What is the ICD 10 code for beta thalassemia?
Beta thalassemia. D56.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What are the symptoms of thalassemia?
If you have thalassemia, your body has problems making hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen through your body. When your blood does not carry enough oxygen to the rest of your body, you have anemia.thalassemia, a genetic disease, can be mild or severe. Some carriers of the gene have no symptoms.
What is the ICD 10 code for Cooley's anemia?
Diagnosis Index entries containing back-references to D56.1: Anemia (essential) (general) (hemoglobin deficiency) (infantile) (primary) (profound) D64.9 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D64.9 Cooley's anemia D56.1 Thalassemia (anemia) (disease) D56.9 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D56.9
What are the treatment options for severe thalassemia?
Severe thalassemia is treated with blood transfusions and treatment to remove excess iron in the blood. ICD-10-CM D56.9 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 791 Prematurity with major problems 793 Full term neonate with major problems
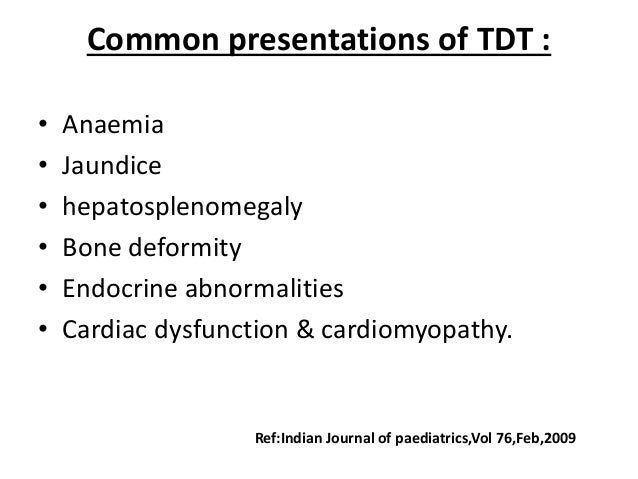
What is the ICD 10 code for thalassemia trait?
D56. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D56.
What is b thalassemia trait?
What is beta thalassemia trait? Beta thalassemia affects the hemoglobin in the red blood cells. All red blood cells contain hemoglobin, which carries oxygen from the lungs to all parts of the body. People with beta thalassemia do not make enough hemoglobin.
What is the difference between thalassemia and thalassemia trait?
A person who has thalassemia trait may not have any symptoms at all or may have only mild anemia, while a person with thalassemia major may have severe symptoms and may need regular blood transfusions.
What is the difference between alpha and beta thalassemia trait?
The thalassemias are a group of inherited hematologic disorders caused by defects in the synthesis of one or more of the hemoglobin chains. Alpha thalassemia is caused by reduced or absent synthesis of alpha globin chains, and beta thalassemia is caused by reduced or absent synthesis of beta globin chains.
What is thalassemia B minor?
Beta thalassemia is a blood disorder that reduces the production of hemoglobin . Hemoglobin is the iron-containing protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to cells throughout the body. In people with beta thalassemia, low levels of hemoglobin lead to a lack of oxygen in many parts of the body.
What are the 4 types of thalassemia?
Alpha thalassemia occurs when some or all of the 4 genes that make hemoglobin (the alpha-globin genes) are missing or damaged....There are 4 types of alpha thalassemia:Alpha thalassemia silent carrier. ... Alpha thalassemia carrier. ... Hemoglobin H disease. ... Alpha thalassemia major.
What is thalassemia trait and carrier?
If you're a carrier of thalassaemia, it means you carry one of the faulty genes that cause thalassaemia, but you do not have thalassaemia yourself. Being a carrier of the trait is sometimes known as having the thalassaemia trait or having thalassaemia minor.
What happens if both parents have beta thalassemia trait?
