What is the ICD 10 code for aphasia?
· Aphasia from hemorrhagic stroke Aphasia from ischemic stroke Present On Admission I69.320 is considered exempt from POA reporting. ICD-10-CM I69.320 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 056 Degenerative nervous system disorders with mcc 057 Degenerative nervous system disorders without mcc Convert I69.320 to ICD-9-CM
What is the ICD 10 code for difficulty speaking after stroke?
· Aphasia (difficulty speaking) due to of stroke Aphasia as late effect of cerebrovascular disease Present On Admission I69.920 is considered exempt from POA reporting. ICD-10-CM I69.920 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 056 Degenerative nervous system disorders with mcc
What is the ICD 10 code for aphasia following intracerebral hemorrhage?
· Aphasia. R47.01 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R47.01 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of R47.01 - other international versions of ICD-10 R47.01 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for acute stroke?
- Aphasia (amnestic) (global) (nominal) (semantic) (syntactic) - R47.01 - following - cerebrovascular disease - I69.920 - cerebral infarction - I69.320 - Sequelae (of) - See Also: …
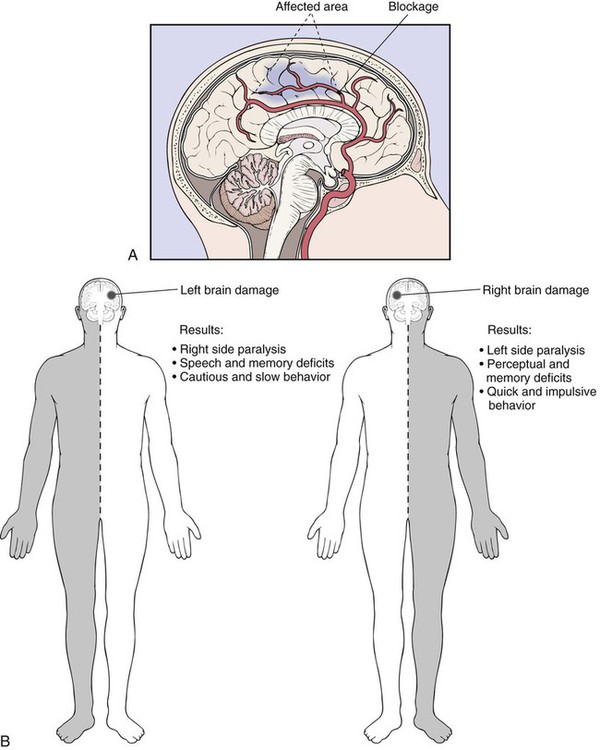
What is ICD-10 code for stroke with aphasia?
I69. 320 - Aphasia following cerebral infarction | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for late effect CVA with dysphagia?
438.82 - Other late effects of cerebrovascular disease, dysphagia | ICD-10-CM.
What is diagnosis code aphasia?
ICD-10 code R47. 01 for Aphasia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the ICD-10 code for difficulty finding words?
ICD-10 Code for Unspecified speech disturbances- R47. 9- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for History of CVA?
When a patient has a history of cerebrovascular disease without any sequelae or late effects, ICD-10 code Z86. 73 should be assigned.
What is the ICD-10 code for CVA?
ICD-10 | Cerebral infarction, unspecified (I63. 9)
What is the meaning of Broca aphasia?
Broca's dysphasia (also known as Broca's aphasia) It involves damage to a part of the brain known as Broca's area. Broca's area is responsible for speech production. People with Broca's dysphasia have extreme difficulty forming words and sentences, and may speak with difficulty or not at all.
What is nominal aphasia?
Anomic aphasia (also known as dysnomia, nominal aphasia, and amnesic aphasia) is a mild, fluent type of aphasia where individuals have word retrieval failures and cannot express the words they want to say (particularly nouns and verbs). Anomia is a deficit of expressive language.
What is I10 diagnosis?
That code is I10, Essential (primary) hypertension. As in ICD-9, this code includes “high blood pressure” but does not include elevated blood pressure without a diagnosis of hypertension (that would be ICD-10 code R03. 0).
What is the ICD-10 code for impaired cognition?
ICD-10 Code for Other specified cognitive deficit- R41. 84- Codify by AAPC.
What is ICD-10 code for speech therapy?
2. F80. 2 — Mixed receptive-expressive language disorder.
What is word finding difficulty?
