What are the ICD-10 codes for atrial fibrillation (AFIB)?
2022 ICD-10-CM Codes I48*: Atrial fibrillation and flutter. ICD-10-CM Codes. ›. I00-I99 Diseases of the circulatory system. ›. I30-I5A Other forms of heart disease. ›. Atrial fibrillation and flutter I48.
What is the ICD 10 code for anticoagulant?
Oct 01, 2021 · Z79.01 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z79.01 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z79.01 - other international versions of ICD-10 Z79.01 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for diagnosis 2022?
Oct 01, 2021 · Unspecified atrial fibrillation 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code I48.91 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I48.91 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for blood alcohol and drug test?
Oct 01, 2021 · Z51.81 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z51.81 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z51.81 - other international versions of ICD-10 Z51.81 may differ. Code Also any long-term (current) drug therapy (
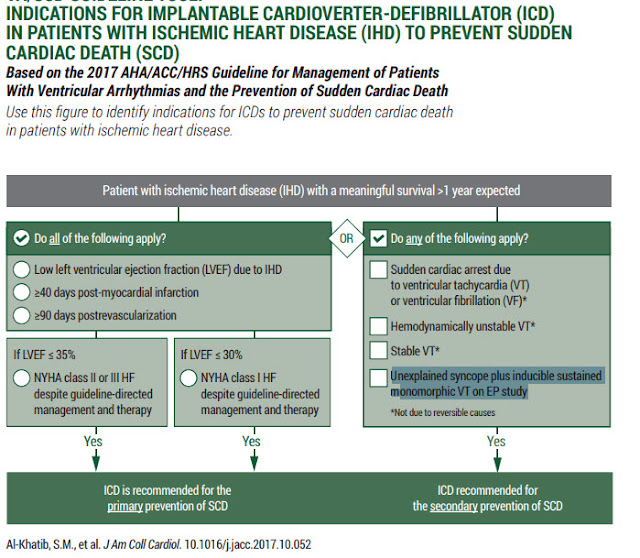
What is the ICD-10 code for atrial fibrillation?
ICD-10 code I48 for Atrial fibrillation and flutter is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
How do you code follow up for atrial fibrillation?
I48. 91 is used to report atrial fibrillation when no further specificity is available. I48. 2 is used to report atrial fibrillation when specified as chronic or permanent (Will be expanded 10/1/19)Aug 2, 2019
What is the ICD-10 code for I48 2?
2: Chronic atrial fibrillation.
Is I48 2 a billable code?
I48. 2 is a non-specific and non-billable diagnosis code code, consider using a code with a higher level of specificity for a diagnosis of chronic atrial fibrillation. The code is not specific and is NOT valid for the year 2022 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is the main term for the following diagnosis atrial fibrillation?
Atrial Fibrillation (also called AFib or AF) is a heart condition that causes an irregular and often rapid heart rate that can increase your risk of stroke, blood clots, heart failure and other heart-related complications.Jul 31, 2018
What is intermittent AFib?
Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation occurs when a rapid, erratic heart rate begins suddenly and then stops on its own within 7 days. It is also known as intermittent A-fib and often lasts for less than 24 hours.
What is the ICD-10 code for AFib with RVR?
I48AFIB with RVR ICD 10 code is I48. AFIB with a rapid ventricular response is a kind of irregular heartbeat. The electrical impulses in your heart cannot work correctly if your heartbeat is too fast.
Is I48 2 still valid?
2 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I48. 2 - other international versions of ICD-10 I48.
What is the ICD-10 code for Hfpef?
3.
What is the ICD-10 code for CVA?
9.
What is the ICD-10 code for non ischemic cardiomyopathy?
Similary for nonischemic cardiomyopathy icd 10 code, when you search in index column it will lead to unspecified code. Hence, most of the coder are using unspecified code I42. 9, for nonischemic cardiomyopathy.Aug 27, 2019
What is chronic AFib?
Overview. Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a type of heart arrhythmia that causes the top chambers of your heart, the atria, to quiver and beat irregularly. AFib used to be described as chronic or acute, with chronic AFib lasting longer than one week.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code. Type 1 Excludes.
What is the meaning of "poisoning by"?
Poisoning by, adverse effect of and underdosing of drugs, medicaments and biological substances. Code First. , for adverse effects, the nature of the adverse effect, such as:
What is a coded reaction to a medication?
Coughing up blood. Heavy periods. Remember for coding, if the patient is taking their medication as prescribed and develops an adverse reaction, such as bleeding, this is coded as an adverse reaction to the prescribed medication and not a poisoning.
How long can you take blood clot medication?
The length for taking these medications depends on the reason for needing to start them in the first place. They can prescribed for a few weeks or for the rest of your life. The site of the blood clot (if that is why they are prescribed) also helps to determine the length the medication will be needed.
What is the purpose of anticoagulant therapy?
Anticoagulation and Antiplatelet Therapy. Anticoagulants and antiplatelets are used for the prevention and treatment of blood clots that occur in blood vessels. Oftentimes, anticoagulants and antiplatelets are referred to as “blood thinners,” but they don’t actually thin the blood at all. These drugs slow down the body’s process of making clots.
What prevents platelets from sticking together?
Antiplatelets prevent platelets from sticking together. Fun Fact! Clots that are formed in the vein are mostly made of fibrin. This includes the diagnoses that we see of deep-vein-thrombosis (DVT). However, clots in the arteries typically are formed with mostly platelets.
Why do blood clots need to be clotted?
This enables the blood to clot. Blood must clot (hemostasis) in order to stop bleeding from injury or diseases that lead to hemorrhage/bleeding. Anticoagulants inhibit the creation of fibrin. Platelets are cells within our blood that bind together to help the blood clot.
How do clot drugs work?
These drugs slow down the body’s process of making clots. Their main function is to keep the patient’s blood from clotting or turning into solid clumps of cells. These drugs do this by interfering with either fibrin or platelets in the blood.
How do platelets respond to a hemorrhage?
When the body is bleeding a signal is sent and the platelets respond by traveling to the area of the bleeding. Once they have arrived at the site of the hemorrhage, they grow long tentacles and resemble spiders or an octopus when viewed under a microscope. Before they are signaled for clotting, they are plate shaped.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd code for cholesterol
- 2. what is the icd-10-cm code for sickle cell disease without crisis
- 3. icd-10-cm code for child with history of chronic constipation with soiling
- 4. icd 10 code for volume bacteremia
- 5. icd 10 code for fall with subsequent striking object
- 6. icd 9 code for pelvic abscess
- 7. icd 10 code for painful erection
- 8. icd 10 code for right tympanic membrane perforation and conductive hearing loss
- 9. icd 9 code for stifiness to extremities
- 10. icd 10 pcs code for repoductive system