How do you treat an atrial septal defect?
What can I do in the hospital to recover from an ASD repair?
- Deep breathe and cough. This will help decrease your risk for a lung infection. Take a deep breath and hold it for as long as you can. ...
- Get out of bed when your healthcare provider says it is okay. Movement will help prevent blood clots. ...
- Wait until your healthcare provider says it is okay to eat and drink. You may be given ice chips at first. ...
What are the causes of atrial septal defect?
Atrial septal defect causes. The cause of congenital heart defects is not understood but several factors are known to be associated: Maternal drug abuse, alcohol abuse and radiation exposure; Maternal infection, particularly rubella; Genetic abnormalities; Chromosomal abnormalities (septal defects are associated with Trisomy 21- Down’s syndrome).
What are the problems of septal deformities?
There are several types of nasal deformities, including:
- Congenital (present at birth) deformities: These include cleft palate, nasal mass or weakness in the structure of the nose.
- Enlarged adenoids: Adenoids are lymph glands found at the back of the nose. ...
- Enlarged turbinates: There are three turbinates, or baffles, on the side of each nostril that clean and humidify the air before it goes to your lungs. ...
What is a venticular septal defect?
What Is a Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)? A ventral septal defect, more commonly known as a ventricular septal defect (VSD), is a hole between your heart’s lower chambers, or ventricles. The defect can occur anywhere in the muscle that divides the two sides of the heart.
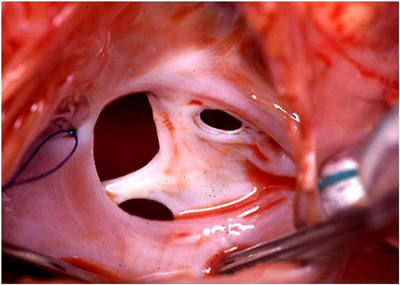
What is the ICD-10 code for atrial septal defect?
ICD-10 code: Q21. 1 Atrial septal defect | gesund.bund.de.
What is a secundum type atrial septal defect?
Secundum atrial septal defect (ASDII) is a common congenital heart defect that causes shunting of blood between the systemic and pulmonary circulations. Patients with an isolated ASDII often remain asymptomatic during childhood and adolescence.
What are the 4 types of atrial septal defect?
There are five types of atrial septal defects ranging from most frequent to least: patent foramen ovale, ostium secundum defect, ostium primum defect, sinus venosus defect, and coronary sinus defect.
What are the 3 types of atrial septal defects?
Types of atrial septal defects include:Secundum. This is the most common type of ASD . ... Primum. This type of ASD affects the lower part of the atrial septum and might occur with other congenital heart defects.Sinus venosus. ... Coronary sinus.
What is the difference between primum and secundum ASD?
ASDs are classified by their different location and development: Secundum ASD occurs in the middle part of the atrial septum. Primum ASD occurs in the lower part of the atrial septum close to the tricuspid and mitral valves.
What causes a secundum ASD?
The exact cause of atrial septal defects isn't fully known. However, congenital heart defects are often caused by genetic changes that happen before birth. Some genetic mutations associated with ASD affect the NKX2.
How many types of atrial septal defects are there?
There are 3 major types of ASDs or interatrial communications: ostium secundum, ostium primum, and sinus venosus (Figure 1A) defects. The ostium secundum is a true defect of the atrial septum and involves the region of the fossa ovalis.
What is the most common cause of atrial septal defect?
Atrial septal defect occurs in 5 to 10 percent of all babies with congenital heart disease. The most common form of ASD is an ostium secundum, an opening in the middle of the atrial septum. For unknown reasons, girls have atrial septal defects twice as often as boys.
Where is atrial septal defect ASD?
An atrial septal defect is a birth defect of the heart in which there is a hole in the wall (septum) that divides the upper chambers (atria) of the heart. A hole can vary in size and may close on its own or may require surgery. An atrial septal defect is one type of congenital heart defect.
Can you live a normal life with atrial septal defect?
ISOLATED atrial septal defect is the third most common form of congenital heart disorder presenting after childhood (bicuspid aortic valve and mitral-valve prolapse are first and second). Even if unrepaired, this defect is often compatible with prolonged survival into adulthood.
Can atrial septal defect be cured?
Open-heart surgery. This open-heart repair surgery is the only way to fix primum, sinus venosus and coronary sinus atrial defects. Sometimes, atrial septal defect repair can be done using small incisions (minimally invasive surgery) and with a robot (robot-assisted heart surgery).
What size ASD requires surgery?
In infants, small ASDs (less than 5 mm) will often not cause problems, or will close without treatment. Larger ASDs (8 to 10 mm), often do not close and may need a procedure.
How common are atrial septal defects in adults?
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is the most prevalent congenital cardiac anomaly in adults1, accounting for ~35% of all congenital heart defects. Late presentation is due to the insidious development of right ventricular remodeling, with enlargement of right cardiac chambers.
What is the ICd 10 code for ASD?
This is a rare type of ASD and accounts for less than 1 percent cases. Relevant ICD-10-CM codes for ASD are: Q21.1 Atrial septal defect – Alternative wording ...
What type of defect must be documented in an AMI?
Documentation must state the exact type of defect the patient has (e.g., type I, type II), and if the condition is congenital or acquired. The contributing factors will indicate the presence of the condition in the setting of an AMI.
What causes Ostium primum ASD?
Ostium primum ASD are caused by incomplete fusion of septum primum with the endocardial cushion. This is the second most common type, accounting for 15-20 percent of cases. Sinus venosus ASD is an abnormal fusion between the embryologic sinus venosus and the atrium. In most cases, the defect lies superior in the atrial septum near the entry ...
What is the most commonly recognized congenital cardiac anomaly presenting in adulthood?
Print Post. Atrial septal defect (ASD) is the most commonly recognized congenital cardiac anomaly presenting in adulthood. An ASD is a defect in the interatrial septum that allows pulmonary venous return from the left atrium to pass directly to the right atrium.
What is the most common type of ASD?
There are four major types of ASD: Ostium secundum ASD results from incomplete adhesion between the flap valve associated with the foramen ovale and the septum secundum after birth. This is the most common type, accounting for 75 percent of all ASD cases.
What is the ICd 10 code for a septal defect?
Atrial septal defect as current complication following acute myocardial infarction 1 I23.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 Short description: Atrial septal defect as current complication following AMI 3 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM I23.1 became effective on October 1, 2020. 4 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I23.1 - other international versions of ICD-10 I23.1 may differ.
When will ICD-10-CM I23.1 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I23.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICd 10 code for a septal defect?
Q21.1 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Atrial septal defect . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
When an excludes2 note appears under a code, is it acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code?
When an Excludes2 note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code together. A “code also” note instructs that two codes may be required to fully describe a condition, but this note does not provide sequencing direction. The sequencing depends on the circumstances of the encounter.
Is Q21.1 POA?
Q21.1 is exempt from POA reporting ( Present On Admission).
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for hypertensive heart disease with heart failure and ckd
- 2. icd 9 cm code for edema both legs
- 3. icd 10 code for li fraumeni syndrome
- 4. icd-10-cm code for respiratory therapy
- 5. icd 10 code for ruptured quadriceps tendon - left lower extremity
- 6. icd 9 code for confusion nos
- 7. icd 10 code for copd with asthma exacerbation
- 8. icd 10 code for cervical abrasion
- 9. icd-10 code for manipulation under anesthesia right knee
- 10. icd 10 code for status post hernia repair