What is the ICD 10 for left shoulder lesion?
Shoulder lesion, unspecified, left shoulder. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM M75.92 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M75.92 - other international versions of ICD-10 M75.92 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for left shoulder instability?
Other instability, left shoulder. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 Billable/Specific Code. M25.312 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM M25.312 became effective on October 1, 2019.
What is a Bankart lesion on the shoulder?
A Bankart lesion is just one possible cause of shoulder pain and instability. The upper part of the glenoid labrum may be damaged, known as a SLAP tear causing pain and instability with overhead movements. You can find out more about other causes in the Common Shoulder Problems section - coming soon.
What is the CPT code for a Bankart lesion?
Repair of a Bankart lesion can be accomplished by either an open procedure or arthroscopic technique. The CPT codes are as follows; 23455 – Capsulorrhaphy, anterior; with labral repair (Bankart procedure) There are parenthetical notes under this CPT code that instruct a coder to report 29806 for the arthroscopic procedure.
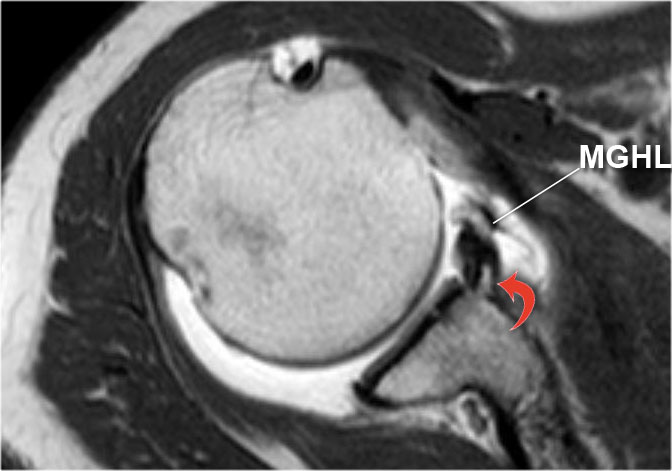
What is a Bankart lesion?
One of the most common labral injuries is known as a Bankart lesion. This condition occurs when the labrum pulls off the front of the socket. This occurs most often when the shoulder dislocates. If a Bankart tear doesn't heal properly, it can cause future dislocations, instability, weakness and pain.
What is the ICD 10 code for right shoulder Bankart lesion?
Bankart Lesion and Hill-Sachs Lesion In S43. 01_ _, Anterior Dislocation of the Shoulder, the Includes note includes "avulsion of the joint or ligament," which would best define/characterize this lesion.
What is Bankart shoulder?
A Bankart injury occurs when an initial shoulder dislocation damages the anterior glenoid labrum of the shoulder joint. The labrum is a thick band of cartilage that lines the glenoid (socket). This attaches to the bone and helps keep the ball of the humerus in place.
What is a Bankart repair of the shoulder?
A Bankart lesion is a shoulder injury that occurs due to a labrum tear causing instability and recurrent dislocations of the shoulder joint. Arthroscopic Bankart repair is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed to reattach and tighten the detached labrum within the shoulder joint.
What is the ICD 10 code for Bankart lesion?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S43. 431A became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of S43.
What is the CPT code for Bankart repair?
CPT, Current Procedural Terminology. CPT 29806 corresponded to arthroscopic stabilization; CPT 23455 to open Bankart repair; and CPT 23460, 23462 to bone block procedure.
What is the difference between Hill-Sachs and Bankart lesion?
Anterior dislocation causes a typical impression fracture on the posterior humeral head, known as a Hill–Sachs lesion. The labrum or the glenoid itself may also be damaged; these injuries are known as Bankart lesions.
What is the difference between a Bankart lesion and a SLAP tear?
A SLAP (Superior Labrum Anterior to Posterior) tear, a specific type of labral tear, involves the attachment site of the biceps tendon located at the top of the shoulder joint. A Bankart tear describes a torn labrum where the humeral head shifts toward the front of the body, as an anterior labral tear.
What is a reverse Bankart lesion?
Reverse Bankart lesion is defined as the detachment of posteroinferior labrum with avulsion of posterior capsular periosteum. This leads to laxity of the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament with posterior displacement of the humeral head.
Is a Bankart lesion a fracture?
A bony Bankart is a Bankart lesion that includes a fracture of the anterior-inferior glenoid cavity of the scapula bone.
What is posterior Bankart repair?
The posterior Bankart procedure is one where the orthopaedic surgeon repairs the torn posterior capsule by re-at- taching it to the glenoid rim. Postoperatively, the patient must be cautious with over aggressive ROM and stretching activities.
Where is a Bankart repair?
A Bankart repair is a surgical procedure to prevent recurring anterior shoulder dislocations due to instability in the back of the shoulder. The most common form of shoulder ligament injury is the Bankart lesion, where the ligaments are torn from the front of the socket.
What is Bankart lesion?
The Bankart Lesion is the tearing away of the anterior glenoid labrum and capsular tissues from the anterior boney rim/margin of the glenoid of the humerus.
What is Hill Sachs lesion?
The Hill-Sachs Lesion is an impaction/articular fracture of the humeral head, located on the back side (posterior aspect) of the humeral head; an indentation resulting from the back of the humeral head being caught, damaged by the anterior boney margin of the glenoid resulting from the dislocation. Since these are indentations, they are not usually ...
What is posterior shoulder instability?
