Cerebral aneurysm, nonruptured. I67.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for aneurysm of other arteries?
Aneurysm of other precerebral arteries. I72.5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM I72.5 became effective on October 1, 2019.
What is the CPT code for aneurysm coil?
Currently, there are two types of coils used: bare platinum coils (BPCs) and bioactive coils. Endovascular embolization of a brain aneurysm using BPCs is classified to code 39.75 and includes bare metal coils.
What is the ICD 10 code for presence of other vascular implants?
Presence of other vascular implants and grafts 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code POA Exempt Z95.828 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM Z95.828 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICD 9 code for brain aneurysm?
Brain aneurysm is assigned to ICD-9-CM code 437.3, Cerebral aneurysm, nonruptured. Code 437.3 also includes an aneurysm of the intracranial portion of the internal carotid artery.

What is the ICD 10 code for coil embolization?
Embolism and thrombosis of other arteries The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I74. 8 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I74.
What is the ICD 10 code for cerebral aneurysm?
ICD-10 code I67. 1 for Cerebral aneurysm, nonruptured is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
How do you code a cerebral aneurysm?
Brain aneurysm is assigned to ICD-9-CM code 437.3, Cerebral aneurysm, nonruptured. Code 437.3 also includes an aneurysm of the intracranial portion of the internal carotid artery.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for ruptured berry aneurysm?
I60. 7 - Nontraumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage from unspecified intracranial artery | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD 10 code for right ICA aneurysm?
I72. 0 - Aneurysm of carotid artery. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD 10 code for family history of brain aneurysm?
49.
What is coiling of an aneurysm?
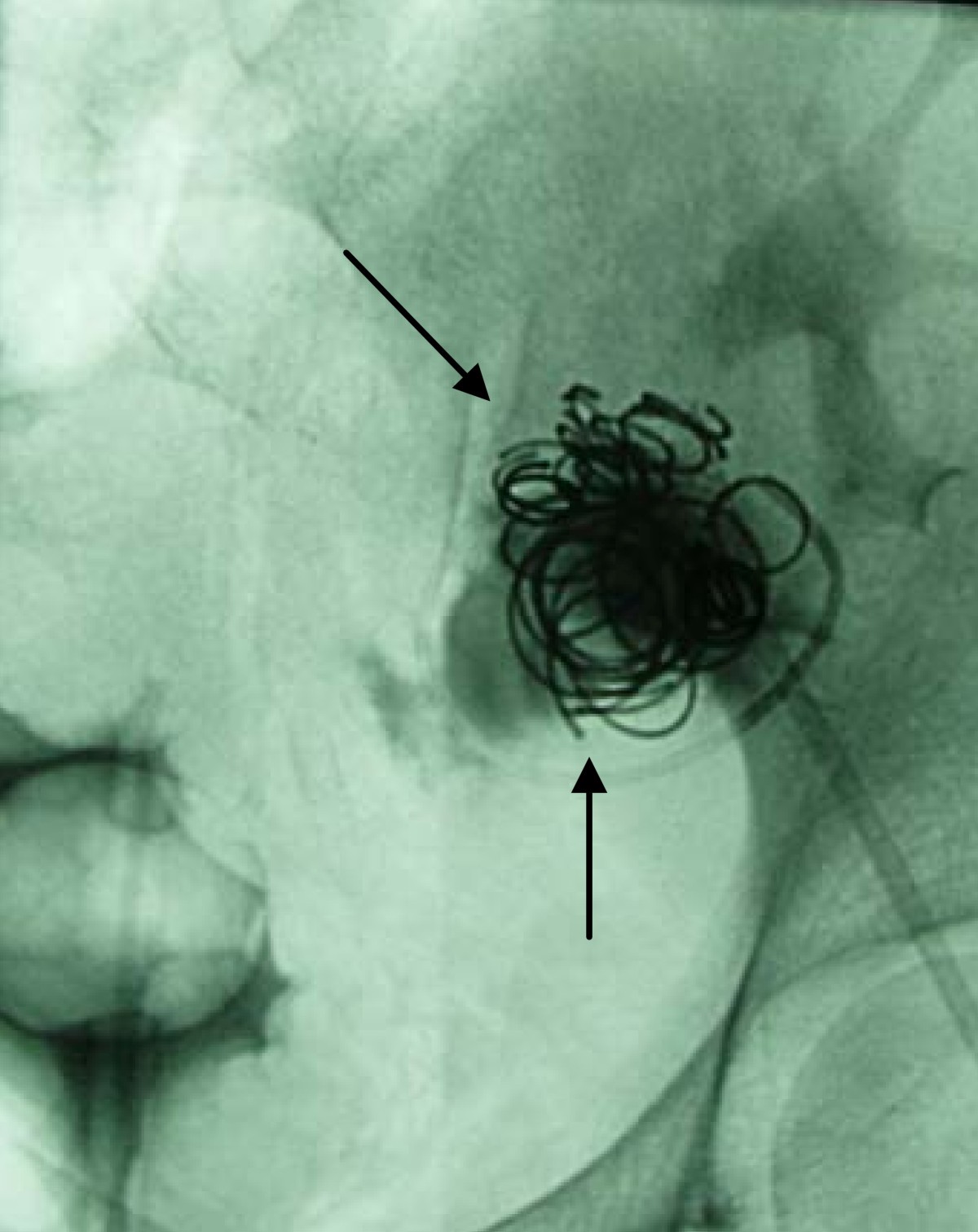
Endovascular coiling is a procedure performed to block blood flow into an aneurysm (a weakened area in the wall of an artery). Endovascular coiling is a more recent treatment for brain aneurysms; it has been used in patients since 1991.
