Can BV go away on its own?
Can bacterial vaginosis go away on its own? BV will often go away on its own within a few days, but it also tends to come back. If you take antibiotics to treat BV, the symptoms may disappear within a day or two, but it’s important to take the full course of pills, which is usually seven days.
Does clindamycin really treat bacterial vaginosis?
Clindamycin isn’t practical because you’re not treating the cause of bacterial vaginosis; you’re only treating the frustrating symptoms you’re experiencing. Another problem you’ll find with using clindamycin to treat bacterial vaginosis is that some women are allergic to this antibiotic.
Why does my BV keep coming back?
Why Does My Bv Keep Coming Back? It is possible for BV to grow bacteria if the vaginal pH is too high, which is too basic or alkaline. Therefore, it is recommended to maintain a vaginal pH that is slightly acidic to prevent recontamination. Gels containing lactic acid can prevent your vaginal pH from becoming too alkaline.
How to recognize bacterial vaginosis symptoms?
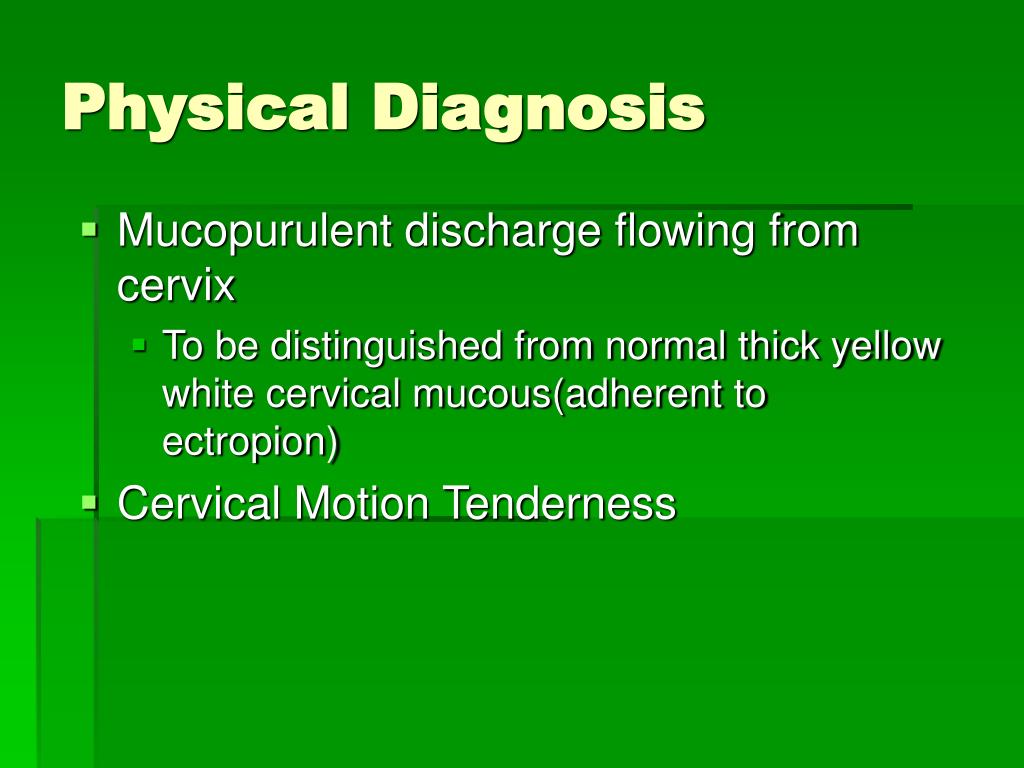
What Are the Symptoms of Bacterial Vaginosis?
- Vaginal itching
- Burning during urination
- Increased vaginal discharge that smells like fish
- Thin gray, green, or white discharge

What is the ICD-10 code for bacterial infections?
ICD-10 code: A49. 9 Bacterial infection, unspecified.
What diagnosis is BV?
