What is considered uncontrolled AFIB?
Uncontrolled atrial fibrillation in adults
- Characteristics of AF. In AF, there's firing of multiple electrical impulses from several pacemaker sites in the atria. ...
- Signs and symptoms of AF. ...
- Emergent care. ...
- Preventing strokes. ...
- Improving quality of life. ...
- Discharge instructions. ...
- Summary. ...
What foods trigger atrial fibrillation?
Trans fats are found in:
- margarine
- foods made with partially hydrogenated vegetable oils
- certain crackers and cookies
- potato chips
- doughnuts
- other fried foods
Can AFIB reverse itself?
Sometimes atrial fibrillation can go away on its own. For example, if you have occasional atrial fibrillation, you will have symptoms for a few minutes, hours or days. You may call your doctor who asks for you to come to the office. But by the time you arrive, you have no symptoms.
How is AFIB diagnosed?
Perform transoesophageal echocardiography (TOE) in people with atrial fibrillation:
- when TTE demonstrates an abnormality (such as valvular heart disease) that warrants further specific assessment
- in whom TTE is technically difficult and/or of questionable quality and when there is a need to exclude cardiac abnormalities
- for whom TOE-guided cardioversion is being considered. [2006]
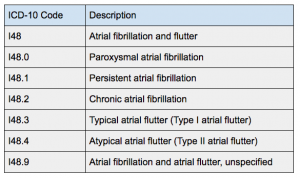
Is I48 2 still valid?
I48. 2 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I48. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is diagnosis code I48 91?
Unspecified atrial fibrillationThe code for “atrial fibrillation with RVR” is I48. 91 Unspecified atrial fibrillation.
How do you code new onset atrial fibrillation?
1 Persistent atrial fibrillation. I48. 11 Longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation.
What is diagnosis code I48 21?
Permanent atrial fibrillation21 - Permanent atrial fibrillation.
What is R06 00?
ICD-10 code R06. 00 for Dyspnea, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
Can you code A-fib and aflutter at the same time?
Conclusion: In certain patients, the occurrence of transient, simultaneous atrial fibrillation and flutter is possible.
How do you document the atrial fibrillation?
Documenting AFib as a confirmed condition if it is suspected; rather, document signs and symptoms in the absence of a confirmed diagnosis. Describing AFib as “history of” if the condition is still active (in diagnosis, “history of” implies the condition has resolved or no longer exists).
What does anemia D64 9 mean?
Code D64. 9 is the diagnosis code used for Anemia, Unspecified, it falls under the category of diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism.
How do you code sick sinus syndrome?
ICD-10 Code for Sick sinus syndrome- I49. 5- Codify by AAPC.
What is the code for long term use of anticoagulants?
ICD-10-CM Code for Long term (current) use of anticoagulants Z79. 01.
What is the ICD-10 code for hypothyroidism?
9 – Hypothyroidism, Unspecified. ICD-Code E03. 9 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Hypothyroidism, Unspecified.
What tests are used to detect AFIB?
Tests to be used to detect Afib are electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, holter monitor, stress test and chest X-ray. Afib can be managed with anti-arrhythmic or anticoagulant drugs. Even after doing ablation procedure to correct Afib there may be need of medication.
How long does AFIB last?
There are different types of afib based on how long it lasts. Persistent – Lasts more than 7 days and it needs an intervention to restore the rhythm. Chronic (Permanent) – Chronic stays more than 12 months and it is called permanent when the abnormal heart rhythm cannot be restored.
Is AFIB fatal?
Atrial Fibrillation is an irregular (often rapid) heartbeat which may lead to blood clot in the heart and travel to other parts of the body and make blocks. Afib itself is not fatal but it is critical when it leads to stroke or heart failure. Hence Afib needs to be managed.
What is the 91 modifier?
The 91 modifier can be used to bill repeat laboratory services, except for the following CPT codes: Q0111 (non- inclusive list). The 91 modifier may not be used when: There are standard CPT/HCPCS codes available that describe a series of results (e.g., glucose tolerance tests, evocation/suppression tests, etc.);
What is CPT 59 used for?
Modifier 59: Used for distinct procedural services such as multiple services submitted by a laboratory for the same member on the same day. These situations usually involve microbiology where samples or cultures are taken from a patient from different anatomical sites or different wounds, use the same CPT code, and are tested on the same day.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for cholecyctitia
- 2. icd 9 code for cryoglobulinemia
- 3. icd 10 code for meat allergy
- 4. icd code for long term use of meds
- 5. icd 10 code for rule out membranes rupture
- 6. icd 9 code for decreased milk production
- 7. what is the icd-10 code for term pregnancy with cephalic presentation
- 8. icd 10 code for unspecified hearing loss
- 9. icd-10-cm code for abdominal hernia
- 10. icd 10 code for atrial flutter with rapid ventricular response