What is the ICD 10 code for antenatal screening?
Encounter for other antenatal screening follow-up 1 Z36.2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM Z36.2 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z36.2 - other international versions of ICD-10 Z36.2 may differ.
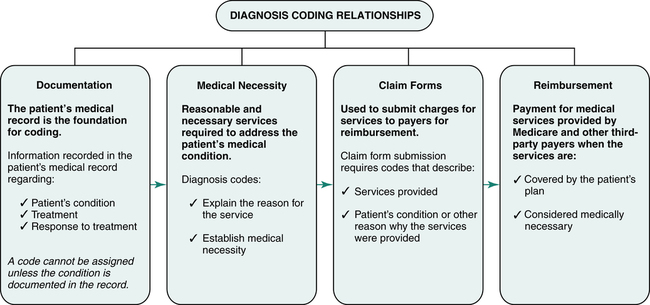
How do I Capture pregnancy diagnosis codes correctly?
To capture pregnancy diagnosis codes correctly, documentation must specify the type and trimester of the pregnancy, as well as all related, present co-conditions in the mother.
What is the ICD 10 code for routine prenatal care?
routine prenatal care ( ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z34. Encounter for supervision of normal pregnancy 2016 2017 2018 2019 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code. Type 1 Excludes any complication of pregnancy (O00-O9A) encounter for pregnancy test (Z32.0-) encounter for supervision of high risk pregnancy (O09.-) Z34)
What is the ICD 10 code for supervision of normal pregnancy?
Encounter for supervision of normal pregnancy, unspecified, second trimester. Z34.92 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM Z34.92 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD-10 code for pregnancy screening?
ICD-10 code Z36 for Encounter for antenatal screening of mother is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the ICD-10 code for dating ultrasound?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z36. 87: Encounter for antenatal screening for uncertain dates.
What is the ICD-10 code for routine obstetric care?
ICD-10-CM Code for Encounter for supervision of normal pregnancy, unspecified Z34. 9.
What is ICD-10 code Z34?
Encounter for supervision of normal pregnancy2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z34: Encounter for supervision of normal pregnancy.
What is the ICD 10 code for pelvic ultrasound?
Any ICD-10-CM code that is not listed in the ICD-10-CM Codes that Support Medical Necessity section of this Billing and Coding: Nonobstetric Pelvic Ultrasound A56671 article.
What is the difference between 76805 and 76811?
Q Are CPT 76805 and 76811 different? Both are for fetal and maternal ultrasound evaluation, yet 76811 includes a detailed fetal anatomic exam.
How do you code prenatal visits?
Primary care physicians providing only prenatal care should bill for the prenatal visits they have provided using CPT Code 59425 (antepartum care only; 4 to 6 visits) or CPT Code 59426 (antepartum care only; 7 or more visits), and will be reimbursed according to Aetna's fee schedule.
How do you bill for initial OB appointment?
Use CPT Category II code 0500F (Initial prenatal care visit) or 0501F (Prenatal flow sheet documented in medical record by first prenatal visit).
How do you code pregnancy?
While she is in fact pregnant, her pregnancy is not the reason for the encounter, and therefore, using the code Z33. 1, Pregnant state, incidental, would be appropriate; Z33.
What are the 3 trimesters of pregnancy?
A pregnancy is divided into three stages called trimesters: first trimester, second trimester, and third trimester.
What is the ICD 10 code for normal first pregnancy?
ICD-10-CM Code for Encounter for supervision of normal first pregnancy Z34. 0.
When should Z33 1 pregnancy state Incidental be used?
The only exception to this is if a pregnant woman is seen for an unrelated condition. In such cases, code Z33. 1 Pregnant State, Incidental should be used after the primary reason for the visit.
What chapter is ICD 10 for pregnancy?
The Pregnancy ICD 10 code belong to the Chapter 15 – Pregnancy, Childbirth, and the Puerperium of the ICD-10-CM and these codes take sequencing priority over all the other chapter codes.
What is the code for ectopic pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy (Code range- O00.00 – O00.91) – This is a potentially life-threatening condition in which the fertilize egg is implanted outside the uterus, usually in one of the fallopian tubes or occasionally in the abdomen or ovaries.
What is the code for Galactorrhea?
Galactorrhea. Other obstetric conditions, not elsewhere classified (Code range O94-O9A) Sequelae (Late effects) of complication of pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium (O94)- Includes conditions or late effects that may occur any time after the puerperium.
What is the code for velamentous insertion of the umbilical cord?
Morbidly adherent placenta (Placenta accrete, Placenta increta, Placenta percreta) Placental infarction. Placenta previa (Code range O44.00- O44.53)- Condition in which the placenta is implanted in the lower parts of the uterus.
What is the code for a hospital visit that is not pregnancy related?
If the provider has documented that the pregnancy is incidental to the visit, which means that the reason for the visit was not pregnancy related and the provider did not care for the pregnancy, the code to be used is Z33.1, Pregnant state, incidental and not the chapter 15 codes.
When should the code for a C section be sequenced first?
If the patient is admitted with a pregnancy complication which necessitated a Cesarean delivery, the code for the complication should be sequenced first. But if the reason for admission was different from the reason for the C-section, the reason for the admission will be sequenced first.
Is it difficult to code for pregnancy?
Coding for Pregnancy is sometimes difficult as there are multiple factors that need to be taken into consideration like the trimester, fetus identification, whether it is a high risk pregnancy or a normal pregnancy and other additional code like the code for the weeks of gestation from chapter 22.
When is the ICd 10 code Z36 effective?
The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM Z36 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is a Z code?