What is a coil embolization procedure?
Coil Embolization is a catheter-based procedure that allows precise occlusion of abnormal blood flow in a blood vessel. A catheter with a metallic occluding coil is inserted into an artery, usually in the groin (the femoral artery). It is then advanced to the abnormal blood vessel.
Is coil embolization occlusion or restriction?
Embolization of a cerebral aneurysm is coded to the root operation Restriction, because the objective of the procedure is not to close off the vessel entirely, but to narrow the lumen of the vessel at the site of the aneurysm where it is abnormally wide.
What is the ICD 10 code for SAH?
6X9 for Traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage with loss of consciousness of unspecified duration is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes .
What is the ICD 10 code for AAA?
ICD-10 code I71. 4 for Abdominal aortic aneurysm, without rupture is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is a ruptured berry aneurysm?
When a berry aneurysm ruptures, blood from the artery moves into the brain. A ruptured aneurysm is a serious condition that needs immediate medical treatment. Keep in mind that, according to the American Stroke Association, only 1.5 to 5 percent of people will develop a brain aneurysm.
What can cause aneurysm brain?
What causes brain aneurysms?Smoking.Blood infection.High blood pressure (hypertension).Amphetamine and cocaine use.Traumatic brain injury (often caused by car crashes).Atherosclerosis (fatty buildup on blood-vessel walls).
What is left MCA aneurysm?
Abstract. Middle cerebral artery (MCA) aneurysm is one of the most popular cerebral aneurysm. MCA aneurysm located in the superficial region of the brain and had relative wide neck, therefore it is usually selected to operate directly. The surgery of MCA aneurysm is basic and good case for young neurosurgeons.
What are the ICD-10 codes for stroke?
For ischaemic stroke, the main codes are ICD-8 433/434 and ICD-9 434 (occlusion of the cerebral arteries), and ICD-10 I63 (cerebral infarction). Stroke is a heterogeneous disease that is not defined consistently by clinicians or researchers [35].
What do you do for an aneurysm?
The only way to treat an aneurysm is to have it repaired with surgery or an endovascular procedure. Sometimes, surgery isn't possible, or it may pose more danger than the aneurysm. Careful monitoring and medication may be best in that case. Your doctor will figure out the size, type, and location of the aneurysm.
What happens if an aneurysm bursts?
If an aneurysm grows large, it can burst and cause dangerous bleeding or even death. Most aneurysms occur in the aorta, the main artery traveling from the heart through the chest and abdomen. Aneurysms also can happen in arteries in the brain, heart and other parts of the body. If an aneurysm in the brain bursts, it causes a stroke. Aneurysms can develop and become large before causing any symptoms. Often doctors can stop aneurysms from bursting if they find and treat them early. Medicines and surgery are the two main treatments for aneurysms.
What are the two main treatments for aneurysms?
Medicines and surgery are the two main treatments for aneurysms. Bulging or ballooning in an area of an artery secondary to arterial wall weakening. Pathological outpouching or sac-like dilatation in the wall of any blood vessel (arteries or veins) or the heart (heart aneurysm).
What is the meaning of "G45.-"?
transient cerebral ischemic attacks and related syndromes ( G45.-) aneurysm (of) aorta ( I71.-) An aneurysm is a bulge or "ballooning" in the wall of an artery. Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to other parts of the body.
