What is the ICD 10 code for glomerular disease?
Glomerular disorders in diseases classified elsewhere 1 N08 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM N08 became effective on October 1, 2018. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N08 - other international versions of ICD-10 N08 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for thin basement membrane disease?
Thin basement membrane dis Thin basement membrane disease ICD-10-CM N02.2 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 698 Other kidney and urinary tract diagnoses with mcc
What is the new ICD 10 for recurrent and Perst hematur W diffuse membranous glomrlneph?
Short description: Recurrent and perst hematur w diffuse membranous glomrlneph The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N02.2 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N02.2 - other international versions of ICD-10 N02.2 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for neovascular glomrlneph?
N02.2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Recurrent and perst hematur w diffuse membranous glomrlneph
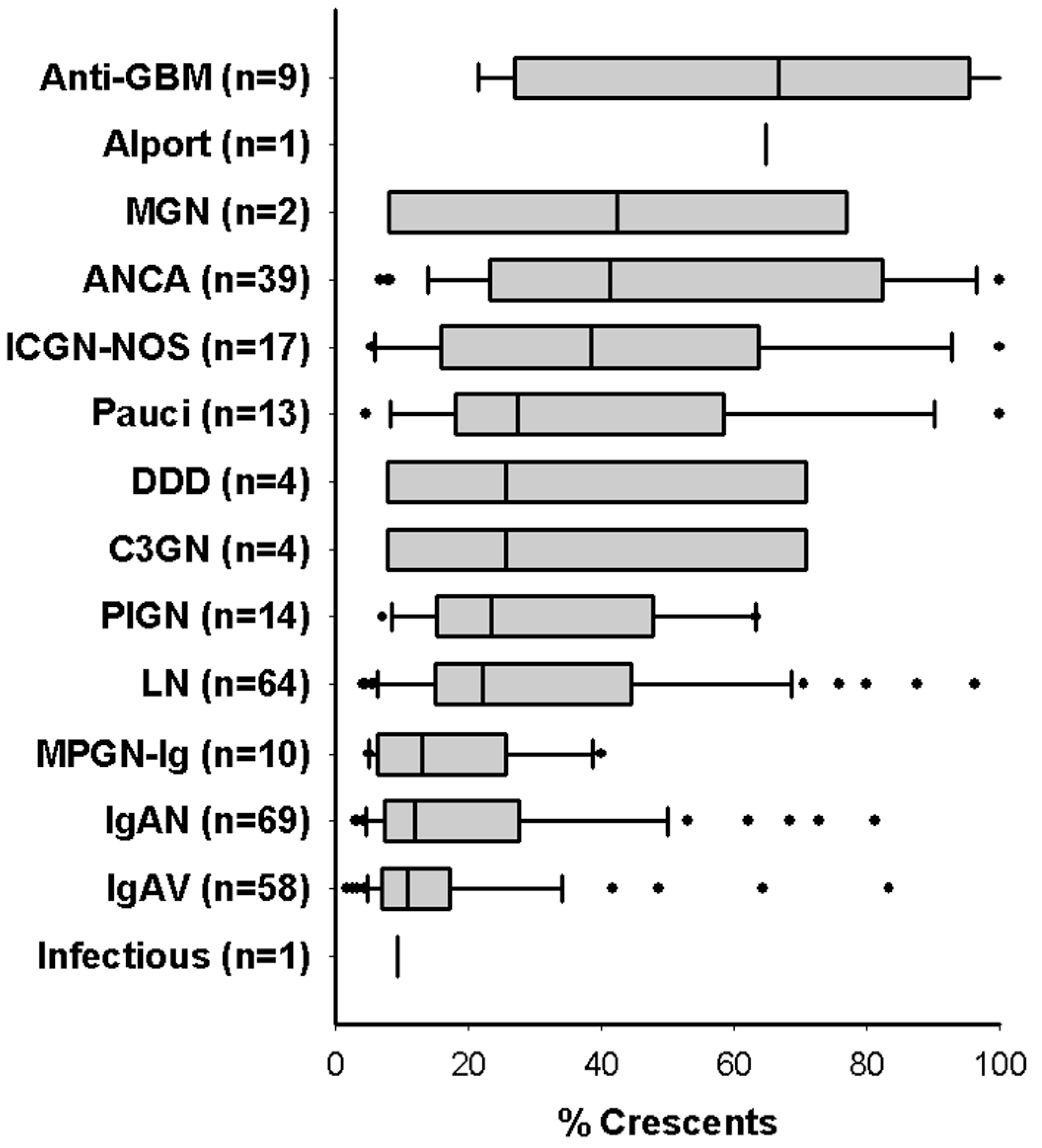
What is anti glomerular basement membrane disease?
Causes. Anti-GBM disease is an autoimmune disorder. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys healthy body tissue. People with this syndrome develop substances that attack a protein called collagen in the tiny air sacs in the lungs and the filtering units (glomeruli) of the kidneys.
What is the ICD-10 code for membranous nephropathy?
ICD-10-CM Code for Nephrotic syndrome with diffuse membranous glomerulonephritis N04. 2.
What is the ICD-10 code for Ureterolithiasis?
