How does a doctor diagnose aortic aneurysm?
Thoracic aortic aneurysm
- Diagnosis. Thoracic aortic aneurysms are often found during routine medical tests, such as a chest X-ray, CT scan or ultrasound of the heart, sometimes ordered for a different reason.
- Treatment. ...
- Clinical trials. ...
- Lifestyle and home remedies. ...
- Coping and support. ...
- Preparing for your appointment. ...
How to pronounce aortic aneurysm?
aortic aneurysm pronunciation with meanings, synonyms, antonyms, translations, sentences and more The correct way to pronounce the word Fukuoka is? fook-oo-ow-kuh
What is the cure of aortic aneurysm?
Treatment
- Monitoring. If your thoracic aortic aneurysm is small, your doctor may recommend imaging tests to monitor the aneurysm, along with medication and management of other medical conditions.
- Medications. ...
- Surgery. ...
What is the prognosis for aortic aneurysm?
The 75-year-old Park Hills resident survived an aortic aneurysm in 2018. Thanks to the help of her cardiologist at St. Luke’s Hospital, her surgeon and nurses at Missouri Baptist Medical Center ...
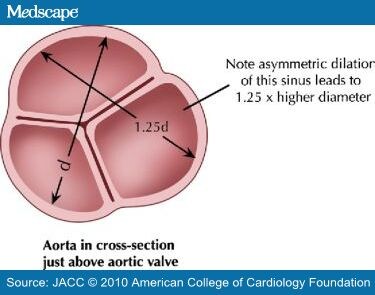
What is an aortic root aneurysm?
An aortic root aneurysm is a type of aneurysm that occurs in the aorta — the body's largest blood vessel. They often have no symptoms and doctors find them during x-rays or CT scans. At the UPMC Heart and Vascular Institute, we offer complete cardiovascular care.
Is the aortic root part of the thoracic aorta?
The Thoracic Aorta has 4 distinct parts: Aortic Root – Lies in the front portion of the chest below the sternum. It starts at the level of the heart and includes the aortic valve and the portion where the coronary arteries arise called the Sinus of Valsalva.
Is aortic root the same as aortic arch?
Your Ascending Aorta and Aortic Arch The ascending aorta begins above the aortic root and extends towards the neck until it begins to turn and give rise to the aortic arch. The ascending aorta is more frequently affected by aneurysms and dissections and requires open heart surgery to be repaired.
What part of the aorta is the aortic root?
The aortic root is the portion of the aorta that is attached to the heart. A major part of the aortic root is the aortic valve, which allows blood to flow from the heart to the rest of the body when it is open and prevents blood from flowing backwards into the heart when it is closed.
Is a dilated aortic root the thoracic?
Aortic aneurysms that occur in the chest area are called thoracic aortic aneurysms and can involve the aortic root, ascending aorta, aortic arch or descending aorta. Aneurysms that involve the aorta as it flows through both the abdomen and chest are called thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms.
Is the ascending aorta and thoracic aorta the same?
The upward part of the arch, which is the section closest to the heart, is called the ascending aorta. The part of the aorta in the chest is called the thoracic aorta. The portion further down in your trunk is called the abdominal aorta. An aneurysm is a bulge that forms in the wall of an artery.
Is a dilated aortic root the same as an aneurysm?
Otherwise known as an aortic root aneurysm, a dilated aortic root is when the first section of the aorta, where the aortic valve resides, becomes enlarged. When this enlargement reaches a critical size, there is a risk of it rupturing or tearing, leading to a life-threatening situation.
How common is an aortic root aneurysm?
Aortic aneurysms have an incidence of 5-10 cases per 100,000 in the United States, and are more common in men over the age of 60. Though aortic aneurysms do not directly cause death, complications arising from an aneurysm – such as dissection or rupture – cause approximately 15,000 deaths annually.
Is aortic root ascending or descending?
The ascending aorta originates beyond the aortic valve and ends right before the innominate artery (brachiocephalic trunc). It is approximately 5 cm long and is composed of two distinct segments. The lower segment, known as the aortic root, encompasses the sinuses of Valsalva and sinotubular junction (STJ).
What is the normal diameter of the aortic root?
The normal range of aortic root diameters in this group was 17 to 33 mm (mean 23.7). A significant difference (P is smaller than 0.001) in aortic root diameters existed between men and women which could not be explained by differences in body surface area.
How is aortic root aneurysm repaired?
More than 99% of aortic root aneurysm and valve replacements are performed through traditional open-heart surgery. It requires making a 10-12 inch vertical incision and splitting the breastbone to access the heart, replace the patient's own heart valve, and mend the aneurysm.
How common is dilated aortic root?
Dilated aortic root (DAR) is a relatively common finding, with a reported prevalence of about 4% measured at the level of the sinuses of Valsalva in the general population.
What are the shapes of an aortic aneurysm?
Shapes include fusiform and saccular. Fusiform is when the aneurysm is enlarged equally in all directions; saccular is when the bulge or sac occurs on only one side of the aorta. Possible locations of an aortic aneurysm are as follows: • Ascending (441.2); if ruptured, use 441.1; • Arch (441.2); if ruptured, use 441.1;
Can an aortic valve be repaired?
The aortic valve may also be repaired or replaced. An endovascular repair may also treat aneurysms. Coding and sequencing for aortic conditions are dependent on the physician documentation in the medical record and application of the Official Coding Guidelines for inpatient care.
Can a pseudoaneurysm rupture without an aneurysm?
Often due to an injury of inner aortic wall and an infection, a pseudoaneurysm is unpredictable and may rupture at smaller sizes. Pseudoaneurysm is classified to the same codes as the other aneurysms, depending on location. Aortic Dissection. Aortic tissue may tear even without an aneurysm .
Does type B involve the ascending aorta?
Type B does not involve the ascending aorta and may be managed medically. The type of aortic dissection does not affect code assignment. The code assignment is only based on the site of the dissecting aneurysm ( AHA Coding Clinic for ICD-9-CM, 1989, fourth quarter, page 10). Diagnosis and Treatment.
Can an aortic dissection cause pain?
Aortic Dissection. Aortic tissue may tear even without an aneurysm. Dissection is the tearing of the inner layer of a vessel that allows blood to leak between the inner and outer layers, possibly causing severe back or chest pain, pallor, pulselessness, paresthesiae, and paralysis.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for finger splint
- 2. icd 10 code for right knee pain\
- 3. icd-9 code for si joint syndrome
- 4. icd 10 code for ccp antibodies
- 5. icd 10 code for status post phlebotomies
- 6. what is the icd 10 code for systemic sclerosis
- 7. icd 10 code for encounter folloiwng emergency department
- 8. icd 10 code for family history of kidney cancer
- 9. icd 10 code for chronic isn
- 10. icd 10 code for lesion in genital aread