What can be done for a brain aneurysm?
Treatment
- Surgery. There are two common treatment options for a ruptured brain aneurysm. ...
- Flow diverters. ...
- Other treatments (ruptured aneurysms) Other treatments for ruptured brain aneurysms are aimed at relieving symptoms and managing complications.
- Treating unruptured brain aneurysms. ...
- Lifestyle changes to lower your risk. ...
What happens in the brain during an aneurysm?
What Happens in a Brain Aneurysm Your brain has many small vessels that carry blood. If the walls of one of those vessels is weak, it can bulge out and form a small blood-filled balloon. This is a...
What are the early symptoms of a brain aneurysm?
- Blurred or double vision
- A drooping eyelid
- A dilated pupil
- Pain above and behind one eye
- Weakness and/or numbness
Is brain aneurysm life threatening?
If an aneurysm in the brain ruptures, it can cause bleeding in the brain, also known as a hemorrhagic stroke. A ruptured aneurysm can be life-threatening and needs to be addressed medically immediately. Many brain aneurysms are detected before they rupture, through tests for other conditions. What Causes A Brain Aneurysm?
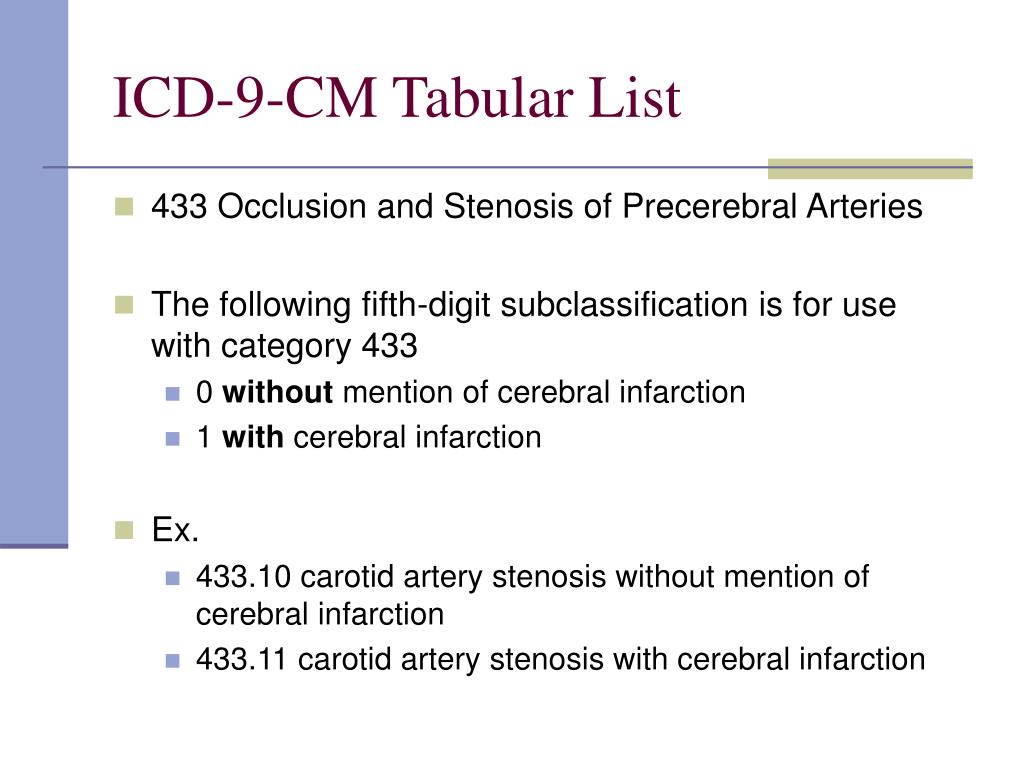
What is the diagnosis code for aneurysm?
I67. 1 - Cerebral aneurysm, nonruptured. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for History of brain aneurysm?
I67. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I67. 1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for I67 1?
ICD-10 code: I67. 1 Cerebral aneurysm and cerebral arteriovenous fistula.
What are the 3 types of brain aneurysms?
There are three types of cerebral aneurysms:Saccular aneurysm. A saccular aneurysm is a rounded sac containing blood, that is attached to a main artery or one of its branches. ... Fusiform aneurysm. A fusiform aneurysm balloons or bulges out on all sides of the artery.Mycotic aneurysm.
What is diagnosis code Z82 49?
Family history of ischemic heart disease and otherICD-10 code Z82. 49 for Family history of ischemic heart disease and other diseases of the circulatory system is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the ICD 10 code for Family history of brain aneurysm?
49.
What is the ICD 10 code for right ICA aneurysm?
I72. 0 - Aneurysm of carotid artery. ICD-10-CM.
What is the cause of a brain aneurysm?
Brain aneurysms are caused by a weakness in the walls of blood vessels in the brain.
What is Supraclinoid ICA aneurysm?
Supraclinoid aneurysms of the carotid artery are a potentially treatable cause of progressive visual impairment. Approximately 10% of these aneurysms present neurological signs associated with a mass effect, such as headache, ophthalmoparesis, and the visual impairment mentioned here.
What is another name for a brain aneurysm?
