What is considered prediabetes A1C ICD 10?
Prediabetes
- R73.03 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R73.03 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of R73.03 - other international versions of ICD-10 R73.03 may differ.
How to code diabetes correctly?
Diabetes Mellitus and the Use of Insulin and Oral Hypoglycemic Drugs If the documentation in a medical record does not indicate the type of diabetes but does indicate that the patient uses insulin: Assign code E11-, Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Assign code Z79.4, Long term (current) use of insulin, or Z79.84, Long-term (current) use of oral
What is ICD 10 for poorly controlled diabetes?
In ICD-10-CM, chapter 4, "Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases (E00-E89)," includes a separate subchapter (block), Diabetes mellitus E08-E13, with the categories:
- E08, Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition
- E09, Drug or chemical induced diabetes mellitus
- E10, Type 1 diabetes mellitus
- E11, Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- E13, Other specified diabetes mellitus
What is diabetes insipidus ICD 10 code?
what is diabetes insipidus icd 10 code 234. Destruction of beta-cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas and consequently development of insulin-dependent diabetes is one ...
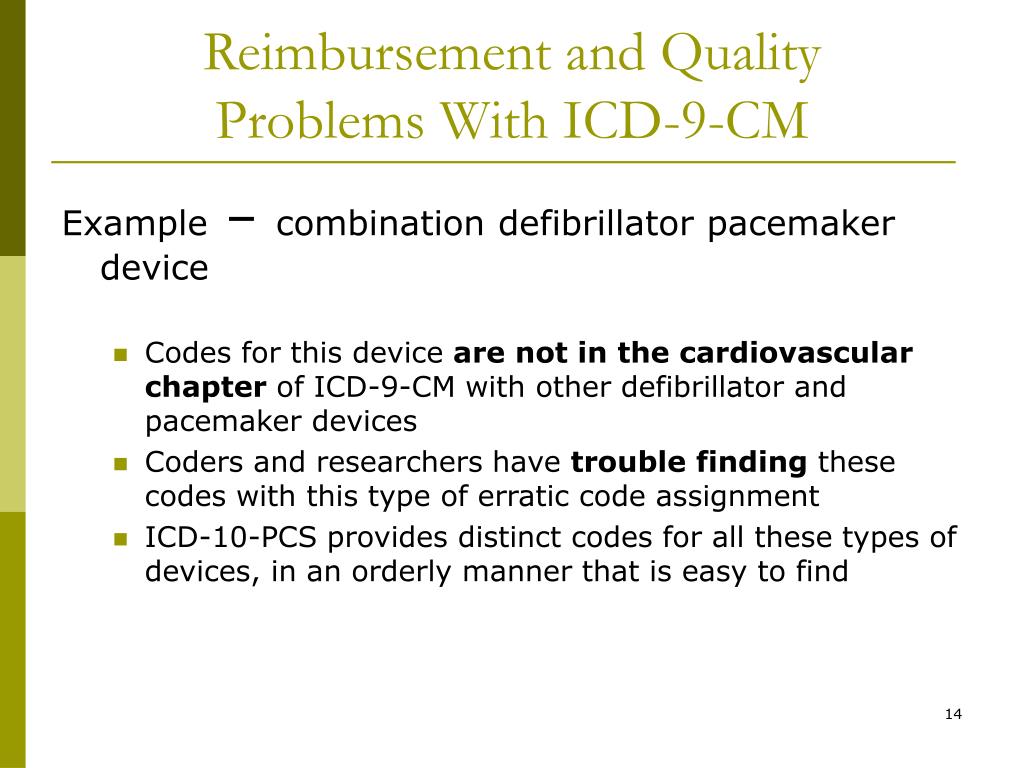
What is the code for insulin dependent diabetes mellitus?
E10 Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetes type 2 with hyperglycemia?
ICD-10 code E11. 65 for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with hyperglycemia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is the ICD-10 code for controlled diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications E11. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Is type 2 diabetes the same as insulin-dependent?
In general, people with diabetes either have a total lack of insulin (type 1 diabetes) or they have too little insulin or cannot use insulin effectively (type 2 diabetes). Type 1 diabetes (formerly called juvenile-onset or insulin-dependent diabetes), accounts for 5 to 10 out of 100 people who have diabetes.
What is the ICD-10 code for type 2 diabetes?
ICD-Code E11* is a non-billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Its corresponding ICD-9 code is 250. Code I10 is the diagnosis code used for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
What is the ICD-10 code for type 2 diabetes without complications with insulin use?
E11. 9 - Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for type 1 diabetes?
ICD-10 code E10. 9 for Type 1 diabetes mellitus without complications is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is the difference between E11 21 and E11 22?
E11. 22 states within its code DM with CKD therefore it is a more accurate code than E11. 21 which is just DM with Nephropathy (any kidney condition).
What is the proper ICD-10 code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with multiple complications?
E11. 69 - Type 2 diabetes mellitus with other specified complication. ICD-10-CM.
Why is type 2 diabetes sometimes referred to as non insulin-dependent?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is also called non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM), since it can be treated with lifestyle changes and/or types of medication other than insulin therapy. Type 2 diabetes is significantly more common than type 1 diabetes.
What's the difference between dm1 and dm2?
People with type 1 diabetes don't produce insulin. You can think of it as not having a key. People with type 2 diabetes don't respond to insulin as well as they should and later in the disease often don't make enough insulin. You can think of it as having a broken key.
What is type 1 vs type 2 diabetes?
