What is the ICD 10 code for hearing loss?
H91.90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM H91.90 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H91.90 - other international versions of ICD-10 H91.90 may differ. hearing loss as classified in H90.-
When does the 2020 ICD-10-CM for hearing loss come out?
Unspecified hearing loss, unspecified ear. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM H91.90 became effective on October 1, 2019. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H91.90 - other international versions of ICD-10 H91.90 may differ.
What is asymmetric hearing loss?
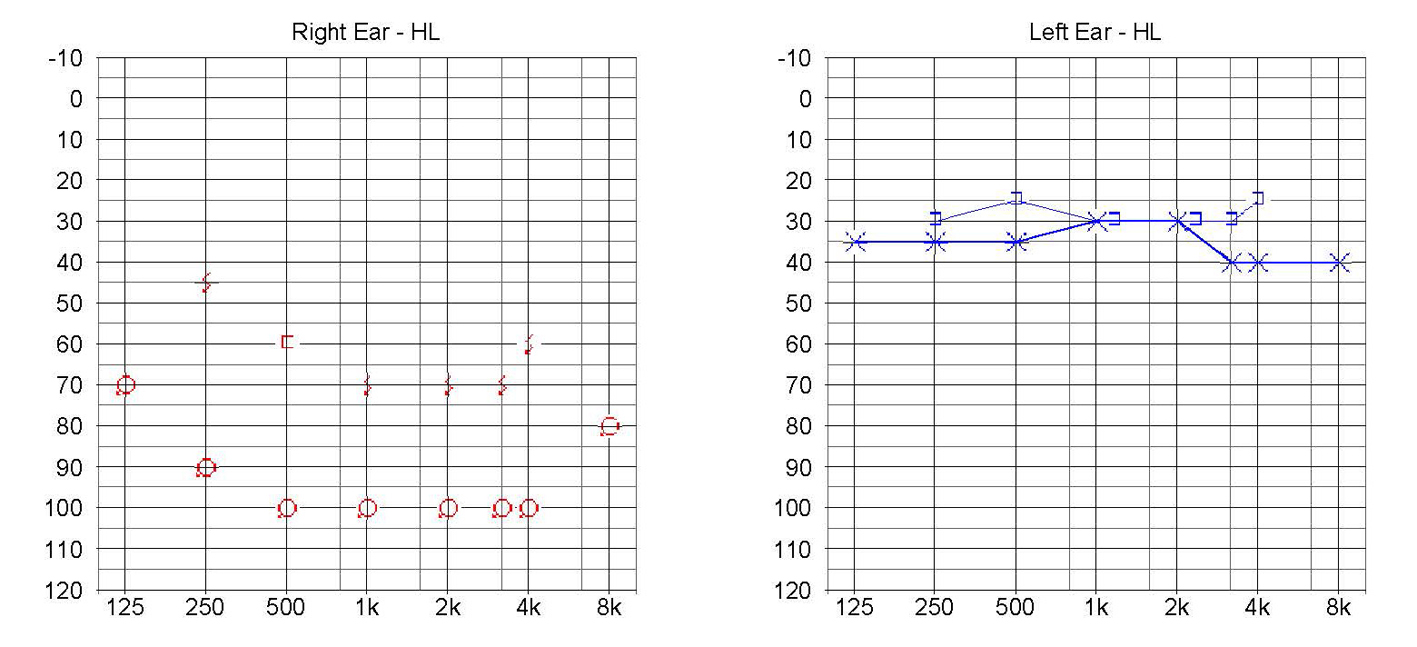
Asymmetric hearing loss is normally defined as a difference of 15 dB between the right and left ears at three contiguous frequencies.
What is the CPT code for ototoxic hearing loss?
Good clinical documentation should indicate the type of hearing loss, laterality and, if ototoxic hearing loss is present, the drug that caused the reaction and whether it was a poisoning or and adverse effect. Codes for hearing loss are H90-H94, Other disorders of the ear.
What is the ICD-10 code for hearing loss?
ICD-10 code H91. 90 for Unspecified hearing loss, unspecified ear is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the ear and mastoid process .
What is the ICD-10 code H90 3?
ICD-10 code: H90. 3 Sensorineural hearing loss, bilateral.
What is the code H90 5?
ICD-10 code: H90. 5 Sensorineural hearing loss, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for bilateral profound sensorineural hearing loss?
3.
What is asymmetric hearing loss?
Asymmetric hearing loss has been defined as a difference of 15 dB between the right and left ears at three contiguous frequencies. No matter the degree of loss, asymmetric hearing loss requires further evaluation. Generally, this workup includes auditory brainstem response (ABR) testing or MRI.
What does 389.9 hearing loss mean?
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 389.9 : Unspecified hearing loss.
What is the ICD-10 code for asymmetric hearing?
Sensorineural hearing loss, bilateral H90. 3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H90. 3 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How does sensorineural hearing loss occur?
About Sensorineural Hearing Loss Sensorineural hearing loss, or SNHL, happens after inner ear damage. Problems with the nerve pathways from your inner ear to your brain can also cause SNHL. Soft sounds may be hard to hear. Even louder sounds may be unclear or may sound muffled.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for unspecified anomaly of the ear with impairment of hearing?
