O36.0191 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Maternal care for anti-D antibodies, unsp trimester, fetus 1. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM O36.0191 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 for anti-D antibodies?
Short description: Maternal care for anti-D antibodies, unsp trimester, fetus 1. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM O36.0191 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is an anti Kell antibody?
Anti-Kell antibodies are usually of the antibody class IgG (IgM is far less common). The antibodies that have been implicated in causing transfusion reactions, which can occasionally be severe in nature include, anti-K, anti-k, anti-Kpa, and anti-Jsb (2).
What is the nomenclature of the K antigen?
But the original K antigen remains of prime importance in transfusion medicine and HDN. Nomenclature Number of Kell antigens: 25 ISBT symbol: KEL ISBT number: 006 Gene symbol: KEL Gene name: Kell blood group Basic biochemistry Common Kell phenotypes
What determines the specificity of Kell antigens?
Amino acid sequence determines the specificity of Kell antigens Antigen-carrying molecules Glycoprotein with enzymatic function The Kell glycoprotein is a transmembrane, single-pass protein that carries the Kell antigens.
Why is anti-Kell 1 important?
How many babies born to a negative mother are kell 1 positive?
What happens if you are negative for kell 1?
What is the test for RhD?
What is the chance of a father being homozygous for the antigen?
Can anti-Kell cause anemia?
Does IgG prevent RBC sensitization?
See more
About this website
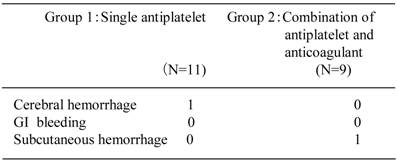
What does R76 mean?
Other abnormal immunological findings in serumR76 - Other abnormal immunological findings in serum.
What does diagnosis code R76 8 mean?
ICD-10 code R76. 8 for Other specified abnormal immunological findings in serum is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the ICD-10 code for Rhogam injection?
Encounter for prophylactic Rho(D) immune globulin Z29. 13 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z29. 13 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for Rh negative in pregnancy?
Z67.918. RE: ICD-10 code for Rh negative status in pregnancy. "Unspecified blood type, Rh negative" is Z67. 91.
What is diagnosis code R53 83?
Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
What is R79 89?
ICD-10 code R79. 89 for Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistry is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the difference between J2790 and 90384?
J2790 and 90384 are the same code. The J code is for Medicare and 990384 code is for commercial insurances. Medicare does not recognize the 90384 code. My research shows that that Medicaid and ILM products may accept the J2790, depending on the ins company's contract, but most lean toward the 90384.
Is RhoGAM considered an immunization?
It is a prescription immune globulin shot that is given to some pregnant and post-partum women to prevent Rh (Rhesus) immunization, which can lead to hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn if you get pregnant again. RhoGAM was approved by the FDA in 1968.
How do you bill for RhoGAM?
CPT instructs coders to also report the code 90782 (therapeutic or diagnostic injection) for the injection procedure. This code describes the injection only, not the actual provision of RhoGAM. The new CPT code for this product is 90384 (Rho [D] immunoglobulin [RhIG], human, full-dose, for intramuscular use).
What is the ICD-10 code for Rh positive in pregnancy?
O36.0191Maternal care for anti-D [Rh] antibodies, unspecified trimester, fetus 1. O36. 0191 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM O36.
What is antibody M in pregnancy?
Anti-M is a common antibody detected in prenatal samples. Most often it is not clinically significant as it is predominantly an IgM antibody which does not cross the placental barrier. To distinguish IgM from IgG anti-M, some antibody identification methods exist that exclude IgM antibodies.
What are anti-M antibodies?
Anti- M is a naturally occurring antibody of the MNS blood group system. This antibody is the most reactive at temperatures below 37°C, with an optimum temperature of 4°C and is considered to be clinically insignificant. However, there are few studies that have reported anti-M as a mixture of IgG and IgM antibodies.
What does having Anti-kell antibodies in the blood indicate?
I am a 51 years old female. I recently had an ankle surgery. I was cross typed and matched in case of blood transfusion. I just received a card in the mail from the hospital which states "Transfusion Restriction, This patient has the following clinically significant antibodies, Anti-Kell". What does this mean? I suffer from macrocytic anaemia but have had no transfusions for the last 11 years.
What is the significance of anti-k antibody? - Doctor.ndtv.com
I found in my 3rd pregnancy that I have anti-k antibody . Therefore, my husband was tested for the antigen, which was positive. Has he always had this antigen and if so then why is the antibody showing in my blood now? What are the chances that the baby will also get the antigen?
Mother with anti-Kell antibodies. What are the recommendations for ...
I have a pregnant patient with anti-Kell antibodies (titer is 1:4). What are the recommendations for managing patients with anti Kell antibodies? The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends determination of the father’s red blood cell antigen status as the first step.
Treatment of hemolytic disease of the newborn caused by anti-Kell ...
Recent data suggest that antibody-mediated suppression of erythroid progenitors may contribute to the anti-Kell-induced alloimmune hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN). A 32-week-old girl who was positive for Kell was born to a mother who was negative for Kell but known to have anti-Kell antibodie …
What is the Kell factor?
The presence of Kell antibodies can be detected by maternal blood testing.If they’re present, your doc will closely monitor your pregnancy through blood tests and ultrasounds.If your baby appears severely affected, blood transfusions, given to your baby while he’s still in utero, can help prevent harm to baby.
Predicting anti-Kell-mediated hemolytic disease of the fetus and ...
