbon dioxide. Sometimes you can have both problems. When you breathe, your lungs take in oxygen. The oxygen passes into your blood, which carries it to your organs.
What causes shortness of breath?
A low oxygen level in the blood can cause shortness of breath and air hunger (the feeling that you can't breathe in enough air). Your skin, lips, and fingernails may also have a bluish color. A high carbon dioxide level can cause rapid breathing and confusion.
Why do you need emergency care for respiratory failure?
Living with respiratory failure may cause fear, anxiety, depression, and stress.
How to treat a swollen nose?
Treatments may include. Oxygen therapy, through a nasal cannula (two small plastic tubes that go in your nostrils) or through a mask that fits over your nose and mouth. Tracheostomy, a surgically-made hole that goes through the front of your neck and into your windpipe.
How to check for arrhythmia?
Listening to your heart to check for arrhythmia. Looking for a bluish color on your skin, lips, and fingernails. Diagnostic tests, such as. Pulse oximetry, a small sensor that uses a light to measure how much oxygen is in your blood. The sensor goes on the end of your finger or on your ear.
Where is the oxygen sensor taken?
Arterial blood gas test, a test that measures the oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in your blood. The blood sample is taken from an artery, usually in your wrist. Once you are diagnosed with respiratory failure, your provider will look for what is causing it.
What are the types of respiratory failure?
Types of respiratory failure are categorized by acute, chronic, acute-on-chronic, AND whether the patient has hypoxia, hypercapnia, or both.
What is the oxygen saturation range for type 2?
The recommended oxygen target saturation range in patients not at risk of type II respiratory failure is 94%–98%; in patients at risk of type II respiratory failure, the range is 88%–92%.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for esophageal/gastric anastomosis stricture status
- 2. icd 9 code for juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- 3. icd 9 code for hematuria with damage to urethra
- 4. icd 10 code for 5 weeks pregnant
- 5. icd 10 code for left shoulder adhesive capsulitis
- 6. icd 10 code for acute cystitis
- 7. icd 10 code for globus syndrome
- 8. icd 10 code for lung inflammation
- 9. icd 10 code for annual physical exam for 50 years’ old
- 10. icd 10 code for lumbar disc herniation unspecified