What is the ICD 10 code for osteomyelitis of the foot?
Other acute osteomyelitis, right ankle and foot. M86.171 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM M86.171 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICD 10 code for osteomyelitis left ankle?
Other acute osteomyelitis, left ankle and foot. M86.172 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM M86.172 became effective on October 1, 2019. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M86.172 - other international versions of ICD-10 M86.172 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for osteoarthritis?
M86.672 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M86.672 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M86.672 - other international versions of ICD-10 M86.672 may differ. postprocedural osteopathies ( M96.-)
What is the ICD 10 code for osteomyelitis left hand?
Other chronic osteomyelitis, left hand. M86.642 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM M86.642 became effective on October 1, 2018.
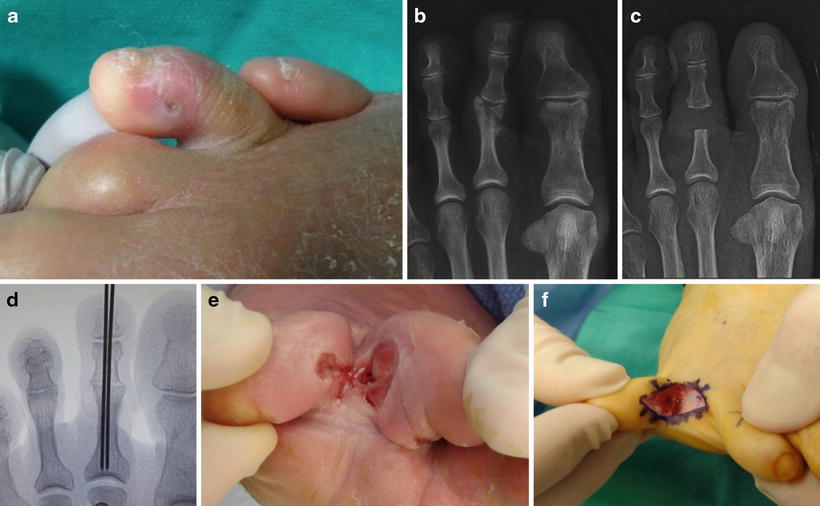
What is the ICD 10 code for toe osteomyelitis?
Other chronic osteomyelitis, unspecified ankle and foot M86. 679 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M86. 679 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for right toe osteomyelitis?
ICD-10-CM Code for Other acute osteomyelitis, right ankle and foot M86. 171.
What is the ICD 10 code for osteomyelitis left toes?
ICD-10 Code for Other acute osteomyelitis, left ankle and foot- M86. 172- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD 10 code M86 9?
Osteomyelitis, unspecifiedICD-10 code: M86. 9 Osteomyelitis, unspecified | gesund.bund.de.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for osteomyelitis?
ICD-10 code M86. 9 for Osteomyelitis, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Osteopathies and chondropathies .
What is the ICD 10 code for osteomyelitis?
There are three subcategories for reporting this condition using ICD-10-CM, including M86. 0 Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis, M86. 1 Other acute osteomyelitis, and M86. 2 Sub-acute osteomyelitis.
What is acute osteomyelitis?
Acute osteomyelitis is the clinical term for a new infection in bone. This infection occurs predominantly in children and is often seeded hematogenously. In adults, osteomyelitis is usually a subacute or chronic infection that develops secondary to an open injury to bone and surrounding soft tissue.
What is osteomyelitis of the foot?
Diabetic foot osteomyelitis (DFO) is mostly the consequence of a soft tissue infection that spreads into the bone, involving the cortex first and then the marrow. The possible bone involvement should be suspected in all DFUs patients with infection clinical findings, in chronic wounds and in case of ulcer recurrence.
What is the meaning of osteomyelitis?
(OS-tee-oh-MY-eh-LY-tis) Inflammation of the bone caused by an infection, which may spread to the bone marrow and tissues near the bone. Osteomyelitis can cause severe pain in the infected bone.
What is the CPT code for osteomyelitis?
CPT® Code 21025 in section: Excision of bone (eg, for osteomyelitis or bone abscess)
What is subacute osteomyelitis?
Subacute osteomyelitis is a hematogenous infection of bone characterized by an insidious course (longer than 2 weeks), and paucity of systemic symptoms with local tenderness or swelling are the only clinical signs.
What is this code M869?
M869 - ICD 10 Diagnosis Code - Osteomyelitis, unspecified - Market Size, Prevalence, Incidence, Quality Outcomes, Top Hospitals & Physicians.
What is the meaning of osteomyelitis?
(OS-tee-oh-MY-eh-LY-tis) Inflammation of the bone caused by an infection, which may spread to the bone marrow and tissues near the bone. Osteomyelitis can cause severe pain in the infected bone.
What is osteomyelitis of the bone?
Osteomyelitis is inflammation or swelling that occurs in the bone. It can result from an infection somewhere else in the body that has spread to the bone, or it can start in the bone — often as a result of an injury. Osteomyelitis is more common in younger children (five and under) but can happen at any age.
What is acute osteomyelitis?
