What are the ICD 10 codes for stroke?
Oct 01, 2021 · I67.81 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I67.81 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I67.81 - other international versions of ICD-10 I67.81 may differ. Applicable To
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
Showing 1-25: ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z82.3 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Family history of stroke. Family history of aneurysm of brain and stroke; Family history of stroke due to brain aneurysm (artery dilation); Conditions classifiable to I60-I64. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z82.3. Family history of stroke.
How to code a stroke?
Acute codes for Stroke/TIA ICD-10-CM code ICD-10-CM description Definition and tip I63.6 Cerebral infarction due to cerebral venous thrombosis, non-pyrogenic I63.8 Other cerebral infarction I63.9 Cerebral infarction unspecified Stroke NOS G45.9 Transient Ischemic Attack, unspecified TIA Sequela of Stroke codes – Monoplegia/hemiplegia/hemiparesis ICD-10-CM …
What is the diagnosis code for stroke?
2017 - New Code 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K55.019 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Acute (reversible) ischemia of small intestine, extent unspecified. Acute ischemia of small intestine, extent unspecified. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K55.019.
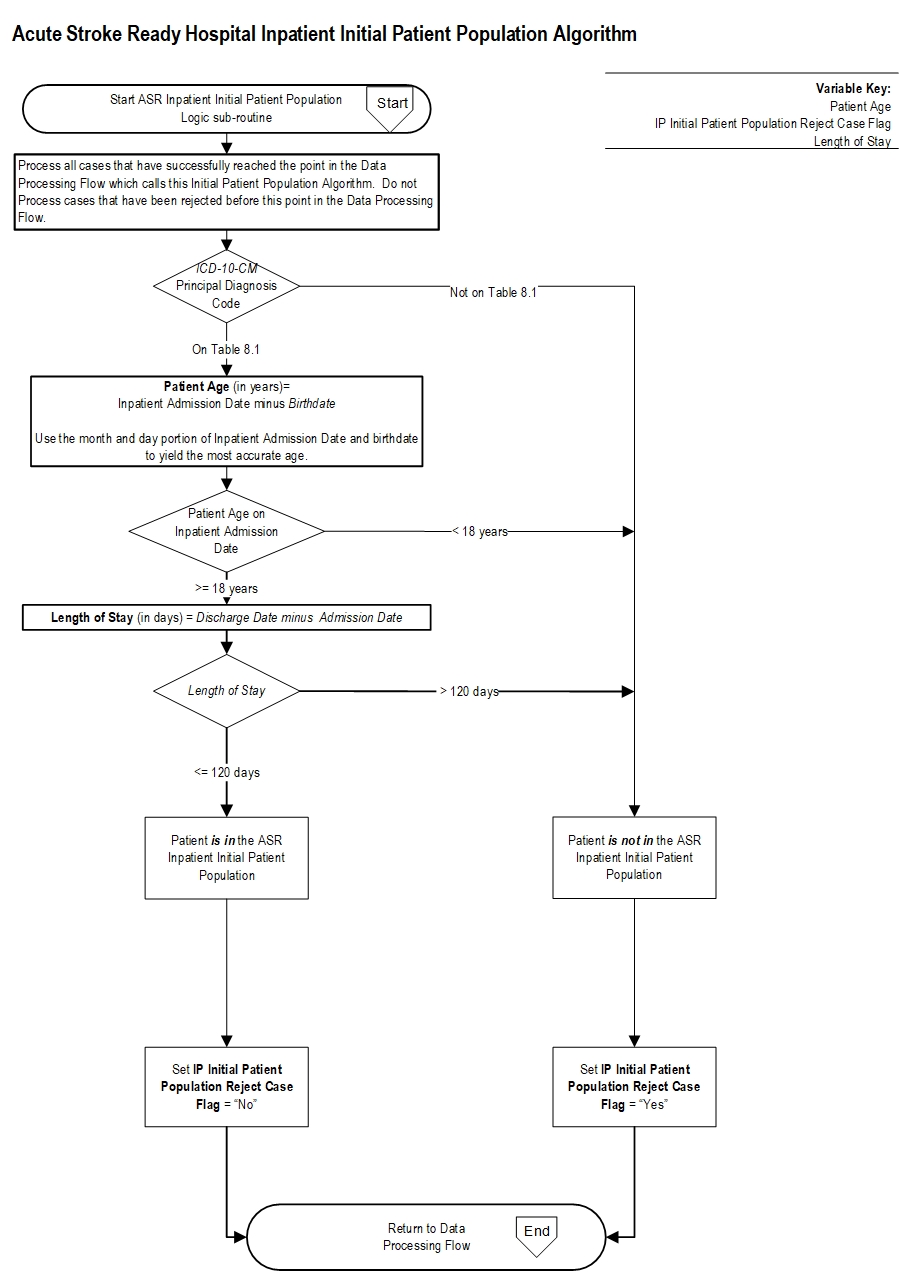
What is the ICD-10 code for recent stroke?
