What causes a baker cyst?
· Synovial cyst of popliteal space [Baker], right knee 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code M71.21 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M71.21 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What happens when bakers cyst ruptures?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M71.22 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Synovial cyst of popliteal space [ Baker ], left knee. Bakers cyst of left knee; Bilateral popliteal cysts; Left popliteal cyst; Synovial cyst of bilateral popliteal spaces; Synovial cyst of left popliteal space. …
Can a MRI see a baker cyst?
· 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M71.2 Synovial cyst of popliteal space [Baker] 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code M71.2 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M71.2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Does Baker's cyst cause stiffness in legs?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M71.22 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Synovial cyst of popliteal space [Baker], left knee. Bakers cyst of left knee; Bilateral popliteal cysts; Left popliteal cyst; Synovial cyst of …

What is a Baker's cyst?
A Baker's cyst can form when joint-lubricating fluid fills a cushioning pouch (bursa) at the back of your knee. A Baker's cyst is a fluid-filled cyst that causes a bulge and a feeling of tightness behind your knee. The pain can get worse when you fully flex or extend your knee or when you're active.
Is a bakers cyst synovial fluid?
Baker cyst is a buildup of joint fluid (synovial fluid) that forms a cyst behind the knee. A Baker cyst is seen as a swelling behind the knee. It forms when joint fluid collects behind the knee.
What type of cyst is a bakers cyst?
A Baker's cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst or synovial cyst, is a soft, fluid-filled lump that forms on the back of your knee. Like many diseases and disorders, this cyst is named after the doctor who first described it.
Is a bakers cyst a true cyst?
They are usually located at or below the joint line. They represent neither a true bursa nor a true cyst, as they occur as a communication between the posterior joint capsule and the gastrocnemius-semimembranosus bursa.
What is the most common cause of a Baker's cyst?
Baker's cysts typically result from a problem inside the knee joint, such as osteoarthritis or a meniscus tear. These conditions cause the joint to produce excess fluid, which can lead to the formation of a cyst.
Will a knee replacement get rid of a Baker's cyst?
The latter changes often accompany osteoarthritis, and we frequently encounter patients with Baker's cysts seeking total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Baker's cysts are not usually subject to extensive preoperative evaluation because the cysts often disappear naturally after surgery, unaccompanied by any adverse symptoms.
How is a Baker's cyst diagnosed?
A Baker's cyst can often be diagnosed with a physical exam. However, because some of the signs and symptoms of a Baker's cyst mimic those of more-serious conditions, such as a blood clot, aneurysm or tumor, your doctor may order noninvasive imaging tests, including: Ultrasound. X-ray.
What can be mistaken for a Baker's cyst?
Popliteal vein thrombosis happens when a blood clot blocks one of the blood vessels behind your knees. It's a serious condition, but it can sometimes be mistaken for a less-dangerous condition called a Baker's cyst.
Can you surgically remove a Baker's cyst?
In some cases, surgery is recommended. Baker's cyst surgery is usually performed as a minimally invasive, outpatient surgery to remove the cyst and repair the knee capsule or synovial lining. Even with surgical removal, Baker's cysts can reoccur if the underlying cause of the cyst is not controlled. Dr.
Is a Baker's cyst the same as a ganglion cyst?
Ganglion cysts are filled with gelatinous and viscous fluid in the neighbourhood of joints or tendon sheaths. They are frequently seen at joints and tendons of the wrist but are rare in the region of knee joint. The most common cysts in the knee region are popliteal also called Baker's cysts.
Is a bakers cyst medial or lateral?
A Baker cyst is seen medially (arrowhead). Transverse ultrasonographic image of the knee in a patient who had recent arthroscopy shows a complex, cystic mass (arrow) in the medial aspect of popliteal fossa. The mass communicates with the knee joint (arrowhead), which is consistent with a Baker cyst.
Is a baker's cyst medial or lateral?
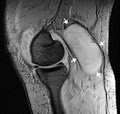
However, a Baker's cyst arises from the medial head of the gastrocnemius muscle and has no stalk-like structure connected with the joint space; hence, we ruled it out. MRI is more helpful in the diagnosis of a popliteal cystic mass.
Where is the cyst in the knee?
A synovial cyst located in the back of the knee, in the popliteal space arising from the semimembranous bursa or the knee joint.
When will the ICd 10-CM M71.2 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M71.2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are synovial cysts?
Synovial cyst of popliteal space [Baker] 1 A benign swelling found behind the knee joint 2 A synovial cyst located in the back of the knee, in the popliteal space arising from the semimembranous bursa or the knee joint.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as M71.2. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
What is the ICD code for a cyst in the right knee?
M71.21 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of synovial cyst of popliteal space [Baker], right knee. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is a popliteal cyst?
A Baker's cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a benign swelling of the semimembranosus or more rarely some other synovial bursa found behind the knee joint. It is named after the surgeon who first described it, William Morrant Baker (1838–1896).
Baker's Cyst Drainage Code 20610
In the 2013 Interventional Radiology Coding Reference on page 424, it advises: " (#10) Use code 20610 for Baker's cyst aspiration." In Dr. Z books for years past, that code has been listed as 10160. CT guidance is the primary method used at our facility (77012).
Need to ask Dr.Z?
Don't see the answer you're looking for in the knowledge base? No problem. You can ask Dr. Z directly!
What is a popliteal cyst?
In adults, a Popliteal Cyst is an extension of the Knee Joint. The cyst is a swelling/fluid collection in a bursa between the Semitendinosus and Medial Gastrocnemius Tendons deep behind the knee. For what it is worth, all humans have the potential of developing a "cyst" from this bursa. There is a connection between the joint and the bursa, ...
Is cyst fluid derived?
The fluid in the cyst is joint fluid derived, but if there long enough can become syrupy or even thicker and gelatinous. The problem is that the fluid flow is usually only one direction, from the joint into the cyst, and usually does not flow backwards from the cyst into the joint.
Can a cyst be distended?
Even if the joint inflammation resolves and excess fluid formation stops (i.e. the effusion resolves), the cyst may remain distended/full. If large and tight enough it can cause symptoms. There probably some patients that have "two way" fluid flow, but they are infrequent in my experience.
Can a cyst resolve on its own?
If that can be resolved, then the cyst may resolve on its own over time . If the joint is inflamed and has an effusion, and a cyst is also present, then aspiration and injection (steroid) of the joint may be sufficient for both. If that helps the joint but the cyst persists and is symptomatic, then aspiration (+/- steroid injection) ...
Is 20610 a correct knee joint?
So, the aspiration and injection (if done) of the cyst is in essence a treatment of the knee joint, and 20610 would be correct.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for diabetes type 1 ketoacidosis
- 2. icd 10 code for other giant cell arteritis
- 3. icd 9 code for upper lip tie
- 4. icd 10 code for skin ulcer on foot with diabetes
- 5. icd 10 code for burn by hot water
- 6. icd 9 code for weight gain unspecified
- 7. icd 10 code for lipoma
- 8. icd 10 code for superficial wound to stump
- 9. icd 10 code for infected bypass site
- 10. icd 10 code for medicare annual wellness visit subsequent