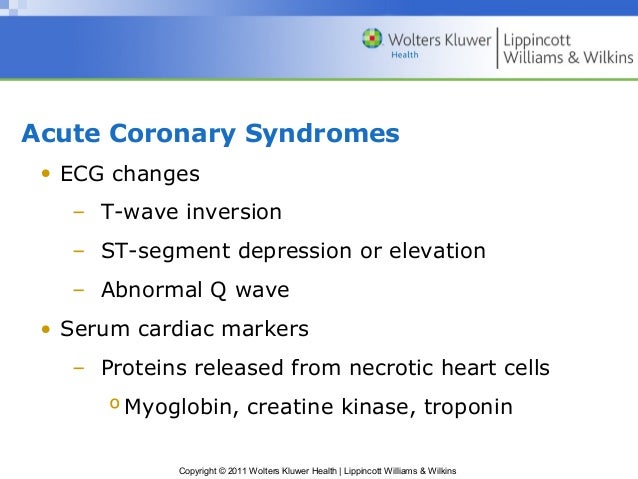
What can cause inverted T waves?
Strain on ventricles can cause T wave inversion. Pre-excitation syndrome is a condition in which the ventricles partially contract prematurely. T wave inversion is often present in this condition.
What does T wave inversion indicate?
To clarify, isolated T-wave inversions indicate that there has been ischemia. Ischemic T-wave inversions are symmetric (the normal T-wave is asymmetric) and maybe, but rarely are, deeper than 10 mm. ECG leads with the opposite angles of observation (opposite to leads with T-wave inversions) usually display positive T-waves.
What do inverted T waves indicate?
What Causes T-Wave Inversion?
- Hypokalaemia
- Pulmonary embolisms
- Some medications e.g. Digoxin
- Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome
- Hypothyroidism
- Acute Myocarditis
- Ventricular Hypertrophy
- Ischemic Heart Condition
Which leads is T wave inversion normal?
The T wave is the ECG manifestation of ventricular repolarization of the cardiac electrical cycle. The T wave is normally upright in leads I, II, and V3 to V6; inverted in lead aVR; and variable in leads III, aVL, aVF, V1, and V2. Thus, T-wave inversions in leads V1 and V2 may be fully normal.
What does diagnosis code R94 31 mean?
ICD-10 code R94. 31 for Abnormal electrocardiogram [ECG] [EKG] is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the ICD-10 code for EKG changes?
R94. 31 - Abnormal electrocardiogram [ECG] [EKG] | ICD-10-CM.
What does diagnosis code R00 2 mean?
R00. 2 Palpitations - ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes.
When do I code I25 2?
Coding Guidance An old or healed MI, not requiring further care, should be coded as I25. 2, Old Myocardial Infarction.
Do you need modifier 25 with EKG?
Yes, you need to add a -25 modifier to your E&M service when billing in conjunction with an EKG or injection admin service done on same DOS. You're sure to get a bundling denial without it.
What is the difference between 93005 and 93010?
93000 is the complete procedure and includes ECG tracing with physician review, interpretation and report. Use 93005 to report the tracing only, and 93010 to report physician interpretation and written report only.
What is R53 83?
ICD-9 Code Transition: 780.79 Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
What is ICD-10 code R51?
ICD-10 code R51 for Headache is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What are R00 2 Palpitations?
A disorder characterized by an unpleasant sensation of irregular and/or forceful beating of the heart. A rapid or irregular heartbeat that a person can feel.
When do I code I25 810?
Atherosclerosis of coronary artery bypass graft(s) without angina pectoris. I25. 810 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I25.
When do you use I25 810?
ICD-10 code I25. 810 for Atherosclerosis of coronary artery bypass graft(s) without angina pectoris is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What does the code I25 10 mean?
Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery withoutICD-10 Code for Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery without angina pectoris- I25. 10- Codify by AAPC.
What is abnormal clinical findings?
These are abnormal tumor markers and/or clinical findings closely related to neoplasm. Just because these tumor markers are high, or the imaging is questionable, that doesn't mean there is a neoplasm.
Is tachycardia a heart disease?
Tachycardia is an increased heart rate for any reason. It can be a usual rise in heart rate caused by exercise or a stress response (sinus tachycardia). Sinus tachycardia is considered a symptom, not a disease. Tachycardia can also be caused by an irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia).
What does pounding heart mean?
Heart palpitations (pal-pih-TAY-shuns) are feelings of having a fast-beating, fluttering or pounding heart. Stress, exercise, medication or, rarely, a medical condition can trigger them. Although heart palpitations can be worrisome, they're usually harmless.
