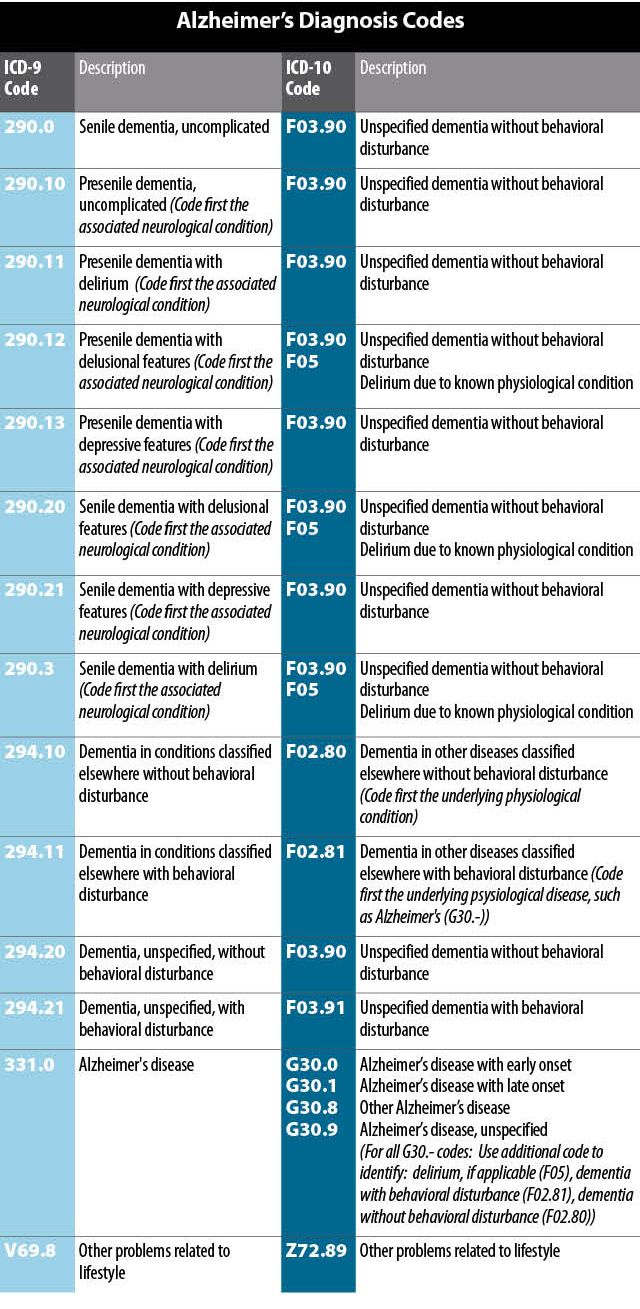
Alzheimer's disease, unspecified. G30.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is ICD 10 used for?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G30.9 Alzheimer's disease, unspecified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code G30.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G30.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G30 Alzheimer's disease 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code G30 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G30 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What does ICD 10 mean?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G30.1 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G30.1 Alzheimer's disease with late onset 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code Adult Dx (15-124 years) G30.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
Feb 20, 2020 · Alzheimer's disease, unspecified G30. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for Alzheimer's?
ICD-10-CM Code for Alzheimer's disease, unspecified G30. 9.
How do you code Alzheimer's dementia?
Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia. Alzheimer's dementia requires two ICD-9-CM codes. Code 331.0 is sequenced first followed by code 294.1x.Oct 15, 2007
What is the ICD-10-CM code for early onset Alzheimer's disease?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G30. 0: Alzheimer's disease with early onset.
What is the ICD 9 code for Alzheimer's disease?
ICD-9-CM gave us one code for Alzheimer's disease, 331.0.Mar 9, 2015
What is the ICD-10 code for end stage Alzheimer's disease?
1.
What is Alzheimer's disease unspecified?
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurologic disorder that causes the brain to shrink (atrophy) and brain cells to die. Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia — a continuous decline in thinking, behavioral and social skills that affects a person's ability to function independently.Feb 19, 2022
What is F02 81 diagnosis?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code F02. 81: Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with behavioral disturbance.
What diagnosis code is reported for behavioral disturbances in patient with early onset Alzheimer?
The Index provides the following documentation: Alzheimer's, early onset, with behavioral disturbance G30. 0 [F02. 81].
What is the ICD-10 code for early dementia?
Code F03. 90 is the diagnosis code used for Unspecified Dementia without Behavioral Disturbance. It is a mental disorder in which a person loses the ability to think, remember, learn, make decisions, and solve problems.
What is diagnosis code G30?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G30: Alzheimer's disease.
What is late onset Alzheimer's disease?
Late-onset Alzheimer disease typically presents with progressive decline in episodic memory, with variable involvement of other cognitive domains. Progressive memory impairment can also be caused by other neurodegenerative processes affecting the medial temporal lobes.
What's the ICD 10 code for hypertension?
