What is the diagnosis code for urinary tract infection?
Urinary tract infection, site not specified N39. 0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. How do you code a urinary tract infection? Code 599.0 is reported to identify UTI as the localized infection. Code E879.
What is Gram negative bacilli ICD 10 code?
Tonsillitis due to Gram negative bacteria (disorder) ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'B96.89 - Other specified bacterial agents as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere' The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code B96.89.
What is ICD 10 code for urinary tract infection?
Urinary tract infection, site not specified
- N39.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N39.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N39.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 N39.0 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for foul smelling urine?
Unspecified abnormal findings in urine
- Valid for Submission. R82.90 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of unspecified abnormal findings in urine.
- Code Classification
- Index to Diseases and Injuries. ...
- Approximate Synonyms
- Convert R82.90 to ICD-9 Code
- Information for Patients. ...
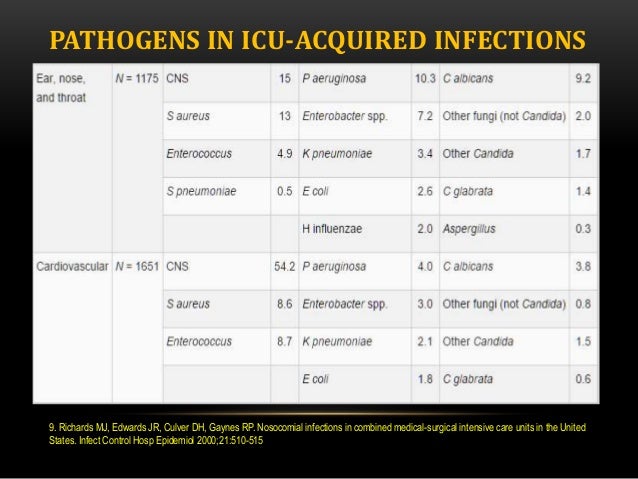
What is ICD 10 code for lower respiratory tract infection?
lower respiratory infection (J44. 0)
What is the ICD 10 code for acute upper respiratory infection with influenza?
J10. 1 Influenza with other respiratory manifestations, seasonal influenza virus identified. Influenzal: acute upper respiratory infection.
What is a bacterial URI?
An upper respiratory tract infection (URI) is a bacterial or viral infection of the nose, sinuses, or throat. Common symptoms of a URI are a runny or stuffy nose and a cough. Examples of URIs include influenza (flu), a cold, and sinusitis.
What is URI unspecified?
A viral upper respiratory infection, or URI, is a condition that affects your upper air passages. The most well-known type is the common cold. An infection caused by a virus, it typically enters your body through your nose or mouth.
How do you code an upper respiratory infection?
J06. 9 - Acute upper respiratory infection, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
Is upper respiratory tract infection a diagnosis?
How are upper respiratory infections diagnosed? Your healthcare provider may diagnose the infection based on a physical exam and your symptoms. They'll look in your nose, ears and throat and listen to your chest to examine your breathing. You often don't need other tests.
What is the ICD 10 code for upper respiratory infection?
ICD-10 code J06. 9 for Acute upper respiratory infection, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
What are 4 types of respiratory infections?
Differences Between the Most Common Respiratory Infections. Four of the most common types of respiratory infections are COVID-19, the flu, pneumococcal disease, and colds.
What is acute URI?
What is a URI? An upper respiratory infection (URI) is a term used to describe an acute infection of the head and chest. Generally, it affects the nose, throat, airways, sinuses and/or ears. URIs are among the most common diagnoses at Cornell Health.
What is the ICD-10 for UTI?
0 Urinary tract infection, site not specified.
What are three common respiratory infections?
General ConceptsUpper Respiratory Infections: Common Cold, Sinusitis, Pharyngitis, Epiglottitis and Laryngotracheitis. Etiology: Most upper respiratory infections are of viral etiology. ... Lower Respiratory Infections: Bronchitis, Bronchiolitis and Pneumonia.
Is bronchitis a URI?
The Basics of Bronchitis Bronchitis (chest cold) is not an upper respiratory tract infection. Rather, it affects the air-transporting tubes of the lungs (bronchioles), which are a part of the lower respiratory tract.
What are some examples of bacteria that cause infections?
Examples of bacteria that cause infections include streptococcus, staphylococcus, and e. Coli.antibiotics are the usual treatment. When you take antibiotics, follow the directions carefully. Each time you take antibiotics, you increase the chances that bacteria in your body will learn to resist them.
When will ICD-10 A49.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM A49.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What do bacteria look like?
Bacteria are living things that have only one cell. Under a microscope, they look like balls, rods, or spirals. They are so small that a line of 1,000 could fit across a pencil eraser. Most bacteria won't hurt you - less than 1 percent of the different types make people sick.
When to use unspecified diagnosis codes?
Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition.
When was the ICd 10 code implemented?
FY 2016 - New Code, effective from 10/1/2015 through 9/30/2016 (First year ICD-10-CM implemented into the HIPAA code set)
What is the J06.9 code?
J06.9 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of acute upper respiratory infection, unspecified. The code J06.9 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. The code is commonly used in family practice , ...
When will the ICD-10 J02.8 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J02.8 became effective on October 1, 2021.
When a respiratory condition is described as occurring in more than one site and is not specifically indexed, it should be?
When a respiratory condition is described as occurring in more than one site and is not specifically indexed, it should be classified to the lower anatomic site (e.g. tracheobronchitis to bronchitis in J40 ).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for hx of nicotine dependence
- 2. 2021 icd 10 code for tbi
- 3. icd 10 code for picc line dressing change
- 4. icd 10 code for high amounts of ]fibrinogen
- 5. icd 9 code for rectus diastasis
- 6. icd 10 code for chronic lv systolic dysfunction
- 7. icd 10 code for indigestin
- 8. icd 10 code for altered speech
- 9. 2015 icd 10 code for iud evaluate
- 10. icd-10 code for history of traumatic brain injury