What are heart palpitations?
When you have heart palpitations, your heartbeat feels uncomfortable or unusual. You may feel it in your chest, neck or throat. Your heartbeat may feel like it is: racing or beating very fast. irregular, with skipped or extra beats (ectopic beats)
What is the clockwise shift of the R/S transition point towards V6?
Clockwise Rotation#N#Clockwise Rotation shift of the R/S transition point towards V6 with a persistent S wave in V6 (Pulmonary disease pattern), implying rotation of the heart due to right ventricular dilatation.
What is the right ventricular strain pattern?
Right Ventricular Strain Pattern#N#Right Ventricular Strain Patternis the T wave inversions in the right precordial leads (V1-4) ± the inferior leads (II, III, aVF). This pattern is seen in up to 34% of patients and is associated with high pulmonary artery pressures.
What is the code for EKG?
R94.31 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of abnormal electrocardiogram [ecg] [ekg]. The code R94.31 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
When was the ICd 10 code implemented?
FY 2016 - New Code, effective from 10/1/2015 through 9/30/2016 (First year ICD-10-CM implemented into the HIPAA code set)
What are the two types of T waves in Wellens syndrome?
Two patterns of T waves can be seen in Wellens syndrome. Type-A T waves are biphasic, with initial positivity and terminal negativity. These T wave findings are present in approximately 25% of cases. Type-B T waves are deeply and symmetrically inverted. These findings are present in approximately 75% of cases. The 2 types of T waves found in Wellens syndrome exist on a spectrum of disease with type-A T waves evolving into type-B T waves. The T-wave abnormalities may be persistent, remaining in place for hours to weeks, even when the patient is pain-free.
How long do T waves last in Wellens syndrome?
The T-wave abnormalities may be persistent, remaining in place for hours to weeks, even when the patient is pain-free. Wellens syndrome is not always an acute process.
What is the ECG pattern of Wellens syndrome?
The ECG pattern of Wellens syndrome is relatively common in patients who exhibit symptoms consistent with unstable angina. In studies performed by Dr. Wellens and colleagues, the ECG pattern was present in 14% to 18% of patients admitted for unstable angina. Pathophysiology.
When was myocardial infarction first identified?
In fact, when Drs. De Zwaan, Wellens, and colleagues first identified the syndrome in the early 1980s, they noted that 75% of patients with these ECG findings went on to develop acute, anterior, wall, myocardial infarction within weeks if they were treated with only medical management.
Is troponin a biomarker?
Cardiac biomarkers including troponin may be falsely reassuring in patients with Wellens syndrome as they frequently result within normal limits. In one prospective study, only 12% of patients with Wellens’ pattern on ECG had elevated cardiac enzymes, and these elevations were less than twice the upper limit of normal.
What is the ECG pattern of Wellens syndrome?
Wellens syndrome describes a pattern of electrocardiographic (ECG) changes, particularly deeply inverted or biphasic T waves in leads V2-V3, that is highly specific for critical, proximal stenosis of the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery. It is alternatively known as anterior, descending, T-wave syndrome. Typically when patients with Wellens syndrome present to the emergency department they are pain-free, and usually cardiac enzymes are normal or only slightly elevated. However, it is important to recognize the ECG patterns as these patients are at high risk for impending large anterior wall acute myocardial infarction. In fact, when Drs. De Zwaan, Wellens, and colleagues first identified the syndrome in the early 1980s, they noted that 75% of patients with these ECG findings went on to develop acute, anterior, wall, myocardial infarction within weeks if they were treated with only medical management. Definitive treatment typically involves cardiac catheterization with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) to relieve the occlusion.
When was myocardial infarction first identified?
In fact, when Drs. De Zwaan, Wellens, and colleagues first identified the syndrome in the early 1980s, they noted that 75% of patients with these ECG findings went on to develop acute, anterior, wall, myocardial infarction within weeks if they were treated with only medical management.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for toddler with chronic tonsillitis and adenoiditis
- 2. icd 10 code for right common extensor teninosis
- 3. icd 10 code for pain in the lung
- 4. icd-10-cm code for keratoderna
- 5. icd 10 code for endometrial thickening on ultrasound
- 6. icd 10 code for periodic breathing of newborn
- 7. icd 10 cm code for cigarete brun
- 8. icd 10 cm code for intra articular knee cyst
- 9. icd 9 code for dm2 uncontrolled
- 10. icd 10 code for pace maker problem