What is the ICD 10 code for left shoulder lesion?
Bankart Lesion ICD-10 Glenoid labral tear ICD-10 S43.491A Other sprain of right shoulder joint, initial encounter S43.492A Other sprain of left shoulder joint, initial encounter S43.82XA Sprain of other specified parts of left shoulder girdle, initial encounter
What is the diagnostic code for a SLAP lesion of the shoulder?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M75.92 Shoulder lesion, unspecified, left shoulder 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code M75.92 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M75.92 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for shoulder injury?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M25.312 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M25.312 Other instability, left shoulder 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code M25.312 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for Bankart tear?
Oct 01, 2021 · ICD-10-CM Code M75.92 Shoulder lesion, unspecified, left shoulder Billable Code M75.92 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Shoulder lesion, unspecified, left shoulder . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 .
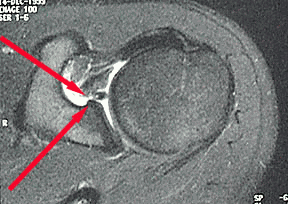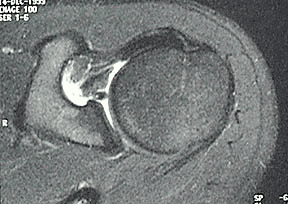
What is a Bankart lesion in shoulder?
One of the most common labral injuries is known as a Bankart lesion. This condition occurs when the labrum pulls off the front of the socket. This occurs most often when the shoulder dislocates. If a Bankart tear doesn't heal properly, it can cause future dislocations, instability, weakness and pain.
Is a Bankart lesion a fracture?
A soft tissue Bankart lesion is an anteroinferior labrum avulsion damage of the glenoid rim. The posterior capsule may be stretched and the inferior glenuhumeral ligament is torn.. A bony Bankart lesion shows besides the soft tissue damage also a fracture of the anteroinferior glenoid rim.
Why is it called a Bankart lesion?
It is an indication for surgery and often accompanied by a Hill-Sachs lesion, damage to the posterior humeral head. The Bankart lesion is named after English orthopedic surgeon Arthur Sydney Blundell Bankart (1879–1951).
What is a Bankart repair of the shoulder?
A Bankart repair is a surgical procedure to prevent recurring anterior shoulder dislocations due to instability in the back of the shoulder. The most common form of shoulder ligament injury is the Bankart lesion, where the ligaments are torn from the front of the socket.Dec 17, 2021
How is a Bankart lesion diagnosed?
A diagnosis of Bankart lesion is usually confirmed intra-operatively during shoulder arthroscopy. A prospective study by Walsworth et al. found that a history of “popping” or “catching” in combination with positive findings on physical examination were highly suggestive of a labral tear (4).Nov 22, 2016
How is a Bankart lesion repair?
Bankart Shoulder Repair Procedure To hold the tissue in place, the surgeon inserts small anchors into the bone on and stitches to suture the labrum in place. With the open shoulder stabilization procedure, the Bankart lesion is repaired and stability of the shoulder is restored.
What is the difference between Hill Sachs and Bankart lesion?
Anterior dislocation causes a typical impression fracture on the posterior humeral head, known as a Hill–Sachs lesion. The labrum or the glenoid itself may also be damaged; these injuries are known as Bankart lesions.
What is the difference between a Bankart lesion and a SLAP tear?
A SLAP (Superior Labrum Anterior to Posterior) tear, a specific type of labral tear, involves the attachment site of the biceps tendon located at the top of the shoulder joint. A Bankart tear describes a torn labrum where the humeral head shifts toward the front of the body, as an anterior labral tear.
Does a Bankart lesion require surgery?
The most frequent treatment for a Bankart lesion is orthopedic reduction of the dislocation and surgical repair, with suturing to stabilize the labrum when the extent of the tear is significant.May 17, 2019
What is the CPT code for Bankart repair?
Arthroscopic Bankart repair is reported using CPT code 29806 (Arthroscopy, shoulder, surgical; capsulorrhaphy).Feb 1, 2022
Does a Perthes lesion need surgery?
Typically, these lesions are repaired via an arthroscopic approach. During arthroscopic surgery, the Perthes lesion may appear indistin- guishable from a normal labrum and intraoperative probing of the labrum is necessary to show the labral detach- ment from the glenoid rim.
What does a Bankart lesion feel like?
A Bankart lesion is the name for a tear that happens in the lower rim of the labrum. Once the labrum is torn, it's much easier for the humerus to slip out of its socket. You may also have pain and feel as if your shoulder is slipping out of place.
What is the ICd 10 code for shoulder tendonitis?
