Angiodysplasia of colon without hemorrhage. K55.20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM K55.20 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What are the common ICD 10 codes?
Oct 01, 2021 · Angiodysplasia of colon without hemorrhage. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. K55.20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K55.20 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K55.2 Angiodysplasia of colon 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code K55.2 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K55.2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Oct 01, 2021 · K31.811 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K31.811 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K31.811 - other international versions of ICD-10 K31.811 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for sigmoid colon?
Oct 01, 2021 · Angiodysplasia of stomach and duodenum without bleeding 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code K31.819 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K31.819 became effective on October 1, 2021.
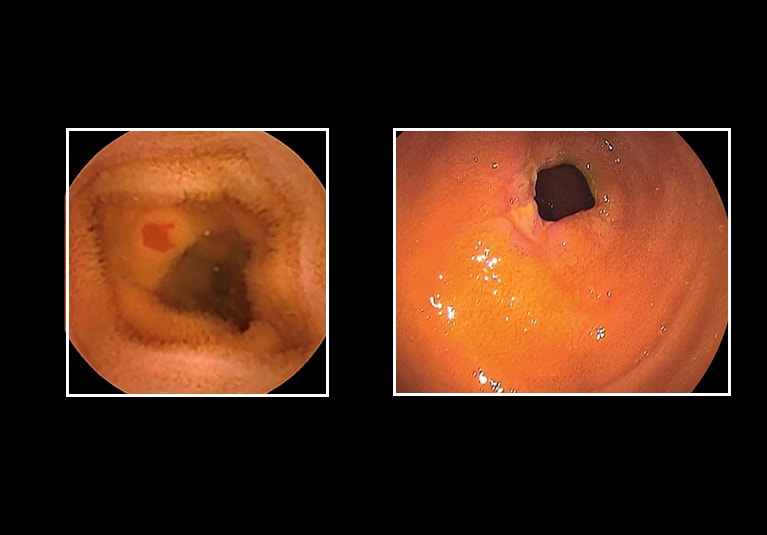
What is Angioectasia of colon?
Angioectasia is characterized by focal accumulation of dilated vessels in the mucosa and submucosa of the intestinal wall[1]. This condition can occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, and most commonly occurs in the colon[2,3]; however, 15% of cases are thought to be located in the small bowel[4].
What is the ICD-10 code for Angiodysplasia?
Angiodysplasia of stomach and duodenum without bleeding K31. 819 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is K63 89 diagnosis?
K63. 89 - Other specified diseases of intestine. ICD-10-CM.
What is Angiodysplasia of the small bowel?
Background: Gastroenteric angiodysplasia (AD) is a vascular lesion characterized by vascular ectasias to the submucous sheath of the gastrointestinal tract. Lesions can be flat or raised, isolated or grouped and can break or ulcerate causing acute hemorrhage or, more commonly, chronic bleeding.
Are angiodysplasia and Angioectasia the same?
Angioectasias, also named angiodysplasias in the literature, are vascular malformations that can be found throughout the gastrointestinal tract, with the most common site being the right colon [1, 2]. These lesions may occasionally cause severe bleeding but they can also be found in symptom-free patients.Sep 28, 2010
What is the difference between angiodysplasia and AVM?
In contrast to angiodysplasia, which is an acquired lesion that develops mainly in elderly patients, arteriovenous malformation (AVM) develops during embryologic or fetal life, and is typically present at birth.
What is the ICD-10 code for mass of colon?
Neoplasm of uncertain behavior of colon D37. 4 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D37. 4 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for incomplete colonoscopy?
Incomplete Colonoscopy B Incomplete Colonoscopies) are 44388, 45378, G0105, and G0121.Jul 8, 2021
What is the ICD-10 for diarrhea?
ICD-10 | Diarrhea, unspecified (R19. 7)
What causes angiodysplasia of colon?
The cause of angiodysplasia is unknown. But normal spasms occurring in the GI tract may be responsible for the enlargement of blood vessels. This enlargement leads to the development of small pathways between a vein and an artery, which can leak with blood.
How is angiodysplasia diagnosis?
Angiodysplasia is usually diagnosed as an incidental finding during colonoscopy for colorectal cancer screening exams or when evaluating the patient for acute or chronic blood loss related anemia. The initial diagnostic modality depends on the characteristics of bleeding and suspicion for the location of the source.Aug 29, 2021
What is abnormal vascularity in colon?
Vascular ectasias (angiodysplasias, arteriovenous malformations) are dilated, tortuous vessels that typically develop in the cecum and ascending colon. They occur mainly in people > 60 and are the most common cause of lower gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. The manifestations depend on the location and rate of bleeding.
What is the code for angiodysplasia of colon without hemorrhage?
K55.20 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of angiodysplasia of colon without hemorrhage. The code K55.20 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is the colon?
Your colon, also known as the large intestine, is part of your digestive system. It's a long, hollow tube at the end of your digestive tract where your body makes and stores stool. Many disorders affect the colon's ability to work properly. Some of these include
How to treat colonic disease?
Treatment for colonic diseases varies greatly depending on the disease and its severity. Treatment may involve diet, medicines and in some cases , surgery. NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Angiodysplasia of the colon (Medical Encyclopedia)
What is the term for a bulge in the wall of an artery?
Aneurysm - a bulge or "ballooning" in the wall of an artery. Atherosclerosis - a disease in which plaque builds up inside your arteries. Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. Blood clots, including deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
What is APC in hemostasis?
A single medium angioectasia (AVM) was seen in the mid jejunum. An Argon-Plasma Coagulator (APC) was applied for hemostasis successfully. When one sees the term “coagulator”, the first thought is destruction of the lesion.
What is EGD in medical terms?
An esophagogastoduodenoscopy (EGD) was performed with the finding of a medium sized angioectasia (AVM) seen in the mid jejunum which was thought to be the source of the bleeding. As a result, the following procedure was performed:

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for left anterior thigh strain
- 2. icd 10 code for malignant cancer of the tonsil with metastasis
- 3. what is the correct icd 10 code for uterus size of 18 weeks non bo
- 4. icd code for pelvic pain
- 5. icd 10 code for nocturia/bph
- 6. icd 10 code for t6 fracture
- 7. icd 10 diagnosis code for iron deficiency anemia
- 8. icd 10 code for balloon sinuplasty
- 9. icd 10 code for shouler pain
- 10. icd-9-cm code for spastic quadriplegic