How to pronounce antiphospholipid syndrome?
Antiphospholipid syndrome or antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS or APLS), or often also Hughes syndrome, is an autoimmune, hypercoagulable state caused by antiphospholipid antibodies.
How is antiphospholipid antibody syndrome diagnosed?
Make a list of:
- Your signs or symptoms and when they began.
- Write down key personal information, including any major recent events or changes in your life.
- Key medical information, including other conditions or infections you have and family medical history, especially close relatives who've had antiphospholipid syndrome.
How is antiphospholipid antibody syndrome treated?
- Have an infection like HIV, syphilis, hepatitis C, or Lyme disease
- Are taking amoxicillin or certain blood pressure, heart-rhythm, and seizure medications
- Have lupus (about half of people with lupus also have APS)
- Have relatives with APS
How to order antiphospholipid antibody?
- LA is reported with a final conclusion as positive/negative
- Comments such as borderline or dubious LA are highly discouraged and in these cases the comment should be “suggest re-testing after one week or more”, without suggesting positive or negative ...
- Along with the analytical results for the three steps, local cut-off values must be reported
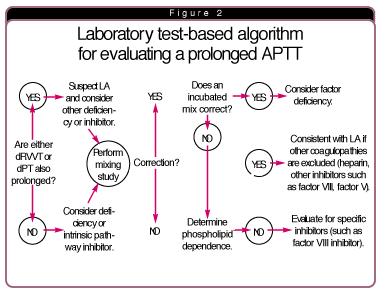
What is the syndrome of antiphospholipid?
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), sometimes known as Hughes syndrome, is a disorder of the immune system that causes an increased risk of blood clots. This means people with APS are at greater risk of developing conditions such as: DVT (deep vein thrombosis, a blood clot that usually develops in the leg.
Is antiphospholipid syndrome the same as lupus?
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is the prototypical autoimmune disease, characterized by an extreme variety of anti-nuclear antibodies and by different clinical presentations. Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) is characterized by the presence of arterial or venous thrombosis and anti-phospholipid antibodies.
Is antiphospholipid syndrome the same as thrombocytopenia?
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is frequently associated with thrombocytopenia, in most cases mild and in the absence of major bleedings. In some patients with a confirmed APS diagnosis, secondary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) may lead to severe thrombocytopenia with consequent major bleeding.
Is APS a blood clotting disorder?
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disorder that causes abnormal blood clots to form. Autoimmune disorders occur when your body's immune system makes antibodies that attack and damage your own tissues or cells.
What causes antiphospholipid syndrome?
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is caused by the body's immune system producing abnormal antibodies called antiphospholipid antibodies. This increases the risk of blood clots developing in the blood vessels, which can lead to serious health problems, such as: DVT (deep vein thrombosis)
Can APS turn into lupus?
The current study confirms that progression from primary APS to SLE or lupus-like disease is unusual, even after a long follow-up. Only 3 patients developed anti-dsDNA antibodies. The presence of a positive Coombs test might be a marker for the development of SLE in patients with primary APS.
Why is there thrombocytopenia in antiphospholipid syndrome?
Thrombocytopenia may be a symptom of APS. Paradoxically, it refers to an elevated thrombotic tendency, not bleeding risk. The causes of decreased platelet number are complex: antiphospholipid antibodies that bind to platelets activate them and induce thrombosis. Thrombocytes are consumed during this process.
Is antiphospholipid syndrome a thrombophilia?
Antiphospholipid syndrome is a disorder characterized by an increased tendency to form abnormal blood clots (thromboses) that can block blood vessels. This clotting tendency is known as thrombophilia.
How do you diagnose antiphospholipid syndrome?
To diagnose APS, the blood needs to be tested for the abnormal antiphospholipid antibodies that increase the risk of blood clots. This requires a blood test specifically designed to look for these antibodies.
What is the ICD 10 code for antiphospholipid antibody?
ICD-10 code D68. 61 for Antiphospholipid syndrome is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism .
Is antiphospholipid syndrome considered a disability?
APS can cause disability, serious illness and even death in a pregnant woman or her unborn baby if untreated. Unfortunately, it is a disease that is often under-recognised and under-diagnosed. This is probably because it can cause so many different problems, many of which have other, more common causes.
What does a positive antiphospholipid antibody mean?
Antiphospholipid antibodies are a group of immune proteins (antibodies) that the body mistakenly produces against itself in an autoimmune response to phospholipids. Tests can detect these autoantibodies that bind to phospholipids and, in a way that is not well understood, increase the risk of excessive blood clotting.
What is the difference between lupus anticoagulant and antiphospholipid syndrome?
The lupus anticoagulant tests are blood clotting tests. The antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) cause the test to be abnormal in the laboratory. Types of clotting tests may include: Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)
What diseases are associated with antiphospholipid syndrome?
Complications of antiphospholipid syndrome can include:Kidney failure. This can result from decreased blood flow to your kidneys.Stroke. ... Cardiovascular problems. ... Lung problems. ... Pregnancy complications.
What are the 4 types of lupus?
But there are four kinds of lupus:Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), the most common form of lupus.Cutaneous lupus, a form of lupus that is limited to the skin.Drug-induced lupus, a lupus-like disease caused by certain prescription drugs.Neonatal lupus, a rare condition that affects infants of women who have lupus.
What is the difference between lupus and lupus anticoagulant?
Lupus and lupus anticoagulant are not the same. Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease, and lupus anticoagulant is a type of antibody found in blood.
The ICD code D686 is used to code Antiphospholipid syndrome
Antiphospholipid syndrome or antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS or APLS), or often also Hughes syndrome, is an autoimmune, hypercoagulable state caused by antiphospholipid antibodies.
Coding Notes for D68.61 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #814-816 - Reticuloendothelial and immunity disorders with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'D68.61 - Antiphospholipid syndrome'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code D68.61. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code D68.61 and a single ICD9 code, 289.81 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for sepsis with acute hypoxic respiratory failure
- 2. icd 10 code for positive thc drug
- 3. icd 10 code for non union of fibula
- 4. icd 10 code for right arm paon
- 5. icd 10 code for pes cavus foot
- 6. icd 10 code for post pain
- 7. icd 9 code for need for vaccination
- 8. icd 10 code for newborn hydronephrosis
- 9. icd 10 code for hemorrhoids internal
- 10. icd 10 code for hepitis panel