Acute osteomyelitis is the clinical term for a new infection in bone. This infection occurs predominantly in children and is often seeded hematogenously. In adults, osteomyelitis is usually a subacute or chronic infection that develops secondary to an open injury to bone and surrounding soft tissue.
What is chronic osteomyelitis?
Chronic osteomyelitis represents a progressive inflammatory process caused by pathogens, resulting in bone destruction and sequestrum formation. It may present with periods of quiescence of variable duration, whereas its occurrence, type, severity and prognosis is multifactorial.
What is the disease of osteomyelitis?
Acute osteomyelitis is an inflammation of the bone caused by an infectious organism. The condition develops rapidly during the course of several days. It is characterized by localized pain, soft-tissue swelling, and tissue warmth at the site of the infection, plus systemic symptoms such as fever, irritability, fatigue, and nausea.
What is chronic multifocal osteomyelitis?
Chronic multifocal osteomyelitis is a rare condition that also is referred to as chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis, or SAPHO syndrome (synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis). The cause of the condition is unknown, and tissue cultures typically fail to identify any infectious organism.
Which code includes Brodie's abscess?
Multiple sites. Other osteomyelitis (M86.8) which includes Brodie’s abscess, requires only the general region (shoulder, upper arm, forearm, hand, thigh, lower leg, ankle/foot, other site, and unspecified site). Laterality is not a component of codes in category M86.8. Unspecified osteomyelitis (M86.9) is not specific to a site.
Is osteomyelitis a chronic disease?
Osteomyelitis is an inflammation of the bone that typically is further differentiated as acute, sub-acute, or chronic. In ICD-9-CM, documentation of the general site of the inflammation/infection (such as shoulder region, forearm, or ankle), along with identification of the inflammation/infection as a current acute/sub-acute infection or a chronic condition, is all that is required to assign the most specific code.
Can osteomyelitis cause sinus drainage?
Chronic osteomyelitis is a severe, persistent inflammation/infection that can recur and be difficult to treat. A chronic infection also may present with a draining sinus, presenting a greater risk for complications, such as major bo ny defects.
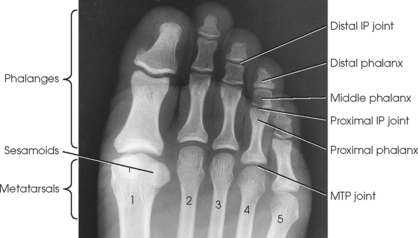
Acute and Sub-Acute Osteomyelitis
- There are three subcategories for reporting this condition using ICD-10-CM, including M86.0 Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis, M86.1 Other acute osteomyelitis, and M86.2 Sub-acute osteomyelitis. Acute hemotogenous osteomyelitis results from an infection at a remote site. The infectious organism then is carried through the bloodstream to the bone. Th...
Chronic Osteomyelitis
- There are four subcategories in ICD-10-CM for chronic osteomyelitis, including M86.3 Chronic multifocal osteomyelitis, M86.4 Chronic osteomyelitis with draining sinus, M86.5 Other chronic hematogenous osteomyelitis, and M86.6 Other chronic osteomyelitis. Chronic multifocal osteomyelitis is a rare condition that also is referred to as chronic recurrent multifocal osteomy…
Other Osteomyelitis
- There are two additional subcategories for the reporting of this condition in ICD-10-CM. Subcategory M86.8 reports other osteomyelitis, and this category includes Brodie’s abscess. Brodie’s abscess previously was classified as a type of chronic osteomyelitis, but most scholarly literature now refers to it as a sub-acute condition. The defining characteristic is the presence o…
Site Specificity in ICD-10-CM
- While ICD-9-CM identifies only the general region of the osteomyelitis, ICD-10-CM includes specific bones for some sites and laterality. Specific sites for subcategories M86.0-M86.6 include: 1. Shoulder 2. Humerus 3. Radius/ulna 4. Hand 5. Femur 6. Tibia/fibula 7. Ankle/foot 8. Other specified sites 9. Multiple sites Other osteomyelitis (M86.8) which includes Brodie’s abscess, re…
Additional Codes
- As with all infectious processes in which the infectious agent is not a component of the code that describes the condition, an additional code from categories B95-B97 should be assigned to identify the infectious agent, assuming it can be identified. Any major osseous defects also should be identified with a code from subcategory M89.7.
Additional Coding Changes For Bone Infections
- One additional coding change is that there are is no longer a separate designation for periostitis without mention of osteomyelitis in ICD-10-CM. In ICD-9-CM, this condition was reported with codes from subcategory 730.3. In ICD-10-CM, the Alphabetic Index provides only a limited number of specific entries for periostitis. There are specific entries for periostitis of the dentoalveolar str…
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for mdd with psychotic features
- 2. icd 10 code for subtherapeutic anticoagulation
- 3. icd 10 code for beta-adrenoceptor
- 4. icd 10 diagnosis code for corneal laceration
- 5. icd 10 code for late effects of radiation
- 6. icd-10 code for myopia
- 7. icd 10 code for annual lab exams
- 8. icd 10 code for deaf unspecified
- 9. icd 10 cm code for vaginal leaking
- 10. icd 10 code for colon polyp surveillance