The ICD-10 code range for Urolithiasis N20-N23 is medical classification list by the World Health Organization (WHO).
What is the ICD-10 code for glomerulonephritis?
Unspecified nephritic syndrome with diffuse membranous glomerulonephritis. N05. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N05.
What is primary membranous nephropathy?
Primary membranous nephropathy (PMN) is a kidney-specific, autoimmune glomerular disease that presents with increased protein in the urine associated with a pathognomonic pattern of injury in glomeruli (Figures 1–3). Both clinical and pathogenetic aspects of the disease have been recently reviewed elsewhere (1–8).
Is primary membranous nephropathy a rare disease?
Primary membranous nephropathy is the most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in white persons without diabetes, but it is a rare disease as defined by the European Commission on Rare Diseases (1 case per 2000 of population) or the Rare Diseases Clinical Research Network (200,000 prevalent cases in the United States).
What is the code N20 1?
Calculus of ureter1: Calculus of ureter.
What is DX Code N20 0?
0: Calculus of kidney.
What K57 92?
ICD-10 code: K57. 92 Diverticulitis of intestine, part unspecified, without perforation, abscess or bleeding.
What is a glomerulonephritis?
Glomerulonephritis is inflammation and damage to the filtering part of the kidneys (glomerulus). It can come on quickly or over a longer period of time. Toxins, metabolic wastes and excess fluid are not properly filtered into the urine. Instead, they build up in the body causing swelling and fatigue.
What is a glomerular disease?
GLOMERULAR DISEASE OVERVIEW. Glomerular disease reduces the kidneys' ability to maintain a balance of certain substances in bloodstream. Normally, the kidneys filter toxins out of the bloodstream and excrete them in the urine but keep red blood cells and protein in the bloodstream.
What is the cause of membranous nephropathy?
Often, membranous nephropathy results from some type of autoimmune activity. Your body's immune system mistakes healthy tissue as foreign and attacks it with substances called autoantibodies. These autoantibodies target certain proteins located in the kidney's filtering systems (glomeruli).
What is glomerular disease?
Glomerular disease characterized by an inflammatory reaction, with leukocyte infiltration and cellular proliferation of the glomeruli, or that appears to be the result of immune glomerular injury. Impairment of health or a condition of abnormal functioning of the kidney. Inflammation of any part of the kidney.
What is renal failure?
A renal disorder characterized by damage in the glomeruli. It may be acute or chronic, focal or diffuse, and it may lead to renal failure. Causes include autoimmune disorders, infections, diabetes, and malignancies. A term referring to any disease affecting the kidneys.
What does "type 1 excludes note" mean?
A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
Attention
Only comments seeking to improve the quality and accuracy of information on the Orphanet website are accepted. For all other comments, please send your remarks via contact us. Only comments written in English can be processed.
Epidemiology
The incidence of the disease is estimated to be approximately 0.6-1.8 cases per million per year in both Asian and European Caucasian (more frequently affected) populations. Men and women seem equally affected.
Clinical description
Anti-GBM disease onset is bimodal, occurring mainly in the third and the seventh decades of life. The majority of patients (80-90%) will present with features of rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. 40 to 60% will have concurrent lung hemorrhage, and a small minority of patients may present with isolated pulmonary disease.
Etiology
Anti-GBM disease is considered to be a vasculitis affecting glomerular capillaries, pulmonary capillaries, or both, with deposition of anti-basement membrane antibodies against the non-collagenous domain 1 of the alpha 3 chain of type IV collagen (alpha3 (IV)NC1).
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis is based on the detection of anti-GBM antibodies either in serum or deposited in tissue, along with pathologic features of crescentic GN, with or without evidence of alveolar hemorrhage.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis includes systemic vasculitis (e.g. Wegener's granulomatosis (GPA), microscopic polyarteritis (MPA), systemic lupus erythematosus, Churg-Strauss syndrome (EGPA)) and other vasculitides (e.g. Behçets disease, cryoglobulinemia).
Management and treatment
Standard therapy consists in plasma exchange combined with high doses of glucocorticoids and cyclophosphamide. Recently, several reports of rituximab use have been reported, either as an adjuvant to standard therapy or as a substitute for cyclophosphamide.
What is the ICd 9 code for rheumatology?
Specialty: Rheumatology. MeSH Code: D019867. ICD 9 Code: 446.21.
What is the ICd code for Goodpasture syndrome?
The ICD code M310 is used to code Goodpasture syndrome. Goodpasture syndrome (GPS; also known as Goodpasture’s disease, antiglomerular basement antibody disease, or anti-GBM disease) is a rare autoimmune disease in which antibodies attack the basement membrane in lungs and kidneys, leading to bleeding from the lungs and kidney failure.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for infant well visit
- 2. icd 1o code for vagal reaction
- 3. icd 9 code for secondary pancreatic cancer
- 4. icd 10 cm code for abnormal lymph nodes
- 5. icd 10 cm code for av block
- 6. icd 10 code for dental carie
- 7. icd 9 code for skin abscess
- 8. icd 10 code for epidural steroid injection
- 9. icd 10 code for personal history of bone marrow transplant
- 10. icd 10 code for graves