How do you code dementia?
ICD-10-CM Codes › G00-G99 Diseases of the nervous system › G30-G32 Other degenerative diseases of the nervous system › Alzheimer's disease G30 Alzheimer's disease G30- Use Additional code to identify: delirium, if applicable ( F05) dementia with behavioral disturbance ( F02.81) dementia without behavioral disturbance ( F02.80) Type 1 Excludes
What is the ICD 10 code for early onset dementia?
Feb 15, 2018 · ICD 10 Code For Alzheimers Dementia Diagnosis. Many of us would remember the 40th President of the United States, late Ronald Reagan, who died of Alzheimer’s disease. There are about 6 million Americans who are afflicted with this disease and a lot more all over the world. The neurodegenerative disease, which was first diagnosed in Auguste ...
What are ICD 10 codes?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code F03 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code F03 Unspecified dementia 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code F03 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a …
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
Oct 01, 2021 · Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with behavioral disturbance F02.81 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Dementia in oth diseases classd elswhr w behavioral disturb The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM ...
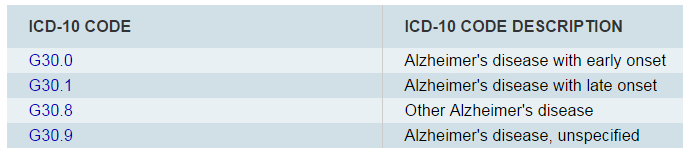
How do you code Alzheimer's dementia?
Alzheimer's disease and dementia coding: Per the ICD-10-CM Alphabetic Index, G30. 9 would be reported first, followed by F02. 81 or F02. 80 to show dementia with or without behavioral disturbances.
What is the ICD-10 code for Alzheimer's?
ICD-10-CM Code for Alzheimer's disease, unspecified G30. 9.
What is the ICD-10 code for dementia?
90 – Unspecified Dementia without Behavioral Disturbance. ICD-Code F03. 90 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Unspecified Dementia without Behavioral Disturbance.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for early onset Alzheimer's disease with behavioral disturbance?
ICD-10-CM Code for Alzheimer's disease with early onset G30. 0.
What is Alzheimer's disease unspecified?
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurologic disorder that causes the brain to shrink (atrophy) and brain cells to die. Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia — a continuous decline in thinking, behavioral and social skills that affects a person's ability to function independently.Feb 19, 2022
What is diagnosis code G30?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G30: Alzheimer's disease.
What is the ICD 10 code for uncomplicated senile dementia?
290.0 - Senile dementia, uncomplicated. ICD-10-CM.
What is the difference between dementia and Alzheimer's?
Dementia is the term applied to a group of symptoms that negatively impact memory, but Alzheimer's is a specific progressive disease of the brain that slowly causes impairment in memory and cognitive function.
What is the DSM 5 code for dementia?
These include: Dementia (290.0–290.4) Alzheimer's (331.0) Mild cognitive impairment (331.83)Jul 30, 2013
What is F02 81 diagnosis?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code F02. 81: Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with behavioral disturbance.
What is behavioral disturbance in dementia?
Behavioral disturbances in dementia are often globally described as “agitation” including verbal and physical aggression, wandering, and hoarding. 56. These symptoms create patient and caregiver distress, and lead to nursing home placement.
What is Alzheimer's disease?
A disabling degenerative disease of the nervous system occurring in middle-aged or older persons and characterized by dementia and failure of memory for recent events, followed by total incapacitation and death. Types of the alzheimer syndrome are differentiated by the age of onset and genetic characteristics.
What is dementia in the brain?
Clinical Information. A brain disorder that usually starts in late middle age or old age and gets worse over time. Symptoms include loss of memory, confusion, difficulty thinking, and changes in language, behavior, and personality. A degenerative disease of the brain characterized by the insidious onset of dementia.
What is the most common form of dementia in older people?
A progressive, neurodegenerative disease characterized by loss of function and death of nerve cells in several areas of the brain leading to loss of cognitive function such as memory and language. Alzheimer's disease (ad) is the most common form of dementia among older people.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
What is dementia in other diseases?
Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with combative behavior. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with violent behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. Alzheimer's disease ( G30.-) "Includes" further defines, or give examples of, the content of the code or category.
What is neurocognitive disorder?
Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with combative behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with violent behavior.
What is Alzheimer's disease?
A disabling degenerative disease of the nervous system occurring in middle-aged or older persons and characterized by dementia and failure of memory for recent events, followed by total incapacitation and death. Types of the alzheimer syndrome are differentiated by the age of onset and genetic characteristics.
