What causes renal aneurysm?
- Long-standing, untreated high blood pressure.
- Blunt and penetrating trauma.
- Recent surgery or radiation.
Does a renal artery contain high urea?
Not especially high concentrations. The renal artery is a branch of the aorta, which means it has the same concentration of urea as the aorta coming from the heart roughly speaking. If there is kidney dysfunction then obviously urea will rise systemically. Mind you blood returning from the kidneys is not urea free either.
What are the risk factors for renal artery stenosis?
What are the possible complications of RAS?
- chronic kidney disease (CKD) —reduced kidney function over a period of time
- coronary artery disease—narrowing and hardening of arteries that supply blood to the heart
- stroke—brain damage caused by lack of blood flow to the brain
How to prevent renal artery stenosis?
- Lower your blood pressure and preserve kidney functions
- Eliminate excess water (diuretics, or “water pills”)
- Lower your cholesterol to stop additional plaque from building up in your renal arteries
- Ease blood flow through partially blocked arteries (aspirin or other blood thinning remedy)

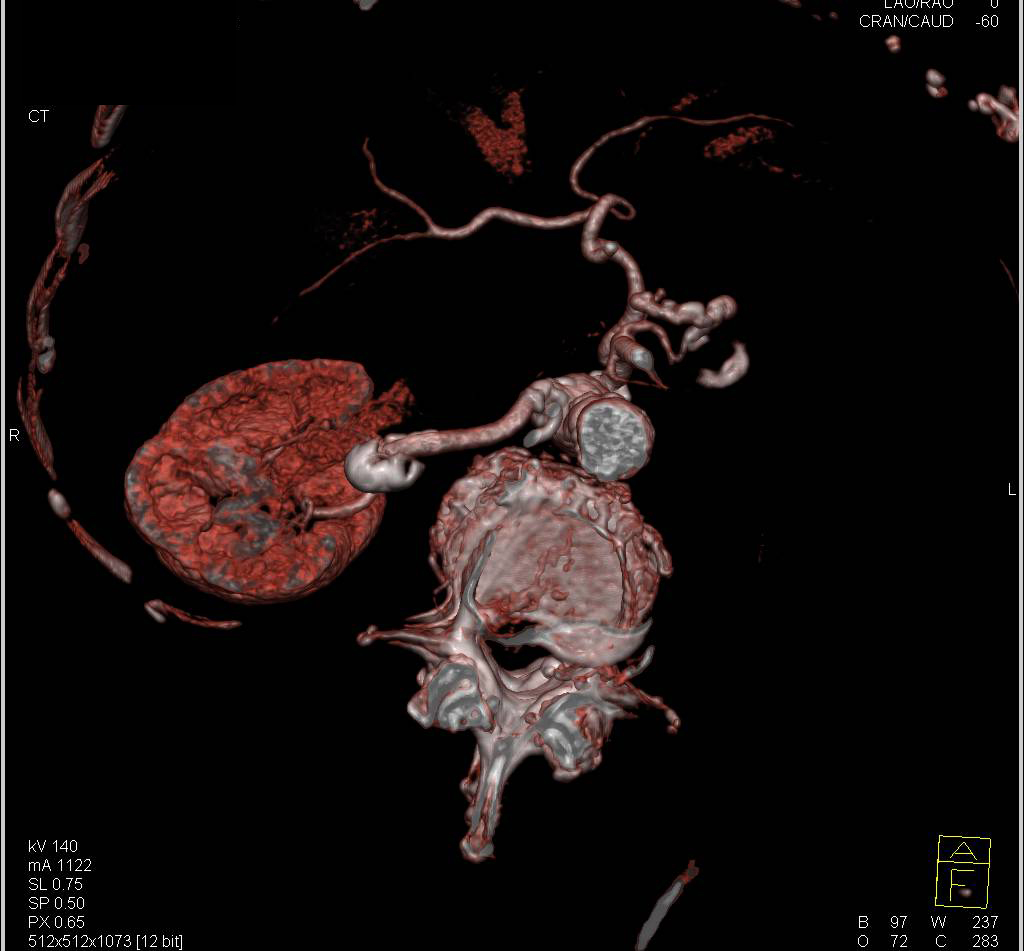
What is renal artery aneurysm?
