Is strep related to breast infection?
Yes: Beta hemolytic streptococci can cause breast infections although staphylococcus aureus is the more common cause. 90,000 U.S. doctors in 147 specialties are here to answer your questions or offer you advice, prescriptions, and more. Get help now: is strep related to breast infection?
How is alpha hemolytic strep treated?
- Beta-hemolytic streptococci produce zones of clear hemolysis around each colony.
- Alpha-hemolytic streptococci (commonly called viridans streptococci) are surrounded by green discoloration resulting from incomplete hemolysis.
- Gamma-hemolytic streptococci are nonhemolytic.
What is the diagnosis code for strep throat?
Streptococcal pharyngitis
- Valid for Submission. J02.0 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of streptococcal pharyngitis.
- Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries. ...
- Index to Diseases and Injuries. ...
- Approximate Synonyms
- Convert J02.0 to ICD-9 Code. ...
- Information for Patients. ...
How is strep pneumonia treated?
What is the treatment for Streptococcus pneumonia? The treatment of the pneumococcal disease that is caused by the Streptococcus bacteria is the consumption of antibiotics. Although there are many kinds of bacteria that cause pneumococcal diseases that have become resistant to many kinds of antibiotics that treat them.
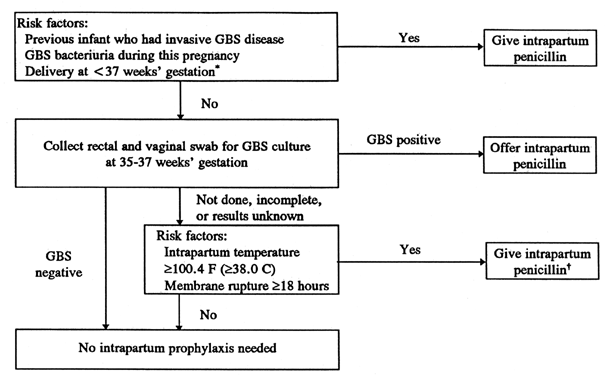
How do you code bacteremia in ICD-10?
What's the diagnosis in ICD-10? Bacteremia – Code R78. 81 (Bacteremia).
What is the ICD-10 code for streptococcal?
ICD-10-CM Code for Streptococcal pharyngitis J02. 0.
What is streptococcal bacteremia?
Group B streptococcal bacteremia (GBSB) in adults is a common disease with significant morbidity and mortality rates. 1. Almost all patients with GBSB have underlying comorbid illnesses, with diabetes mellitus2 as a major predisposing condition as described in several studies of GBSB.
Can strep cause bacteremia?
Group A streptococcus (GAS) can cause a variety of infections and rarely can cause bacteremia, especially in the elderly with underlying conditions such as diabetes mellitus, heart failure, and soft tissue infections. The course of GAS bacteremia is rapid and requires prompt diagnosis and treatment.
What is the diagnosis code for Streptococcus A as cause of disease classified elsewhere?
0 for Streptococcus, group A, as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases .
What is the ICD-10 code for gram negative bacteremia?
To identify patients with possible Gram-negative bacteremia in the NPR, we used diagnoses of “septicemia/sepsis due to other Gram-negative organisms” (ICD-10 code A41. 5).
What is streptococcal septicemia?
Septicemia is an infection in the bloodstream (also called bacteremia) that may travel to different body organs. GBS septicemia is caused by the bacterium Streptococcus agalactiae, which is commonly called group B strep, or GBS. GBS is commonly found in adults and older children and usually does not cause infection.
What would the most common abbreviation for Streptococcus be?
Strep is short for Streptococcus, a type of bacteria. There are several types. Two of them cause most of the strep infections in people: group A and group B.
What is Streptococcus group?
INTRODUCTION. The Streptococcus bovis/Streptococcus equinus complex (SBSEC; formerly group D streptococci) includes four major species (table 1) [1]. SBSEC members are gram-positive cocci that are an important cause of bacteremia and infective endocarditis (IE) in adults.
What is beta hemolytic Streptococcus Group G?
Large colony-forming group G β-hemolytic streptococci (GGS) were first isolated in patients with puerperal sepsis in 1935 (1). GGS are known to be commensals and pathogens in domestic animals. In humans, they may colonize the pharynx, skin, gastrointestinal and female genital tract (2).
How is group A strep bacteremia treated?
Therapy consists of appropriate antimicrobials given parenterally to control the infection. If group A streptococcus has been identified as the etiologic agent, penicillin can be used. Patients allergic to penicillin can be treated with clindamycin, vancomycin, or cefazolin.
What is a streptococcus viridans infection?