That code is I10, Essential (primary) hypertension. As in ICD-9, this code includes “high blood pressure” but does not include elevated blood pressure without a diagnosis of hypertension (that would be ICD-10 code R03. 0).
What is Alzheimer's disease?
A disabling degenerative disease of the nervous system occurring in middle-aged or older persons and characterized by dementia and failure of memory for recent events, followed by total incapacitation and death. Types of the alzheimer syndrome are differentiated by the age of onset and genetic characteristics.
What is dementia in other diseases?
Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with combative behavior. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with violent behavior. Major neurocognitive disorder in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior.
What is dementia in the brain?
Clinical Information. A brain disorder that usually starts in late middle age or old age and gets worse over time. Symptoms include loss of memory, confusion, difficulty thinking, and changes in language, behavior, and personality. A degenerative disease of the brain characterized by the insidious onset of dementia.
What is the most common form of dementia in older people?
A progressive, neurodegenerative disease characterized by loss of function and death of nerve cells in several areas of the brain leading to loss of cognitive function such as memory and language. Alzheimer's disease (ad) is the most common form of dementia among older people.
Is G30 a reimbursement code?
G30 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM G30 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of G30 - other international versions of ICD-10 G30 may differ. Certain conditions have both an underlying ...
What is the ICD code for Alzheimer's?
ICD Code G30 is a non-billable code. To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the four child codes of G30 that describes the diagnosis 'alzheimer's disease' in more detail. G30 Alzheimer's disease. NON-BILLABLE. BILLABLE.
What is the ICD code for neurodegeneration?
The ICD code G30 is used to code Neurodegeneration. Neurodegeneration is the umbrella term for the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, including death of neurons.
What is the ICD code for acute care?
G30 . Non-Billable means the code is not sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code G30 is a non-billable code.
What are the parallels between neurodegenerative disorders?
There are many parallels between different neurodegenerative disorders including atypical protein assemblies as well as induced cell death. Neurodegeneration can be found in many different levels of neuronal circuitry ranging from molecular to systemic. Specialty:
What is the use of additional code?
Use Additional Code. Use Additional Code note means a second code must be used in conjunction with this code. Codes with this note are Etiology codes and must be followed by a Manifestation code or codes. Code to identify: Delirium, if applicable See Code F05.
What is F02.80?
F02.80 describes the manifestation of an underlying disease, not the disease itself. This block comprises a range of mental disorders grouped together on the basis of their having in common a demonstrable etiology in cerebral disease, brain injury, or other insult leading to cerebral dysfunction. The dysfunction may be primary, as in diseases, ...
Is Alzheimer's disease a primary or secondary disease?
The dysfunction may be primary, as in diseases, injuries, and insults that affect the brain directly and selectively; or secondary, as in systemic diseases and disorders that attack the brain only as one of the multiple organs or systems of the body that are involved. Alzheimer's ( G30.-)
What is the second most common type of dementia?
Vascular dementia: This is the second most common type of dementia. Vascular dementia can occur if a stroke blocks an artery in the brain. Other causes include conditions that damage blood vessels, affect circulation, and deprive the brain of vital oxygen and nutrients.
What are the three things that a physician must do to diagnose dementia?
Ability to focus and pay attention. Reasoning and judgment. Visual perception. To diagnose the cause of the dementia, the physician must identify the pattern of the loss of skills and function and determine what functions the person can still perform.
What should be documented in a dementia patient?
In addition to the objective examination, the physician should document behavioral disturbances such as sleep disturbance, aggression, agitation, hallucination, delusion, and wandering.
What is frontotemporal dementia?
Frontotemporal dementia: This is a group of dementias caused by progressive nerve cell damage in the brain’s frontal lobes or its temporal lobes. This causes deterioration in behavior, personality and/or difficulty with producing or comprehending language.
What are the causes of dementia?
Dementia occurs when the brain cells are damaged and cannot communicate with each other. Thinking, behavior and feelings can be affected when brain cells are unable to communicate normally. Progressive dementia types are not reversible and include:
What are the characteristics of dementia?
According to www.alz.org, at least two of the following core mental abilities must be significantly affected to be considered dementia: 1 Memory 2 Communication and language 3 Ability to focus and pay attention 4 Reasoning and judgment 5 Visual perception
Is dementia easy to diagnose?
Due to its debilitating effects, caring for a patient with dementia is also not easy. As they provide patients with individualized care, ...
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for stomach pain
- 2. icd 9 code for patient has diagnosis poisoning assault hair dye. initial encounter.
- 3. icd-10 code for homocysteine blood test
- 4. icd 10 code for tingling in extremities
- 5. icd 10 code for ureteral mass
- 6. icd 10 code for old stroke with residual left hemiparesis
- 7. icd 10 code for pathologic fracture acetabulum
- 8. icd 10 code for crest syndrome
- 9. icd 10 code for twin pregnancy first trimester
- 10. icd 10 cm code for chronic serous otitis media