Introduction. Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN) is caused by red blood cell (RBC) antibodies developed by the mother and transferred to the fetus.1, 2 Kell (K) alloantibodies are second to RhD alloantibodies in importance as the cause of severe HDFN.1, 2 K alloantibodies cause hemolysis of fetal erythrocytes and inhibit the fetal erythropoiesis.3, 4, 5 Without treatment, HDFN ...
Special Instructions
This test does not include little k (cellano). To order little k typing, refer to test 006096.
Expected Turnaround Time
Turnaround time is defined as the usual number of days from the date of pickup of a specimen for testing to when the result is released to the ordering provider. In some cases, additional time should be allowed for additional confirmatory or additional reflex tests. Testing schedules may vary.
Storage Instructions
Specimens should be tested as soon as possible or within 72 hours of collection. Samples that cannot be tested immediately should be stored at 2°C to 8°C. Do not freeze red cells.
Limitations
Presence of potent cold agglutinins, positive direct antiglobulin test, and (in some cases) bacteremia may interfere with test interpretation.
Why is anti-Kell 1 important?
Anti-Kell 1 is becoming relatively more important as prevention of Rh disease is also becoming more effective. Hemolytic disease of the newborn (anti-Kell 1) is caused by a mismatch between the Kell antigens of the mother and fetus. About 91% of the population are Kell 1 negative and about 9% are Kell 1 positive.
How many babies born to a negative mother are kell 1 positive?
Therefore, about 4.5% of babies born to a Kell 1 negative mother are Kell 1 positive. The disease results when maternal antibodies to Kell 1 are transferred to the fetus across the placental barrier, breaching immune privilege.
What happens if you are negative for kell 1?
Mothers who are negative for the Kell 1 antigen develop antibodies after being exposed to red blood cells that are positive for Kell 1. Over half of the cases of hemolytic disease of the newborn owing the anti-Kell antibodies are caused by multiple blood transfusions, with the remainder due to a previous pregnancy with a Kell 1 positive baby.
What is the test for RhD?
This test can help with knowledge for the current baby, as well as aid in the decision about future pregnancies. With RhD, the test is called the RhD genotype. With RhCE, and Kell antigen it is called an antigen phenotype.
What is the chance of a father being homozygous for the antigen?
If he is homozygous for the antigen, there is a 100% chance of all offspring in the pairing to be positive for the antigen and at risk for HDN. If he is heterozygous, there is a 50% chance of offspring to be positive for the antigen.
Can anti-Kell cause anemia?
Anti-Kell can cause severe anemia regardless of titer. Anti-Kell suppresses the bone marrow, by inhibiting the erythroid progenitor cells. Hemolytic disease of the newborn can also be caused by anti-Kell 2, anti-Kell 3 and anti-Kell 4 IgG antibodies. These are rarer and generally the disease is milder.
Does IgG prevent RBC sensitization?
It has been hypothesized that IgG anti-Kell 1 antibody injections would prevent sensitization to RBC surface Kell 1 antigens in a similar way that IgG anti-D antibodies ( Rho (D) Immune Globulin) are used to prevent Rh disease, but the methods for IgG anti-Kell 1 antibodies have not been developed at the present time.
Why is anti-Kell 1 important?
Anti-Kell 1 is becoming relatively more important as prevention of Rh disease is also becoming more effective. Hemolytic disease of the newborn (anti-Kell 1) is caused by a mismatch between the Kell antigens of the mother and fetus. About 91% of the population are Kell 1 negative and about 9% are Kell 1 positive.
How many babies born to a negative mother are kell 1 positive?
Therefore, about 4.5% of babies born to a Kell 1 negative mother are Kell 1 positive. The disease results when maternal antibodies to Kell 1 are transferred to the fetus across the placental barrier, breaching immune privilege.
What happens if you are negative for kell 1?
Mothers who are negative for the Kell 1 antigen develop antibodies after being exposed to red blood cells that are positive for Kell 1. Over half of the cases of hemolytic disease of the newborn owing the anti-Kell antibodies are caused by multiple blood transfusions, with the remainder due to a previous pregnancy with a Kell 1 positive baby.
What is the test for RhD?
This test can help with knowledge for the current baby, as well as aid in the decision about future pregnancies. With RhD, the test is called the RhD genotype. With RhCE, and Kell antigen it is called an antigen phenotype.
What is the chance of a father being homozygous for the antigen?
If he is homozygous for the antigen, there is a 100% chance of all offspring in the pairing to be positive for the antigen and at risk for HDN. If he is heterozygous, there is a 50% chance of offspring to be positive for the antigen.
Can anti-Kell cause anemia?
Anti-Kell can cause severe anemia regardless of titer. Anti-Kell suppresses the bone marrow, by inhibiting the erythroid progenitor cells. Hemolytic disease of the newborn can also be caused by anti-Kell 2, anti-Kell 3 and anti-Kell 4 IgG antibodies. These are rarer and generally the disease is milder.
Does IgG prevent RBC sensitization?
It has been hypothesized that IgG anti-Kell 1 antibody injections would prevent sensitization to RBC surface Kell 1 antigens in a similar way that IgG anti-D antibodies ( Rho (D) Immune Globulin) are used to prevent Rh disease, but the methods for IgG anti-Kell 1 antibodies have not been developed at the present time.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for complication left infected stump\
- 2. icd 10 code for traumatic spinal cord injury unspecified
- 3. icd 10 code for migrane profilaxis
- 4. icd 10 code for counseling for covid vaccination
- 5. icd 10 code for large r testicle
- 6. icd 9 code for bradycardia due to first degree av block
- 7. icd 10 code for left charcot foot
- 8. icd 10 code for old meniscus tear
- 9. icd 10 code for demetia
- 10. icd code for excessive sweating