An aneurysm in the brain (also called a cerebral aneurysm or an intracranial aneurysm) is a bulging, weakened area in the middle layer of the wall of a blood vessel in the brain, resulting in an abnormal widening. An aneurysm may occur in any artery, but is often seen in arteries in the brain.
What is the most common type of aneurysm?
The most common, "berry aneurysm," occurs more often in adults. It can range in size from a few millimeters to more than two centimeters. A family history of aneurysms may increase your risk.
What is the most fatal aneurysm?
An abdominal aortic aneurysm is dangerous because it is a weakening of the wall of the main blood vessel in your body. Once that wall becomes too weakened, it can burst. The hemorrhage most likely will lead to death. There are more than 10,000 deaths per year from ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms.
What are three major causes of an aneurysm?
Any condition that causes your artery walls to weaken can bring one on. The most common culprits are atherosclerosis and high blood pressure. Deep wounds and infections can also lead to an aneurysm. Or you may be born with weakness in one of your artery walls.
Can you live a normal life after a brain aneurysm?
With rapid, expert treatment, patients can often recover fully. An unruptured brain aneurysm may cause zero symptoms. People can live with them for years before detection. If a brain aneurysm is unruptured, no blood has broken through the blood vessel walls.
How big is an aneurysm before it bursts?
Less than 3 mm in size have a low risk of rupture. Larger than 3 mm have a higher risk of bursting.
What is the most common site for aneurysm?
The most common location of an aneurysm is the aorta, which carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the body. The thoracic aorta is the short segment of the aorta in the chest cavity. The abdominal aorta is the section of the aorta that runs through the abdomen.
What is an aneurysm?
Aneurysms are classified by location, etiology, or other characteristics. Pathological, blood-filled distension of blood vessel. Protruding sac in the wall of a vein, artery, or heart, frequently caused by microbial infection; may present as pain, pressure on nearby organs, or cardiac weakening.
What are the two main treatments for aneurysms?
Medicines and surgery are the two main treatments for aneurysms. Bulging or ballooning in an area of an artery secondary to arterial wall weakening. Pathological outpouching or sac-like dilatation in the wall of any blood vessel (arteries or veins) or the heart (heart aneurysm).
What happens if an aneurysm bursts?
If an aneurysm grows large, it can burst and cause dangerous bleeding or even death. Most aneurysms occur in the aorta, the main artery traveling from the heart through the chest and abdomen. Aneurysms also can happen in arteries in the brain, heart and other parts of the body. If an aneurysm in the brain bursts, it causes a stroke. Aneurysms can develop and become large before causing any symptoms. Often doctors can stop aneurysms from bursting if they find and treat them early. Medicines and surgery are the two main treatments for aneurysms.
Where do aneurysms occur?
Most aneurysms occur in the aorta, the main artery traveling from the heart through the chest and abdomen. Aneurysms also can happen in arteries in the brain, heart and other parts of the body. If an aneurysm in the brain bursts, it causes a stroke. Aneurysms can develop and become large before causing any symptoms.
When will ICD-10-CM I72.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I72.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the code for a brain aneurysm?
A congenital brain aneurysm is classified to code 747.81, Anomalies of cerebrovascular system. Most brain aneurysms don’t cause problems or symptoms. However, some may leak or even rupture, which causes bleeding in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke). A ruptured brain aneurysm is classified to code 430, Subarachnoid hemorrhage.
What is the code for clipping a cerebral aneurysm?
It is interesting to note that clipping of a cerebral aneurysm through a craniotomy is classified to code 03VG0CZ. Most of the characters are the same as the endovascular embolization with the exception of the approach (fifth character), which is open, and device (sixth character), which is an extraluminal device.
What is the most common type of device used to treat brain aneurysms?
The most common type of device used to treat brain aneurysms are coils. Currently, there are two types of coils used: bare platinum coils (BPCs) and bioactive coils. Endovascular embolization of a brain aneurysm using BPCs is classified to code 39.75 and includes bare metal coils . Endovascular embolization of a brain aneurysm using bioactive coils ...
What is the code for coil embolization of an intracranial artery?
Therefore, the code assignment for coil embolization of an intracranial artery is 03VG3DZ. The following explains the meaning of each character:
What are the symptoms of a ruptured brain aneurysm?
Symptoms specific to ruptured brain aneurysms are a sudden and extremely severe headache, which the patient may describe it as the “worst headache ever”; nausea and vomiting; a stiff neck or neck pain; sensitivity to light; a seizure; and loss of consciousness or fainting.
What is the procedure to seal off an aneurysm?
Endovascular embolization involves inserting a catheter into an artery, usually one in the groin, and threads a device into the aneurysm to disrupt the blood flow and cause the blood to clot. This procedure seals off the aneurysm from the artery.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for slip nd fall
- 2. the icd-10-cm code(s) for atony of colon is
- 3. icd-10 code for aspirin
- 4. icd 10 code for fall from tripping
- 5. icd 10 code for tear of the anterior talofibular ligament
- 6. icd 10 cm code for riding jet ski
- 7. icd 10 code for elevated hepatic function
- 8. icd 10 code for 146.3
- 9. icd-10 code for right eyebrow laceration subsequent encounter
- 10. icd 10 code for passing out