Z codes represent reasons for encounters. A corresponding procedure code must accompany a Z code if a procedure is performed.
What is the ICd 10 code for antenatal screening?
Encounter for antenatal screening for malformations 1 Z36.3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM Z36.3 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z36.3 - other international versions of ICD-10 Z36.3 may differ.
What is a screening test?
Screening is the testing for disease or disease precursors in asymptomatic individuals so that early detection and treatment can be provided for those who test positive for the disease. Type 1 Excludes. diagnostic examination- code to sign or symptom.
What is the Z34.92?
Z34.92 is applicable to maternity patients aged 12 - 55 years inclusive. Z34.92 is applicable to mothers in the second trimester of pregnancy, which is defined as between equal to or greater than 14 weeks to less than 28 weeks since the first day of the last menstrual period.
What is a Z00-Z99?
Categories Z00-Z99 are provided for occasions when circumstances other than a disease, injury or external cause classifiable to categories A00 -Y89 are recorded as 'diagnoses' or 'problems'. This can arise in two main ways:
What Is Maternal-Fetal Medicine?
MFM is the practice of caring for patients with complications of pregnancy. In essence, MFM is consultative. MFM specialists generally don’t always perform deliveries; but they might determine when it’s time for delivery.
Global Care vs. Consultative Services
The obstetric package includes prenatal visits, delivery, and postpartum care. The CPT® codes for these services, depending on delivery method, include:
Coding Fetal Ultrasounds
Ultrasound code selection is based on the gestational age, number of fetuses, and medical necessity. The physician or other qualified healthcare professional may perform an ultrasound on a patient in her first trimester to determine the number of sacs and to survey the fetal structures, amniotic fluid, and maternal structure.
Biophysical Profiles
BPPs are physiologic tests, not anatomic ultrasounds. A physician may conduct a BPP to look at fetal heart tones, amniotic fluid, and breathing, and may or may not conduct NST. The codes are:
Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis may be diagnostic or therapeutic. A diagnostic amnio may involve sending the fluid to a lab for genetic testing.
ICD-10-CM Coding
One of the basic guidelines that we learn early on is that Chapter 15 codes take priority over every other chapter in the book. “This is a problem because when you have a high-risk diabetic patient, the plan of care may include visits with other specialties,” stated Stilley.
Common ICD-10 OBGYN Codes
The clinical concepts for OBGYN guide includes common ICD-10 codes, clinical documentation tips and clinical scenarios.
Noninflammatory Disorders of Ovary, Fallopian Tubes, and Broadligament
N83.0 Follicular cyst of ovary N83.1 Corpus luteum cyst N83.20* Unspecified ovarian cysts N83.29 Other ovarian cysts N83.31 Acquired atrophy of ovary N83.32 Acquired atrophy of fallopian tube N83.33 Acquired atrophy of ovary and fallopian tube N83.4 Prolapse and hernia of ovary and fallopian tube N83.51 Torsion of ovary and ovarian pedicle N83.52 Torsion of fallopian tube N83.53 Torsion of ovary, ovarian pedicle and fallopian tube N83.6 Hematosalpinx N83.7 Hematoma of broad ligament N83.8 Other noninflammatory disorders of ovary, fallopian tube & broad ligament N83.9* Noninflammatory disorder of ovary, fallopian tube and broad ligament, unspecified.
What factors are considered when coding a pregnancy?
When coding, consider all documented factors such as current and pre-existing conditions, trimester, and age. To capture pregnancy diagnosis codes correctly, documentation must specify the type and trimester of the pregnancy, as well as all related, present co-conditions in the mother.
What is the code for champagne on New Year's Eve?
Anything a patient experiences — a cold, a slip and fall resulting in a sprained ankle, an asthma attack, having champagne on New Year’s Eve — may require code (s) from category O09 Supervision of high risk pregnancy.
What is the CDC's Division of Reproductive Health?
CDC’s Division of Reproductive Health conducts research to better understand pregnancy-related problems, with the aims of making pregnancy healthier, preventing or managing complications, and reducing poor pregnancy outcomes, including death— the most extreme adverse outcome.
How does pregnancy affect medical decisions?
Pregnancy Affects Medical Decision-making. When a patient is pregnant, anything done for the mother may affect the baby. This, in turn, affects the provider’s medical decision-making, as does any condition (s) the mother had prior to her pregnancy.
What is the code for marijuana use?
For marijuana use, assign O99.321 -O99.323 Drug use complicating pregnancy (last character depends on trimester) and, depending on documentation, a code in the F12.90 (Cannabis use, unspecified, uncomplicated) range. If the mother had an occasional glass of wine throughout the pregnancy, report O99.311-O99.313 Alcohol use complicating pregnancy ...
Why does accurate coding matter?
This is one reason, but it’s not the only reason. Accurate coding matters because many organizations and associations gather this information and track the patterns of complications, whether in the mother, the fetus, or both.
What percentage of pregnant women are overweight?
More than 50 percent of pregnant women in the U.S. are overweight or obese, according to the American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Being obese raises the risk for high blood pressure, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, stillbirth, neural tube defects, and cesarean delivery.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10-cm code for bilateral meniere's disease
- 2. icd 10 code for e coli staph infection
- 3. icd 9 code for incision and drainage
- 4. icd 10 code for ingestion of bora
- 5. icd 10 code for benign neoplasm of skin of external genitalia
- 6. icd 10 code for proteinuria due to diabetes
- 7. icd 10 cm code for recheck laceration, left leg
- 8. icd-10 code for wolff-parkinson-white disorder
- 9. icd 10 code for heavy lifting
- 10. icd 10 code for osteoarthrits cervical spine