What is the ICD 10 code for intermittent tachycardia?
Ventricular tachycardia.I47. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the diagnosis code for tachycardia?
R00.0 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of tachycardia, unspecified. The code R00.0 is valid during the fiscal year 2022 from October 01, 2021 through September 30, 2022 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. The ICD-10-CM code R00.0 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like abnormal pulse rate, borderline fast pulse, irregular tachycardia, pacemaker re-entrant tachycardia, pulse fast , pulse rate finding, etc.
What is the ICD 10 code for atrial fibrillation with RVR?
Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. I48.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is ectopic atrial tachycardia and how is it treated?
Treatment of atrial ectopic tachycardia may be attempted with medications such as beta blockers (propranolol), sodium channel blockers (flecainide), or class III antiarrhythmic medications (sotalol, amiodarone). The majority of neonatal AETs resolve spontaneously in the first 6 months of life, and long-term therapy is rarely necessary.
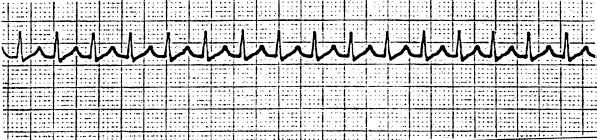
What is a paroxysmal atrial tachycardia?
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia is a type of arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat. Paroxysmal means that the episode of arrhythmia begins and ends abruptly. Atrial means that arrhythmia starts in the upper chambers of the heart (atria). Tachycardia means that the heart is beating abnormally fast.
What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for atrial tachycardia?
I47. 1 - Supraventricular tachycardia | ICD-10-CM.
Is paroxysmal atrial tachycardia the same as SVT?
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is as an irregularly fast or erratic heartbeat (arrhythmia) that affects the heart's upper chambers. SVT is also called paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. The typical heart beats about 60 to 100 times a minute.
What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia?
ICD-10-CM Code for Supraventricular tachycardia I47. 1.
What is the diagnosis for ICD 10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is the ICD 10 code for AAA?
I71.4ICD-10 Code for Abdominal aortic aneurysm, without rupture- I71. 4- Codify by AAPC.
How can you tell the difference between atrial tachycardia and SVT?
SVT is always more symptomatic than sinus tach. Sinus tachycardia has a rate of 100 to 150 beats per minute and SVT has a rate of 151 to 250 beats per minute. With sinus tach, the P waves and T waves are separate. With SVT, they are together.
Is atrial tachycardia the same as atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation is another type of atrial tachycardia that is closely related to atrial flutter. However, the arrhythmia that occurs in AFib is much more chaotic and results in a fast and usually very irregular heart rhythm or an atypical and irregular ventricular rate that can affect heart health.
What is paroxysmal atrial tachycardia quizlet?
Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia is an abrupt change from NSR to Atrial Tachycardia. Atrial Tachycardia. Any rhythm in the atria besides in the SA node at a rate 150-250. It will display as a TP pattern. This is where where the P is on top of the T wave.
What is supraventricular tachycardia?
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a faster heart rate in the atria, caused by electrical impulses in the atria firing abnormally. Supraventricular tachycardia includes atrial tachycardia, atrioventricular tachycardia, atrioventricular re-entrant tachycardia, junctional tachycardia, and nodal tachycardia.
What is the most common type of arrhythmia in children?
SVT is the most common type of arrhythmia in children. Example: An 8-year-old boy is brought in by his parents with complaints of chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue for one month. Upon examination his heart rate was 160 BPM. Labs and ECG are performed and he is diagnosed with supraventricular tachycardia.
What is the name of the condition where the electrical signal travels along a pathway within the right atrium?
Atrial flutter describes a condition in which the electrical signal travels along a pathway within the right atrium. It moves in an organized circular motion, or “ circuit,” causing the atria to beat faster than the ventricles. Clinical documentation should include the type of tachycardia (re-entry, ventricular, etc.).
What does it mean when your heart beats 100 beats per minute?
Tachycardia typically means a heart rate of more than 100 beats per minute. Symptoms of tachycardia include dizziness, shortness of breath, chest pain, and more.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for personal history of hep c
- 2. icd 10 code for cellulitis of toe
- 3. icd 10 code for urinary retention secondary to benign prostatic hypertrophy.
- 4. icd 10 code for memory loxss
- 5. icd 10 code for chest x-ray b-read
- 6. icd 9 code for degenerative joint disease of the knee
- 7. icd code for pararenal mass
- 8. icd 10 code for angular kholitis
- 9. icd 10 code for acute pharyngotonsillitis
- 10. icd 10 code for rheumatoid arthriris