What is dementia in the brain?
Clinical Information. A brain disorder that usually starts in late middle age or old age and gets worse over time. Symptoms include loss of memory, confusion, difficulty thinking, and changes in language, behavior, and personality. A degenerative disease of the brain characterized by the insidious onset of dementia.
What is the most common form of dementia in older people?
A progressive, neurodegenerative disease characterized by loss of function and death of nerve cells in several areas of the brain leading to loss of cognitive function such as memory and language. Alzheimer's disease (ad) is the most common form of dementia among older people.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
What is the brain disorder that affects a person's ability to carry out daily activities?
Dementia is a brain disorder that seriously affects a person's ability to carry out daily activities. Ad begins slowly. It first involves the parts of the brain that control thought, memory and language. People with ad may have trouble remembering things that happened recently or names of people they know.
What is dementia in other diseases?
Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with combative behavior. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with violent behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. Alzheimer's disease ( G30.-) "Includes" further defines, or give examples of, the content of the code or category.
What causes dementia?
There are many causes of dementia, including alzheimer disease, brain cancer, and brain injury. Dementia usually gets worse over time. An acquired organic mental disorder with loss of intellectual abilities of sufficient severity to interfere with social or occupational functioning.
What is the condition where you lose the ability to think, remember, learn, make decisions, and solve problems?
Clinical Information. A condition in which a person loses the ability to think, remember, learn, make decisions, and solve problems. Symptoms may also include personality changes and emotional problems. There are many causes of dementia, including alzheimer disease, brain cancer, and brain injury.
What causes dementia?
There are many causes of dementia, including alzheimer disease, brain cancer, and brain injury. Dementia usually gets worse over time. An acquired organic mental disorder with loss of intellectual abilities of sufficient severity to interfere with social or occupational functioning.
What causes intellectual impairment in elderly?
Causes include alzheimer's disease, brain injuries, brain tumors, and vascular disorders.
What is dementia clinical?
Severe dementia. Clinical Information. A condition in which a person loses the ability to think, remember, learn, make decisions, and solve problems. Symptoms may also include personality changes and emotional problems. There are many causes of dementia, including alzheimer disease, brain cancer, and brain injury.
What is exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. A type 2 excludes note represents "not included here".
When is the ICd 10 code for dementia effective?
The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM F03 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
What is F02.81?
F02.81 describes the manifestation of an underlying disease, not the disease itself. Applicable To. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with combative behavior. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with violent behavior.
What is dementia in other diseases?
Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with violent behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with combative behavior.
What should be documented in a dementia patient?
In addition to the objective examination, the physician should document behavioral disturbances such as sleep disturbance, aggression, agitation, hallucination, delusion, and wandering.
What is frontotemporal dementia?
Frontotemporal dementia: This is a group of dementias caused by progressive nerve cell damage in the brain’s frontal lobes or its temporal lobes. This causes deterioration in behavior, personality and/or difficulty with producing or comprehending language.
What is the second most common type of dementia?
Vascular dementia: This is the second most common type of dementia. Vascular dementia can occur if a stroke blocks an artery in the brain. Other causes include conditions that damage blood vessels, affect circulation, and deprive the brain of vital oxygen and nutrients.
What are the causes of dementia?
Dementia occurs when the brain cells are damaged and cannot communicate with each other. Thinking, behavior and feelings can be affected when brain cells are unable to communicate normally. Progressive dementia types are not reversible and include:
What are the symptoms of parkinsonian movement?
Common signs and symptoms include changes in thinking and reasoning, sleep disturbances, delusions and hallucinations, confusion and alertness that varies significantly from day to day or from time of day to another, slowness, tremors, and other parkinsonian movement features.
Why is it important to have a good medical record?
Good medical record documentation is essential to describe the severity of illness, to improve and measure quality of care, to provide better data for research, and for optimal reimbursement.
What are the three things that a physician must do to diagnose dementia?
Ability to focus and pay attention. Reasoning and judgment. Visual perception. To diagnose the cause of the dementia, the physician must identify the pattern of the loss of skills and function and determine what functions the person can still perform.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for mcmurray sign of both knees
- 2. icd 10 code for ckd3b
- 3. icd-10 code for anticoagulation monitoring
- 4. icd 10 code for right intertrochanteric hip fracture
- 5. icd 10 code for chronic asthma
- 6. what is the icd 10 code for abdominal hysterectomy
- 7. icd-10 code for routine foot exam
- 8. icd 10 code for wound vac dressing change
- 9. icd 10 code for contaact with people
- 10. what is the correct icd 10 code for right perihilar mass