Q16. 9 - Congenital malformation of ear causing impairment of hearing, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
What is a bilateral hearing loss?
A bilateral hearing loss is a hearing loss in both ears. A bilateral hearing loss can have different degrees: mild, moderate, severe or profound. The bilateral hearing impairment may be caused by factors in the outer, middle or inner ear or a combination of these areas.
How do you code unilateral hearing loss?
ICD-10 Code for Sensorineural hearing loss, unilateral, right ear, with unrestricted hearing on the contralateral side- H90. 41- Codify by AAPC.
What is the correct code for mixed conductive and sensorineural hearing loss unilateral left ear with unrestricted hearing on the contralateral side?
"H90. 71 - Mixed Conductive and Sensorineural Hearing Loss, Unilateral, Right Ear, With Unrestricted Hearing On the Contralateral Side." ICD-10-CM, 10th ed., Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services and the National Center for Health Statistics, 2018.
What is the ICD-10 CM code for chronic allergic otitis media right ear?
H65. 41 - Chronic allergic otitis media. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for BPH?
Code N40. 1 is the diagnosis code used for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms, also called benign enlargement of the prostate (BEP or BPE). It is a benign (noncancerous) increase in size of the prostate.
What is the ICD-10 code for glaucoma?
H40. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H40.
What is ICD-10 code for osteoporosis?
0 – Age-Related Osteoporosis without Current Pathological Fracture. ICD-Code M81. 0 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Age-Related Osteoporosis without Current Pathological Fracture.
What is the ICD-10 code for a disease?
The ICD-10 is also used to code and classify mortality data from death certificates.
When was ICD-10-CM implemented?
ICD-10 was implemented on October 1, 2015, replacing the 9th revision of ICD (ICD-9).
What is the difference between ICD-10 and CM?
The ICD-10-CM has two types of excludes notes. Each note has a different definition for use but they are both similar in that they indicate that codes excluded from each other are independent of each other.
Do audiologists have to report ICD-10?
Audiologists practicing in a health care setting, especially a hospital, may have to code diseases and diagnoses according to the ICD-10. Payers, including Medicare, Medicaid, and commercial insurers, also require audiologists to report ICD-10 codes on health care claims for payment.
What is the term for hearing loss that occurs when sound is not conducted efficiently through the outer ear canal?
Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound is not conducted efficiently through the outer ear canal to the eardrum and ossicles of the middle ear. Conductive hearing loss usually involves a reduction in sound level or the ability to hear faint sounds. This type of hearing loss can often be corrected medically or surgically.
What causes hearing loss?
Hearing loss is a common problem caused by noise, aging, disease, and heredity. According to the National Institutes of Health, an estimated one-third of people in the U.S. between the ages of 65 and 75 have some degree of hearing loss, while close to one-half of people over 75 years of age are affected.
What is H90.0?
There is also a subcategory (H91.2) for sudden idiopathic hearing loss, which is for sudden hearing loss with no known no cause. H90.0 Conductive hearing loss, bilateral.
Is ototoxic medication considered ototoxic?
Any medication that damages the ear and causes hearing loss is considered ototoxic. The damage may be permanent, or may return to normal after the medication is stopped. It may occur in one or both ears, and may not be to the same degree in both ears. Presbycusis is hearing loss that occurs gradually as a person ages.
Can hearing loss be corrected?
This type of hearing loss can often be corrected medically or surgically. Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) occurs when there is damage to the inner ear (cochlea), or to the nerve pathways from the inner ear to the brain. SNHL reduces the ability to hear faint sounds.
Is tinnitus a history of ear discharge?
There is no history of ear discharge, tinnitus, vertigo, or trauma. Otoscopic exam reveals both ear canals and TMs to be normal. Tuning for tests confirmed left conductive hearing loss. Proper coding is H90.12 Conductive hearing loss, unilateral, left ear, with unrestricted hearing on the contralateral side.
What is an asymmetric hearing loss?
An asymmetric hearing loss is when a hearing loss is larger in the one ear than the other. When a person has a hearing loss, the hearing loss is almost never exactly the same in both ears. But to be characterized as an asymmetric hearing loss, there has to be a certain difference in severity between the two ears in a number of frequencies as well as being a hearing loss in both ears ( bilateral hearing loss ). If there is only a hearing loss in one ear it is called a unilateral hearing loss.
How is asymmetric hearing loss diagnosed?
An asymmetric hearing loss is identified through a hearing test and it is normally treated with hearing aids or hearing implants.
Is bilateral hearing loss bilateral?
But to be characterized as an asymmetric hearing loss, there has to be a certain difference in severity between the two ears in a number of frequencies as well as being a hearing loss in both ears ( bilateral hearing loss ). If there is only a hearing loss in one ear it is called a unilateral hearing loss.

Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the icd 10 code for family history of rheumatoid arthritis
- 2. icd-10 code for vaginal atrophy
- 3. icd 9 code for cellulitis of leg without abscess
- 4. icd 9 code for tinea pedis
- 5. icd 10 code for cns lymphoma
- 6. icd 10 code for lesion of bladder
- 7. icd 10 code for chronic subluxation of biceps tendon
- 8. icd 10 code for sprain left forearm
- 9. icd 10 code for canker sores in mouth
- 10. icd 10 code for belching