Clinical Information. Any of the several infectious disorders caused by members of streptococcus, a genus of gram positive bacteria belonging to the family streptococcaceae. Streptococcal infections are classified into groups a, b, c, d and g. Infections with bacteria of the genus streptococcus.
What are the two groups of streptococci?
Streptococcal infections are classified into groups a, b, c, d and g . Infections with bacteria of the genus streptococcus. Streptococcal infections (strep for short) cause a variety of health problems. There are two types: group a and group b. Antibiotics are used to treat both.group a strep causes.
What is the name of the sore, red, white rash on the tonsils?
strep throat - a sore, red throat, sometimes with white spots on the tonsils. scarlet fever - red rash on the body. impetigo - a skin infection. toxic shock syndrome. cellulitis and necrotizing fasciitis (flesh-eating disease) group b strep can cause blood infections, pneumonia and meningitis in newborns.
What is the B95?
B95 Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and Enterococcus as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere. B95.0 Streptococcus, group A, as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere. B95.1 Streptococcus, group B, as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere. B95.2 Enterococcus as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere.
Is B95 a reimbursement code?
Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and Enterococcus as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere. B95 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM B95 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the O98.2 infection?
gonococcal infections complicating pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium ( O98.2) infections with a predominantly sexual mode of transmission NOS complicating pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium ( O98.3) syphilis complicating pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium ( O98.1) tuberculosis of genitourinary system complicating pregnancy, ...
What are the criteria for SIRS?
The idea behind defining SIRS was to establish a clinical response to a nonspecific condition of either infectious or noninfectious origin. SIRS criteria include: 1 Fever of more than 38°C (100.4°F) or less than 36°C (96.8°F) 2 Heart rate of more than 90 beats per minute 3 Respiratory rate of more than 20 breaths per minute or arterial carbon dioxide tension (PaCO 2) of less than 32mm Hg 4 Abnormal white blood cell count (>12,000/µL or < 4,000/µL or >10 percent immature [band] forms)
What is the ICd 10 code for severe sepsis?
When a patient has sepsis with evidence of organ dysfunction, this is known as severe sepsis, and it is classified in ICD-10-CM either with the code R65.20, severe sepsis without septic shock, or R65.21, severe sepsis with septic shock. According to the ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting, an acute organ dysfunction must be associated with the sepsis in order to assign the severe sepsis code. If the clinical documentation is not clear as to whether acute organ dysfunction is related to the sepsis or another medical condition, querying the provider is recommended.
What is the clinical feature of sepsis?
Sepsis can be defined as the presence of both an infection and a systemic inflammatory response. The clinical features include two or more of the SIRS criteria occurring as a result of a suspected or documented infection, taking into consideration the entire clinical picture of the patient. In the ICD-10-CM world, in order to accurately reflect ...
How many codes are needed for severe sepsis?
The coding of severe sepsis requires a minimum of two codes. The first code will identify the underlying systemic infection, followed by a code from subcategory R65.2, severe sepsis. The codes for severe sepsis from subcategory R65.2 can never be assigned as a principal diagnosis.
What is the ICd 10 code for bacteremia?
It is often transient and of no consequence; however, sustained bacteremia may lead to widespread infection and sepsis. The ICD-10-CM code for bacteremia, R78.81, can be found in Chapter 18, Symptoms, Signs, and Abnormal Clinical and Laboratory Findings.
What is AHIMA in healthcare?
However, based on the recently published American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) recommendations regarding diagnosis options for providers, the options available in such a case must be clinically significant and reasonable, as supported by clinical indicators in the health record.
Is urosepsis a coding term?
The ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting indicate quite clearly that urosepsis is a nonspecific term that is not synonymous with sepsis. There is no default code for urosepsis in ICD-10-CM, and the provider must be queried for clarification when this term is documented. However, based on the recently published American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) recommendations regarding diagnosis options for providers, the options available in such a case must be clinically significant and reasonable, as supported by clinical indicators in the health record. A statement of urosepsis should not automatically generate a clarification for sepsis if there are no clinical indicators, risk factors or treatment documented to substantiate a clinical diagnosis of sepsis.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 diagnosis code for flank pain
- 2. rfa icd code for dental filling
- 3. icd 10 code for bronchiolitis due to rsv
- 4. icd-10 code for moderate protein calorie malnutrition
- 5. icd 10 code for right ankle peroneal tendonitis
- 6. icd 10 code for pain low back
- 7. icd-10 code for left leg
- 8. icd 10 code for bleeding with sex
- 9. icd 10 code for family history of skin ca
- 10. icd 10 cm code for other symptoms of genitourinary