In Type 1 diabetes, your pancreas doesn't make any insulin. In Type 2, your pancreas doesn't make enough insulin, and the insulin it is making doesn't always work as it should. Both types are forms of diabetes mellitus, meaning they lead to hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetes?
For gestational diabetes (diabetes that occurs during pregnancy) women should be assigned a code under the 024.4 subheading and not any other codes under the 024 category.
What type of diabetes codes should be used?
If the type of diabetes that the patient has is not documented in the medical record, E11 codes for type 2 diabetes should be used as a default. If the medical record doesn’t say what type of diabetes the patient has but indicates that the patient uses insulin, the Type 2 diabetes codes should also be used.
When to use unspecified ICD-10?
The “unspecified” codes can be used when not enough information is known to give a more specific diagnosis; in that case, “unspecified” is technically more accurate than a more specific but as yet unconfirmed diagnosis. For more guidelines on using ICD-10 codes for diabetes mellitus, you can consult this document.
What is diabetes mellitus?
A heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance. A metabolic disorder characterized by abnormally high blood sugar levels due to diminished production of insulin or insulin resistance/desensitization. A subclass of diabetes mellitus that is not insulin-responsive or dependent (niddm). It is characterized initially by insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia; and eventually by glucose intolerance; hyperglycemia; and overt diabetes. Type ii diabetes mellitus is no longer considered a disease exclusively found in adults. Patients seldom develop ketosis but often exhibit obesity. A type of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by insulin resistance or desensitization and increased blood glucose levels. This is a chronic disease that can develop gradually over the life of a patient and can be linked to both environmental factors and heredity. Diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose, or sugar, levels are too high. Glucose comes from the foods you eat. Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to give them energy. With type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well. Without enough insulin, the glucose stays in your blood.over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause serious problems. It can damage your eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Diabetes can also cause heart disease, stroke and even the need to remove a limb. Pregnant women can also get diabetes, called gestati Continue reading >>
What is DM in medical terms?
Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a syndrome characterized by hyperglycemia from impaired insulin production. Associated Risk factors: Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) Non-ketotic hyperglycemic-hyperosmolar coma (NKHHC) Late Complications: Retinopathy Nephropathy Atherosclerotic coronary dz Peripheral arterial dz. Neuropathy ect Insulin Normally, insulin made by the pancreas gives the signal to your body’s cells to store glucose from the blood. A person with diabetes body’s cells are unable to store glucose. Without insulin glucose levels in the blood rise and spill over into the urine. Excess amounts of glucose in the blood may affect many organ systems including kidneys, vascular systems, eyes and nerves. Type 1 Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes is AKA insulin – dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM), juvenile diabetes or childhood onset diabetes. Hereditary accounts for 10%-15% of IDDM patient. Type 1 patients must take insulin from childhood on since the pancreas cannot produce insulin. Treatment is daily insulin injections and diet control. Patients are rarely overweight. Coding type 1 in ICD-9 Use the fifth digit of either “1†or “3†to indicate a person with type 1. Use fifth digit “1†when the providers documentation DOES NOT STATE that the diabetes is uncontrolled Use fifth digit “3†when the documentation states the patient’s condition is uncontrolled. Usually the provider does not document whether the diabetes is uncontrolled. The provider needs to understand the coder cannot choose uncontrolled unless it is clearly stated in the EMR. Type II AKA non-insulin diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) or adult onset diabetes. It makes up approximately 90% of diabetic cases. Onset usually after age 30 and is associated with obe Continue reading >>
Is there more than one type of diabetes?
I'm pretty sure all of you who made it thus far in this article are familiar with the fact that there are at least two major types of diabetes: type I, or juvenile, and type II, with usual (though not mandatory) adult onset. Just like ICD-9, ICD-10 has different chapters for the different types of diabetes. The table below presents the major types of diabetes, by chapters, in both ICD coding versions. Diabetes Coding Comparison ICD-9-CM ICD-10-CM 249._ - Secondary diabetes mellitus E08._ - Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition E09._ - Drug or chemical induced diabetes mellitus E13._ - Other specified diabetes mellitus 250._ - Diabetes mellitus E10._ - Type 1 diabetes mellitus E11._ - Type 2 diabetes mellitus 648._ - Diabetes mellitus of mother, complicating pregnancy, childbirth, or the puerperium O24._ - Gestational diabetes mellitus in pregnancy 775.1 - Neonatal diabetes mellitus P70.2 - Neonatal diabetes mellitus This coding structure for diabetes in ICD-10 is very important to understand and remember, as it is virtually always the starting point in assigning codes for all patient encounters seen and treated for diabetes. How To Code in ICD-10 For Diabetes 1. Determine Diabetes Category Again, "category" here refers to the four major groups above (not just to type 1 or 2 diabetes): E08 - Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition E09 - Drug or chemical induced diabetes mellitus E10 - Type 1 diabetes mellitus E11 - Type 2 diabetes mellitus E13 - Other specified diabetes mellitus Note that, for some reason, E12 has been skipped. Instructions on Diabetes Categories Here are some basic instructions on how to code for each of the diabetes categories above: E08 - Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition. Here, it is Continue reading >>

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for other articular cartilage disorders left knee
- 2. icd code for domestic violence death
- 3. icd 10 code for abscess buttock
- 4. 2013 icd 9 code for ashd
- 5. icd 10 code for sanfilippo syndrome
- 6. icd 10 code for contact with glass
- 7. icd 10 code for corneal edema both eyes
- 8. icd 10 code for paroxysmal hypertension
- 9. icd 10 code for cytomegaloviral pneumonitis
- 10. icd 10 code for history of left hip dislocation