A 'word retrieval difficulty' or 'word finding problem' is when a person knows and understands a particular word, but has difficulty retrieving it and using it in their speech. This is similar to when we feel that a word (for example a name) is on the tip of our tongue.
When will ICD-10-CM I69.920 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I69.920 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is Category I69?
Category I69 is to be used to indicate conditions in I60 - I67 as the cause of sequelae. The 'sequelae' include conditions specified as such or as residuals which may occur at any time after the onset of the causal condition. Type 1 Excludes.
What is cognitive disorder?
Cognitive disorder marked by an impaired ability to comprehend or express language in its written or spoken form; caused by diseases which affect the language areas of the dominant hemisphere; general categories include receptive, expressive, and mixed forms of aphasia.
When will ICD-10-CM R47.01 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R47.01 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for aphasia?
I69.320 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of aphasia following cerebral infarction. The code I69.320 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code I69.320 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like aphasia as late effect of cerebrovascular accident, aphasia as late effect of cerebrovascular disease, aphasia due to and following embolic cerebrovascular accident, aphasia due to and following hemorrhagic cerebrovascular accident or aphasia due to and following ischemic cerebrovascular accident. The code is exempt from present on admission (POA) reporting for inpatient admissions to general acute care hospitals.
What are the different types of aphasia?
There are four main types: Expressive aphasia - you know what you want to say, but you have trouble saying or writing what you mean. Receptive aphasia - you hear the voice or see the print, but you can't make sense of the words. Anomic aphasia - you have trouble using the correct word for objects, places, or events.
What are the treatments for stroke?
Treatments for stroke include medicines, surgery, and rehabilitation. Which treatments you get depend on the type of stroke and the stage of treatment. The different stages are. Acute treatment, to try to stop a stroke while it is happening. Post-stroke rehabilitation, to overcome the disabilities caused by the stroke.
What is the primary risk factor for a stroke?
High blood pressure. This is the primary risk factor for a stroke.
What is a condition similar to a stroke?
Another condition that's similar to a stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA). It's sometimes called a "mini-stroke." TIAs happen when the blood supply to the brain is blocked for a short time. The damage to the brain cells isn't permanent, but if you have had a TIA, you are at a much higher risk of having a stroke.
What causes a stroke to be ischemic?
Ischemic stroke is caused by a blood clot that blocks or plugs a blood vessel in the brain. This is the most common type; about 80% of strokes are ischemic.
What to do if you think someone has a stroke?
Immediate treatment may save someone's life and increase the chances for successful rehabilitation and recovery.
When will ICD-10-CM I69.120 be effective?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I69.120 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is Category I69?
Category I69 is to be used to indicate conditions in I60 - I67 as the cause of sequelae. The 'sequelae' include conditions specified as such or as residuals which may occur at any time after the onset of the causal condition. Type 1 Excludes.
When will ICD-10-CM I69.398 be effective?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I69.398 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is Category I69?
Category I69 is to be used to indicate conditions in I60 - I67 as the cause of sequelae. The 'sequelae' include conditions specified as such or as residuals which may occur at any time after the onset of the causal condition. Type 1 Excludes.
What is the ICD-10 code for stroke?
Explicitly document findings to support diagnoses of › Stroke sequela codes (ICD-10 category I69.-) should acute stroke, stroke and subsequent sequela of be used at the time of an ambulatory care visit stroke, and personal history of stroke without sequela, oce, which is considered subsequent to any acute
What is the term for a stroke that occurs when there is disruption of blood flow to brain tissue?
stroke occurs when there is disruption of blood flow to brain tissue, this leads to ischemia (deprivation of oxygen) and potentially infarction (dysfunctional scar tissue). Strokes can be either hemorrhagic, or embolic/thrombotic. Hemorrhagic strokes occur as a result of a ruptured cerebral blood vessel. Embolic/thrombic strokes occur as a result of an obstructed cerebral vessel.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for acute rib fracture
- 2. icd-10 code for chronic lung disease
- 3. icd 10 code for blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm
- 4. icd 10 code for pulmonary low p02
- 5. icd 10 code for shoulder injury right
- 6. icd 10 code for pseudomonas of nail
- 7. icd 10 code for juvenile petitmal seizures
- 8. icd-10 code for sternal pain
- 9. icd 9 code for epigastric pain
- 10. icd 10 cm code for seasonal affective disorder