If both parents have the beta thalassaemia trait, there's a: 1 in 4 chance each child they have will not inherit any faulty genes and will not have thalassaemia or be able to pass it on. 1 in 2 chance each child they have will just inherit a copy of the faulty gene from 1 parent and be a carrier.
What are the types of beta thalassemia?
Beta thalassemia has three main forms – minor, intermedia and major, which indicate the severity of the disease. Individuals with beta thalassemia minor usually do not have any symptoms (asymptomatic) and individuals often are unaware that they have the condition. Some individuals do experience a very mild anemia.
What type of anemia is beta thalassemia?
Beta thalassemia intermedia. People with beta thalassemia intermedia have moderately severe anemia and some will need blood transfusions and other medical treatment. Blood transfusions deliver healthy hemoglobin and RBCs to the body. Beta thalassemia major (also called Cooley's anemia).
Can you have alpha and beta thalassemia trait?
EXPERTS MAKE THE CALL. Your patient indeed has both beta and alpha thalassemia. The high A2 and F in the presence of microcytosis confirm the presence of beta thalassemia trait (possibly deletional–beta thalassemia since both A2 and F are high).
What is the difference between beta thalassemia major and minor?
They are thalassemia minor and thalassemia major (which is also called Cooley's anemia). Thalassemia minor: The individual with thalassemia minor has only one copy of the beta thalassemia gene (together with one perfectly normal beta-chain gene). The person is said to be heterozygous for beta thalassemia.
What is postpartum thalassemia?
Thalassemia in pregnancy. Thalassemia postpartum. Clinical Information. A group of hereditary hemolytic anemias in which there is decreased synthesis of one or more hemoglobin polypeptide chains.
What is the term for a group of hereditary hemolytic anemias that have in common a decreased
Heterogeneous group of hereditary hemolytic anemias which have in common a decreased rate of synthesis of one or more hemoglobin polypeptide chains. If you have thalassemia, your body has problems making hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen through your body.
What is the trait of thalassemia?
Clinical Information. A condition in which a person has reduced protein production from one of the four alpha-globin alleles. A condition in which a person has reduced protein production from two of the four alpha-globin alleles.
What does "type 1 excludes note" mean?
It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as D56.3. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together , such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. alpha thalassemia (.
What is thalassemia inherited?
An inherited form of anemia. Heterogeneous group of hereditary hemolytic anemias which have in common a decreased rate of synthesis of one or more hemoglobin polypeptide chains. If you have thalassemia, your body has problems making hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen through your body.
When does thalassemia appear?
It usually appears during the first two years of life. Severe thalassemia is treated with blood transfusions and treatment to remove excess iron in the blood. Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015 require the use of ICD-10-CM codes.
What is hemolytic anemia?
A group of hereditary hemolytic anemias in which there is decreased synthesis of one or more hemoglobin polypeptide chains. There are several genetic types with clinical pictures ranging from barely detectable hematologic abnormality to severe and fatal anemia.
What is the ICd code for thalassemia?
The ICD code D561 is used to code Beta thalassemia. Beta thalassemias (β thalassemias) are a group of inherited blood disorders. They are caused by reduced or absent synthesis of the beta chains of hemoglobin that result in variable outcomes ranging from severe anemia to clinically asymptomatic individuals. Global annual incidence is estimated ...
What is beta thalassemia?
Beta thalassemia (β thalassemia) is a form of thalassemia caused by mutations in the HBB gene on chromosome 11, inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion. The severity of the disease depends on the nature of the mutation. Specialty:

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for foreign body (fb) in soft tissue of foot
- 2. icd 10 code for paraplegia
- 3. icd-10 code for leukemia, unspecified
- 4. icd 10 code for ischemic adenopathy
- 5. icd 10 code for chronic cer
- 6. how to code icd for scuba diving accidents that get decommpression sickness
- 7. icd 10 code for bulbar als
- 8. 2011 icd-9 code for hyponatremia
- 9. icd 10 code for history of fracture
- 10. icd-10 code for hep c