A renal artery aneurysm is a bulge or "balloon" that forms in the wall of an artery that travels to a kidney. In most cases, there are no symptoms associated with renal artery aneurysms, and they are often discovered accidentally during examinations for other medical conditions.
What type of aneurysm is common below the renal arteries?
Extraparenchymal aneurysms predominate, comprising approximately 85% of all RAAs. The other 15% are intraparenchymal. Of the extraparenchymal type, roughly 70% are saccular, 20% are fusiform, and 10% are dissecting. Schematic of renal artery anatomy.
Where is a renal aneurysm located?
Renal artery aneurysm. This is a bulging, weak area in the wall of an artery to the kidney. Most are small and don't cause symptoms.
What is the most common cause of renal artery aneurysm?
Renal Artery Aneurysms The most common cause is typically fibromuscular dysplasia. Other etiologies include degenerative disorders, trauma, and vasculitis. Treatment is generally recommended for any RAA greater than 2 cm.
How common is a renal artery aneurysm?
Renal artery aneurysms (RAAs) are uncommon, occurring in approximately 0.09% of the general population. Most clinicians will likely encounter this entity as an incidental finding, as more frequent magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, and arteriographic studies are being performed for other diseases.
How rare is a renal artery aneurysm?
Renal artery aneurysms (RAAs) are a rare occurrence, with an incidence of about 1% (1, 2). Most patients are asymptomatic and are diagnosed through incidental findings on imaging. In rare instances, the aneurysm can rupture and cause significant morbidity and mortality.
When is renal artery aneurysm treated?
When to treat RAAs and what's the best treatment option? Repair of RAAs is recommended for patients who have medically refractory hypertension, renal artery stenosis (narrowing of the artery), or symptoms (bloody urine or upper abdomen, back or side pain), regardless of the size of the aneurysm.
What happens if a renal artery aneurysm ruptures?
Acute dissecting renal aneurysms may cause renal colic, nausea, vomiting, and worsening of antecedent hypertension. Hematuria indicates severe renal ischemia. Dissecting aneurysms are true surgical emergencies warranting immediate intervention. Chronic dissections present as hypertension in most cases.
What is renal artery pseudoaneurysm?
Abstract. Renal pseudoaneurysm is a rare vascular lesion that arises when an arterial injury within the kidney leads to contained hemorrhage. The associated hematoma forms outside the arterial wall and is typically surrounded by a layer of fibrous inflammatory tissue and blood clot.
What is a calcified renal artery aneurysm?
Renal artery aneurysms (RAAs) are uncommon and usually asymptomatic, but some demonstrate clinical symptoms such as hypertension, abdominal pain, and haematuria and have a risk for rupture [1–3]. RAAs can be associated with calcifications, which may lead to misdiagnoses as renal calculi.
What is the ICD code for aneurysm of renal artery?
Code is only used for patients 15 years old or older. I72.2 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of aneurysm of renal artery.
What is the ICD code for aneurysm?
The ICD code I72 is used to code Aneurysm. An aneurysm or aneurism (from Greek: ἀνεύρυσμα, aneurysma, "dilation", from ἀνευρύνειν, aneurynein, "to dilate") is a localized, blood-filled balloon-like bulge in the wall of a blood vessel. Angiography of an aneurysm in a cerebral artery.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd code for recreation area
- 2. icd 100 code for parkinson's
- 3. icd 9 code for edema anterior pararenal
- 4. icd 10 code for papilledema. what is l4
- 5. icd 9 code for chf acute on chronic combined
- 6. icd 10 code for elevated blood sugar level
- 7. icd 10 code for right frontal brain tumor
- 8. icd 10 code for grade 1 ligament sprain left knee
- 9. icd code for degenerative osteoarthritis
- 10. icd 10 code for benign neoplasm of left ovary