What is the ICD 10 code for atrioventricular block?
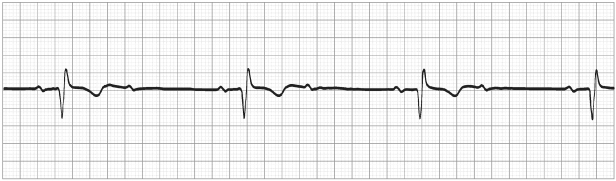
In ICD-10-CM the codes are categorized by degree: First degree AV block (I44.0 Atrioventricular block, first degree) – All atrial impulses reach the ventricles, but the conduction is delayed within the AV node. Patients are generally asymptomatic and the first-degree AV block is usually an incidental finding on electrocardiography (ECG).
What is the ICD 10 code for excluded note?
I51.3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I51.3 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I51.3 - other international versions of ICD-10 I51.3 may differ. A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes.
What is the ICD 10 version for transient cerebral ischemic attacks?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I49.8 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I49.8 - other international versions of ICD-10 I49.8 may differ. transient cerebral ischemic attacks and related syndromes ( G45.-) A derangement in the normal functioning of the sinoatrial node.
What is first-degree atrioventricular (AV) block?
Patients are generally asymptomatic and the first-degree AV block is usually an incidental finding on electrocardiography (ECG). People with newly diagnosed first-degree AV block may be well-conditioned athletes, or they may have a history of myocardial infarction or myocarditis.

What is ICD-10 NOS code?
Toxic effect of nitrogen oxides, accidental (unintentional), initial encounter. T59. 0X1A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM T59.
What is diagnosis code I48 91?
Unspecified atrial fibrillationThe code for “atrial fibrillation with RVR” is I48. 91 Unspecified atrial fibrillation.
What is diagnosis code I48 92?
I48. 92 - Unspecified atrial flutter. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD 10 code for Ventricular arrhythmia?
ICD-10 code I47. 0 for Re-entry ventricular arrhythmia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is R06 00?
ICD-10 code R06. 00 for Dyspnea, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What I25 10?
ICD-10 code: I25. 10 Atherosclerotic heart disease: Without hemodynamically significant stenosis.
Is atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation the same?
Normally, the top chambers (atria) contract and push blood into the bottom chambers (ventricles). In atrial fibrillation, the atria beat irregularly. In atrial flutter, the atria beat regularly, but faster than usual and more often than the ventricles, so you may have four atrial beats to every one ventricular beat.
What is the ICD-10 code for atrial tachycardia?
I47. 1 - Supraventricular tachycardia | ICD-10-CM.
What is ventricular arrhythmia?
Ventricular arrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms that make the lower chambers of your heart twitch instead of pump. This can limit or stop your heart from supplying blood to your body. While some of these arrhythmias are harmless and don't cause symptoms, some can have serious — or even deadly — effects on your body.
Is V-tach a code?
In ICD-10-CM the codes would be I47. 2, ventricular tachycardia, and code I46. 9, Cardiac arrest, unspecified. As far as the coding of these conditions, under (I46) cardiac arrest there is an Excludes 1 note for cardiogenic shock (R57.
What is an AV block?
Atrioventricular (AV) block involves impairment of the conduction between the atria and ventricles of the heart. In ICD-10-CM the codes are categorized by degree:#N#First degree AV block (I44.0 Atrioventricular block, first degree) – All atrial impulses reach the ventricles, but the conduction is delayed within the AV node. Patients are generally asymptomatic and the first-degree AV block is usually an incidental finding on electrocardiography (ECG). People with newly diagnosed first-degree AV block may be well-conditioned athletes, or they may have a history of myocardial infarction or myocarditis. First-degree AV block also may represent the first sign of degenerative processes of the AV conduction system.#N#Second degree AV block (I44.1 Atrioventricular block, second degree) – Atrial impulses fail to conduct to the ventricles. Patients may be asymptomatic, but may experience pre-syncope or syncope and sensed irregular heartbeats. The latter usually is observed in more advanced conduction disturbances, such as Mobitz II second-degree AV block. A history of medications that affect atrioventricular node (AVN) function (e.g., digitalis, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers) may be contributory and should be obtained. Other terms for a second degree AV block are Wenckebach’s and Mobitz blocks.#N#Third degree AV block (I44.2 Atrioventricular block, complete) – No supraventricular impulses are conducted to the ventricles. Patients have symptoms of fatigue, dizziness, light-headedness, pre-syncope, or syncope. Syncopal episodes due to slow heart rates are called Morgagni-Adams-Stokes (MAS) episodes, in recognition of the pioneering work of these researchers on syncope. Patients with third-degree AV block may have associated symptoms of acute myocardial infarction either causing the block or related to reduced cardiac output from bradycardia in the setting of advanced atherosclerotic coronary artery disease.#N#Proper coding of AV block requires documentation of severity:
Which vein is used for the implantation of a transvenous pacemaker?
PROCEDURE: Insertion of right atrial and right ventricular transvenous leads through the left subclavian vein and implantation of a dual-chamber permanent pacemaker.
Is AV block asymptomatic?
Patients are generally asymptomatic and the first-degree AV block is usually an incidental finding on electrocardiography (ECG). People with newly diagnosed first-degree AV block may be well-conditioned athletes, or they may have a history of myocardial infarction or myocarditis.
What is the rate of a sudden onset of atrial contractions?
A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia with abrupt onset and sudden termination of atrial contractions with a rate of 150-250 beats per minute. The rhythm disturbance originates in the atria.
When will ICD-10-CM I47.1 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I47.1 became effective on October 1 , 2021.
When will ICD-10-CM I49.3 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I49.3 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the most common arrhythmia?
Premature ventricular beats, the most common of all arrhythmias; in the absence of heart disease, they are not of great clinical significance, but in patients with coronary disease, they represent a constant danger of ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation and sudden death.
Popular Posts:
- 1. z code for icd patient treatment not possible
- 2. icd 10 code for croupy cough
- 3. icd 10 code for complication of jackson pratt drain
- 4. icd 10 code for dominant right olecranon fracture and surgical repair
- 5. icd 10 code for history of diabetes
- 6. icd 10 code for left facial folbiculitis
- 7. icd 10 code for chronic hydronephrosis
- 8. icd 9 code for fetal demise
- 9. icd 10 code for visual dizziness
- 10. icd 10 code for rectal bleed episode