Posterior shoulder instability may result in injury to the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament as well as the posterior labrum, or a reverse Bankart lesion. Tears can extend to involve multiple regions of the labrum and have other associated injuries.
What is the labrum?
The labrum also serves as an attachment point for the long head of the biceps tendon, the glenohumeral ligaments, and the long head of the triceps tendon, forming a periarticular system of fibers that gives the shoulder joint much needed stability .
What is the labrum of the shoulder?
The glenoid labrum is a densely fibrous tissue that is located along the periphery of the glenoid portion of the scapula. It functions to provide increased stability, while still allowing great range of motion. In addition, it serves as an attachment point for tendons and ligaments. Tears can occur in all regions of the labrum. The two most common sites include the superior labral anterior-posterior (SLAP) tear, occurring with forced traction of the shoulder and/or direct compression, and the Bankart lesion, created by episodes of anterior instability. Symptoms of deep-seated pain (SLAP tears) or anterior instability (Bankart lesions) are the most common presentations, but concomitant shoulder pathology makes diagnosis challenging and clouds many physical exam findings. Physical exam includes several clinical tests, with the O’Brien’s test being the most common for SLAP tears and the surprise test as the most accurate for Bankart lesions. As in any case of shoulder pain, the initial imaging of choice is plain radiography. With a high clinical likelihood of labral disease, this should be followed by either magnetic resonance imaging or magnetic resonance arthrography. Initial management of SLAP tears involves exhausting non-operative treatment, focusing on stretching and strengthening of the dynamic shoulder stabilizers. Initial management of Bankart lesions (after reduction) may be conservative or operative and depends on demographic and radiographic factors. Surgical management of SLAP tears are reserved for those who have failed conservative management. Operative treatment of Bankart tears are reserved for those with recurrent instability despite conservative treatment.
What is the effect of the labrum and capsule on the shoulder?
If the labrum or capsule is injured, such as in the Bankart lesion, this suction seal is lost, and this decreases the stability of the shoulder.
What happens to the labrum as it transitions from the periphery to the articulation?
As the outer labrum transitions from the periphery to its articulation with the glenoid, the histology changes from fibrous to a small fibrocartilaginous zone at the junction with the glenoid articular cartilage. The labrum increases the height and width of the glenoid while also giving extra depth to the joint.
What is the most studied injury to the labrum?
Tears can occur in all regions of the labrum. The most studied injury to the labrum is the superior labral anterior-posterior (SLAP) tear.
How to tell if a slap tear is a slap?
A patient with a SLAP tear will most commonly present with symptoms of deep-seated pain, which can be sharp or dull. It is usually located deep within the center of the shoulder and can be made worse with overhead activities, pushing heavy objects, lifting, or reaching behind the back. Patients may have mechanical symptoms, such as catching, popping, or grinding with rotation of the shoulder. One study found that in 139 patients demonstrating a SLAP lesion on shoulder arthroscopy, 123 patients (88%) also had other intra-articular lesions, making clinical diagnosis challenging.
What Next?
A Bankart lesion is just one possible cause of shoulder pain and instability. The upper part of the glenoid labrum may be damaged, known as a SLAP tear causing pain and instability with overhead movements.
What is a boney bankart?
Damage to the glenoid (the socket part) is known as a Bony Bankart. This is when there is a fracture (break) in the anteroinferior (lower front) part of the glenoid cavity, as well as a labrum tear. Bankart lesions may also be associated with fractures of the head of humerus (the ball), such as a Hill-Sachs lesion, ...
What causes Bankart lesion?
A Bankart lesion is when there is damage to the lower portion of the glenoid labrum, causing it to tear away from the bony socket. This tends to happen when the shoulder dislocates anteriorly, meaning the head of the humerus is forced forwards and pops out of the glenoid socket. As it is forced forwards, it can damage the labrum, causing it to tear.
How does Bankart repair a labral tear?
The labral tear surgery aims to repair and tighten overstretched and damaged ligaments, joint capsule and cartilage. Suture anchors are placed in the bone and the torn glenoid labrum is reattached to the glenoid fossa. You can usually go home the same day, or the following day after a Bankart repair.
What is the cartilage around the socket called?
So, around the rim of the socket is a special band of cartilage known as the glenoid labrum. This is made of fibrocartilaginous material and works to deepen the socket to improve the connection of the joint and improving stability without restricting mobility. A Bankart lesion is when there is damage to the lower portion of the glenoid labrum, ...
What is a bankart tear?
A Bankart lesion, aka glenoid labrum tear, is where there is damage to the special layer of cartilage lining the shoulder joint. A bankart tear usually occurs when the shoulder dislocates forwards and most commonly affects young athletes. Damage to the labrum makes the shoulder more prone to instability and there is a high risk ...
How long does it take for a Bankart shoulder to heal?
You will be given a rehab programme to follow, progressing to more challenging exercises over time. It usually takes around 4-6 months to recover completely from a Bankart repair and be able to return to contact sports.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 cpt code for gross examination of bone
- 2. icd 9 code for speech therapy
- 3. icd 10 code for joint pain other
- 4. icd 10 code for history of anemia
- 5. icd 10 cm code for left great toe wound
- 6. icd 10 code for aspirati
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for metastatic renal carcinoma
- 8. icd 10 cm code for chronic anemia,
- 9. icd 9 code for status post lumbar laminectomy
- 10. icd 10 code for hand stiffness