What is an aneurysm?
Aneurysms are classified by location, etiology, or other characteristics. Pathological, blood-filled distension of blood vessel. Protruding sac in the wall of a vein, artery, or heart, frequently caused by microbial infection; may present as pain, pressure on nearby organs, or cardiac weakening.
Where do aneurysms occur?
Most aneurysms occur in the aorta, the main artery traveling from the heart through the chest and abdomen. Aneurysms also can happen in arteries in the brain, heart and other parts of the body. If an aneurysm in the brain bursts, it causes a stroke. Aneurysms can develop and become large before causing any symptoms.
When will ICD-10-CM I72.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I72.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
ICD-10 use follow up visits after coiling ruptured aneurysm
If a patient had a ruptured aneurysm that was treated prior (coiling couple years ago) and now comes in periodically for follow-up, would we code the diagnosis of the ruptured aneurysm still as I60.7? Or would we code the aneurysm non-ruptured (I67.1)? My thinking on this as to why I question it...
Need to ask Dr.Z?
Don't see the answer you're looking for in the knowledge base? No problem. You can ask Dr. Z directly!
What is the code for clipping a cerebral aneurysm?
It is interesting to note that clipping of a cerebral aneurysm through a craniotomy is classified to code 03VG0CZ. Most of the characters are the same as the endovascular embolization with the exception of the approach (fifth character), which is open, and device (sixth character), which is an extraluminal device.
What is the most common type of device used to treat brain aneurysms?
The most common type of device used to treat brain aneurysms are coils. Currently, there are two types of coils used: bare platinum coils (BPCs) and bioactive coils. Endovascular embolization of a brain aneurysm using BPCs is classified to code 39.75 and includes bare metal coils . Endovascular embolization of a brain aneurysm using bioactive coils ...
What is the procedure to seal off an aneurysm?
Endovascular embolization involves inserting a catheter into an artery, usually one in the groin, and threads a device into the aneurysm to disrupt the blood flow and cause the blood to clot. This procedure seals off the aneurysm from the artery.
What is the code for coil embolization of an intracranial artery?
Therefore, the code assignment for coil embolization of an intracranial artery is 03VG3DZ. The following explains the meaning of each character:
What is 430 code?
Code 430 also includes a ruptured berry aneurysm and ruptured congenital brain aneurysm. Subarachnoid hemorrhage is bleeding in the space between the brain and the thin tissues covering the brain. A ruptured brain hemorrhage can be life threatening and requires immediate treatment. Symptoms.
What are the symptoms of a ruptured brain aneurysm?
Symptoms specific to ruptured brain aneurysms are a sudden and extremely severe headache, which the patient may describe it as the “worst headache ever”; nausea and vomiting; a stiff neck or neck pain; sensitivity to light; a seizure; and loss of consciousness or fainting.
What is the term for a bulging or ballooning in a weakened area in the wall of an?
A brain aneurysm is a bulging or ballooning in a weakened area in the wall of an artery that supplies blood to the brain. Also called a cerebral or intracranial aneurysm, it most often occurs in arteries at the base of the brain and looks like a berry hanging on a stem.
What is I60.6Nontraumatic?
I60.6Nontraumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage from other intracranial arteries
What is the I60.00?
I60.00Nontraumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage from unspecified carotid siphon and bifurcation
What is 03VG3DZ?
03VG3DZ Restriction of intracranial artery with intraluminal device, percutaneous approach
Who assigns HCPCS codes?
HCPCS device codes are assigned by the entity that purchased and supplied the device to the patient. In the case of Axium
Where to contact Medtronic for reimbursement?
For questions please contact us at [email protected]
Can HCPCS codes be assigned?
provided in the hospital outpatient setting. HCPCS device codes cannot be assigned or billed for procedure s performed in the
Is MS-DRG paid separately?
and are not paid separately. Only one MS-DRG is assigned for each inpatient stay, regardless of the number of procedures
Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the icd 10 code for wheezing
- 2. icd 10 cm code for visual acuity
- 3. icd-10 code for lumbar spondylolisthesis
- 4. icd 10 code for shin ulcer
- 5. what is the icd 10 code for hearing loss
- 6. icd 10 cm code for morphine
- 7. icd 10 code for right eye blindness and left eye low vision
- 8. icd 10 code for c dif
- 9. icd 10 cm code for pollen exposure
- 10. icd 10 code for personal history of gallstones