What is a bacterial vaginosis test? A bacterial vaginosis test is a way to diagnose a bacterial vaginal infection. It's sometimes called a vaginal pH test or a wet mount test. The test uses a sample of fluid from your vagina.
What is ICD-10 acute vaginitis?
ICD-10 code N76. 0 for Acute vaginitis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
Is BV and vaginosis the same thing?
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) and vaginal yeast infections have similar symptoms but different causes and treatments. A yeast infection and BV are both infections that cause vaginitis. Vaginitis is the medical term for inflammation of the vagina....Differences.Bacterial vaginosisYeast infectionvaginal itchingvaginal itching5 more rows•Apr 14, 2020
How can I tell the difference between BV and yeast infection?
One easy way to distinguish between these two conditions is the smell or lack thereof. Discharge from BV has a distinctive fishy odor, while yeast infection discharge tends to be odorless. BV discharge is also fairly thin, while yeast infection discharge has a thick consistency often resembling cottage cheese.
What bacteria causes BV?
BV is often caused by gardnerella vaginalis, the most common type of bacteria in your vagina. Anything that changes the chemistry of your vagina's pH balance can mess with bacteria levels and lead to infection — like douching or using vaginal deodorants and other irritating products.
What is the ICD-10 code for atrophic vaginitis?
ICD-10 | Postmenopausal atrophic vaginitis (N95. 2)
What is the ICD-10 code for gardnerella?
89: Other specified bacterial agents as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere.
What is the ICD-10 code for vaginal bleeding?
ICD-10 code: N93. 9 Abnormal uterine and vaginal bleeding, unspecified.
Can a man's sperm make a woman smell fishy?
Can a man's sperm make a woman smell fishy? Not likely. As we've said, our vagina is a self-cleaning system, and it's perfectly capable of handling semen. Semen does have a slight odor to it, but it's often described as smelling slightly like bleach or chlorine.
What is the ICd code for BV?
The ICD code B96 is used to code Bacterial vaginosis. Bacterial vaginosis (BV), also known as vaginal bacteriosis or Gardnerella vaginitis, is a disease of the vagina caused by excessive growth of bacteria. Common symptoms include increased vaginal discharge that often smells like fish. The discharge is usually white or gray in color.
Does BV cause itching?
Itching is uncommon. Occasionally there may be no symptoms. Having BV increases the risk of infection by a number of other sexually transmitted infections including HIV/AIDS. It also increases the risk of early delivery among pregnant women. Specialty: Gynecology, Infectious Disease. MeSH Code: D016585. ICD 9 Code:
What is the ICd 10 code for a vaginal discharge?
First, according to ICD-10, N76.0 is any disorder that is characteristic of a process of infection that involves the vagina. Secondly, N76.0 is a process of infection that affects the vagina with symptoms of purulent discharge along with pain.
What is the ICd 9 code for senile vaginitis?
However, the code 616.10 does not include non-infective leucorrhea and postmenopausal along with senile vaginitis. For a physician to appropriately identify organisms using ICD-9-CM 616.10, additional codes are used. For instance, for the organism, Escherichia coli additional codes of (041.41-041.49) are used.
When was the ICD-9 code used?
Generally, diseases are classified internationally using codes. Initially, before the 30th of September 2015, the ICD-9 codes were used for classification. However, after the 1st of October 2015 ICD-10 codes of classification were adopted.
When is the 616.10 code applied?
The code 616.10 however, should only be applied to claims that have a service date of before the 30th of September 2015. Due to the coding classification system of ICD-9, the disease is also given synonym names.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for dm with hlp
- 2. 2017 icd 10 code for tongue numbness
- 3. icd 10 code for left sided weakness due to a tramatic accident
- 4. 2016 icd 10 code for laceration bit toe
- 5. icd 10 code for carotid artery stenosis
- 6. icd 10 code for foreign body left foot
- 7. medicare icd 10 code for tdap vaccine
- 8. icd 10 code for rt knee contusion
- 9. icd 10 code for family history of copd
- 10. icd-9 code for schizophrenia