M75.92 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of shoulder lesion, unspecified, left shoulder. The code M75.92 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code M75.92 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like bilateral tendonitis of shoulders, tendonitis of left shoulder or tendonitis of right shoulder.#N#The code is commonly used in orthopedics medical specialties to specify clinical concepts such as selected shoulder conditions.#N#Unspecified diagnosis codes like M75.92 are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition. Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition. Specific diagnosis codes should not be used if not supported by the patient's medical record.
How to diagnose shoulder pain?
Health care providers diagnose shoulder problems by using your medical history, a physical exam, and imaging tests. Often, the first treatment for shoulder problems is RICE. This stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Other treatments include exercise and medicines to reduce pain and swelling.
What are the different types of tendonitis?
The following clinical terms are approximate synonyms or lay terms that might be used to identify the correct diagnosis code: 1 Bilateral tendonitis of shoulders 2 Tendonitis of left shoulder 3 Tendonitis of right shoulder
What are the bones of the shoulder?
Your shoulder joint is composed of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone). Your shoulders are the most movable joints in your body. They can also be unstable because the ball of the upper arm is larger than the shoulder socket that holds it.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code M75.92 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
What is posterior shoulder instability?
Posterior shoulder instability may result in injury to the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament as well as the posterior labrum, or a reverse Bankart lesion. Tears can extend to involve multiple regions of the labrum and have other associated injuries.
What is the labrum of the shoulder?
The glenoid labrum is a densely fibrous tissue that is located along the periphery of the glenoid portion of the scapula. It functions to provide increased stability, while still allowing great range of motion. In addition, it serves as an attachment point for tendons and ligaments. Tears can occur in all regions of the labrum. The two most common sites include the superior labral anterior-posterior (SLAP) tear, occurring with forced traction of the shoulder and/or direct compression, and the Bankart lesion, created by episodes of anterior instability. Symptoms of deep-seated pain (SLAP tears) or anterior instability (Bankart lesions) are the most common presentations, but concomitant shoulder pathology makes diagnosis challenging and clouds many physical exam findings. Physical exam includes several clinical tests, with the O’Brien’s test being the most common for SLAP tears and the surprise test as the most accurate for Bankart lesions. As in any case of shoulder pain, the initial imaging of choice is plain radiography. With a high clinical likelihood of labral disease, this should be followed by either magnetic resonance imaging or magnetic resonance arthrography. Initial management of SLAP tears involves exhausting non-operative treatment, focusing on stretching and strengthening of the dynamic shoulder stabilizers. Initial management of Bankart lesions (after reduction) may be conservative or operative and depends on demographic and radiographic factors. Surgical management of SLAP tears are reserved for those who have failed conservative management. Operative treatment of Bankart tears are reserved for those with recurrent instability despite conservative treatment.
How to tell if a slap tear is a slap?
A patient with a SLAP tear will most commonly present with symptoms of deep-seated pain, which can be sharp or dull. It is usually located deep within the center of the shoulder and can be made worse with overhead activities, pushing heavy objects, lifting, or reaching behind the back. Patients may have mechanical symptoms, such as catching, popping, or grinding with rotation of the shoulder. One study found that in 139 patients demonstrating a SLAP lesion on shoulder arthroscopy, 123 patients (88%) also had other intra-articular lesions, making clinical diagnosis challenging.
Where do biceps tendons come from?
Approximately 40% to 60% of biceps tendons originate from the supraglenoid tubercle, and the remaining fibers insert into the labrum. The biceps insertion into the labrum is variable, but most commonly is in a more posterior position. Normal anatomy of the shoulder. Tears can occur in all regions of the labrum.
What imaging is used for shoulder pain?
As in any case of shoulder pain, the initial imaging of choice is plain radiography. With a high clinical likelihood of labral disease, this should be followed by either magnetic resonance imaging or magnetic resonance arthrography.
What is the labrum?
The labrum also serves as an attachment point for the long head of the biceps tendon, the glenohumeral ligaments, and the long head of the triceps tendon, forming a periarticular system of fibers that gives the shoulder joint much needed stability .
What is SLAP tear?
The most studied injury to the labrum is the superior labral anterior-posterior (SLAP) tear. Anterior dislocations of the shoulder can be associated with a disruption of the anteroinferior labrum and anterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament, also known as a Bankart lesion.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for pelvic pressure
- 2. icd 10 code for ng tube placement
- 3. what icd 10 code to use for ckd stage 3-4
- 4. icd 10 code for heterozygous factor v leiden mutation
- 5. icd 10 code for left weakness
- 6. icd 10 code for abnormal protein in blood
- 7. icd 10 code for screening celiac artery stenosis
- 8. icd 10 code for right sided colitis
- 9. icd 10 code for prostate pain
- 10. what is the icd 10 code for elevated heart pressures