When a patient has a history of cerebrovascular disease without any sequelae or late effects, ICD-10 code Z86. 73 should be assigned.
What is diagnosis code for stroke?
For ischaemic stroke, the main codes are ICD-8 433/434 and ICD-9 434 (occlusion of the cerebral arteries), and ICD-10 I63 (cerebral infarction).Aug 20, 2015
What is the ICD-10 code for personal history of stroke?
ICD-10-CM Code for Personal history of transient ischemic attack (TIA), and cerebral infarction without residual deficits Z86. 73.
Is a stroke considered acute?
Acute stroke is defined as the acute onset of focal neurological findings in a vascular territory as a result of underlying cerebrovascular disease. In the United States, there are 800,000 new strokes every year. There is one new stroke every 40 seconds.Sep 29, 2021
How do you code an acute stroke?
Acute Ischemic Stroke (ICD-10 code I63.
What is the ICD-9 code for stroke?
Acute stroke includes ischemic stroke (ICD-9-CM codes 433-434 and 436) and hemorrhagic stroke (ICD-9-CM codes 430-432). Hospitalizations of residents of the area (state, region, county) for which the primary diagnosis was given as ICD-9 codes 433-434 and 436.
How do you code a hemorrhagic stroke?
The case definition of using the ICD-10-CM code of I60 or I61 as the primary diagnosis to identify acute hemorrhagic stroke yielded a PPV and sensitivity of 98.2% and 93.1%, respectively.Jan 14, 2021
What is the ICD-10 code for multiple strokes?
Multiple and bilateral precerebral artery syndromes G45. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Is stroke and cerebral infarction the same?
Doctor's response. A cerebral infarction (also known as a stroke) refers to damage to tissues in the brain due to a loss of oxygen to the area. The mention of "arteriosclerotic cerebrovascular disease" refers to arteriosclerosis, or "hardening of the arteries" that supply oxygen-containing blood to the brain.
What is an acute stroke ward?
An acute stroke unit is generally defined as a stroke unit accepting patients acutely but with early discharge (usually<1 week). The conservative care of patients with primary intracranial haemorrhage in the acute stroke unit was mainly the same as for patients with cerebral infarctions.
What is the difference between acute and chronic stroke?
The initial phase is called the acute phase and lasts for about 2 weeks after the onset of the lesion. The second phase is the subacute phase, and this usually lasts up to 6 months after onset. Finally, the chronic phase begins months to years after stroke, and it may continue for the remainder of the person's life.
What is the difference between acute and subacute stroke?
Three main stages are used to describe the CT manifestations of stroke: acute (less than 24 hours), subacute (24 hours to 5 days) and chronic (weeks). Acute stroke represents cytotoxic edema, and the changes can be subtle but are significant.
What is the ICD-10 code for stroke?
Explicitly document findings to support diagnoses of › Stroke sequela codes (ICD-10 category I69.-) should acute stroke, stroke and subsequent sequela of be used at the time of an ambulatory care visit stroke, and personal history of stroke without sequela, oce, which is considered subsequent to any acute
What is the term for a stroke that occurs when there is disruption of blood flow to brain tissue?
stroke occurs when there is disruption of blood flow to brain tissue, this leads to ischemia (deprivation of oxygen) and potentially infarction (dysfunctional scar tissue). Strokes can be either hemorrhagic, or embolic/thrombotic. Hemorrhagic strokes occur as a result of a ruptured cerebral blood vessel. Embolic/thrombic strokes occur as a result of an obstructed cerebral vessel.
What is the ICD-10 code for stroke?
In ICD-10 CM, code category I63 should be utilized when the medical documentation indicates that an infarction or stroke has occurred. Coding of sequelae of stroke and infarction also demands a level of detail often missing in medical records. There are specific codes which indicate the cause of the infarction, such as embolism or thrombosis, as well as the specific affected arteries. The sixth digit provides additional information which designates the affected side when applicable.
What is the ICD-10 code for cerebral infarction?
The patient is admitted into hospital and diagnosed with cerebral infarction, unspecified ( ICD-10 code I63.9). At the 3-week post-discharge follow-up appointment for the cerebral infarction, the office visit note states the patient had a stroke and has a residual deficit of hemiplegia, affecting the right dominant side.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for abnormal inr
- 2. icd 10 code for self inflicted stab wound to abdomen
- 3. icd 10 code for gaulan
- 4. icd 10 code for bleach ingestion
- 5. icd code for thyroid basic panel
- 6. icd 10 code for right fifth toe blister
- 7. icd-10 code for valvular heart dz occlusion of vena cava
- 8. icd 10 code for 141.9
- 9. icd 10 code for itching unspecified
- 10. icd 10 code for right hip periprosthetic infection