Superior glenoid labrum lesion of right shoulder, initial encounter. S43.431A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM S43.431A became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the CPT code for a Bankart lesion?
Repair of a Bankart lesion can be accomplished by either an open procedure or arthroscopic technique. The CPT codes are as follows; 23455 – Capsulorrhaphy, anterior; with labral repair (Bankart procedure) There are parenthetical notes under this CPT code that instruct a coder to report 29806 for the arthroscopic procedure.
What is Bankart lesion and Hill Sachs lesion?
Bankart Lesion and Hill-Sachs Lesion Both of these are elements/consequences of an anterior shoulder dislocation. The Bankart Lesion is the tearing away of the anterior glenoid labrum and capsular tissues from the anterior boney rim/margin of the glenoid of the humerus.
What are the symptoms of a Bankart lesion?
Typical symptoms of a Bankart lesion include joint instability or repeat dislocations with a popping sound and/or mechanical catching within the joint. Repair of a Bankart lesion can be accomplished by either an open procedure or arthroscopic technique.
What is a Bankart lesion of the shoulder?
One type of labral tear is known as a Bankart lesion. Within the shoulder capsule there are a number of ligaments that act as restraints, reinforcing the shoulder joint holding the humeral head in the glenolabral cup or socket. At the front lower portion of the shoulder (anteroinferior) - you will find the inferior glenohumeral ligament.
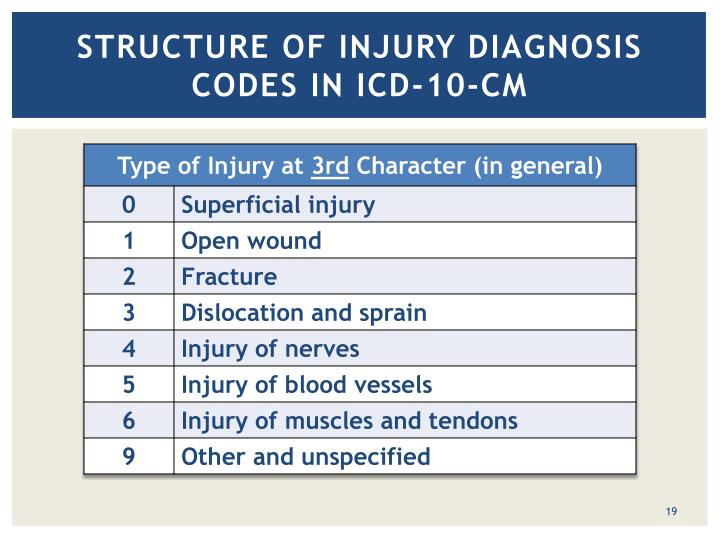
What is Bankart lesion?
A glenoid labrum tear in the anterior joint is called a Bankart lesion. When the labrum is torn, the shoulder joint is less stable, and allows the humeral head to move around more than normal. Posterior dislocation (when the arm is forced backwards) can also lead to a tear in the labrum, though less commonly.
What is the ICD 10 code for Hill Sachs lesion of right shoulder?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S42. 29 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is a Bankart lesion a fracture?
A bony Bankart is a Bankart lesion that includes a fracture of the anterior-inferior glenoid cavity of the scapula bone.
What is a Bankart repair of the shoulder?
A Bankart lesion is a shoulder injury that occurs due to a labrum tear causing instability and recurrent dislocations of the shoulder joint. Arthroscopic Bankart repair is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed to reattach and tighten the detached labrum within the shoulder joint.
What is the ICD 10 code for right shoulder Bankart lesion?
Bankart Lesion and Hill-Sachs Lesion In S43. 01_ _, Anterior Dislocation of the Shoulder, the Includes note includes "avulsion of the joint or ligament," which would best define/characterize this lesion.
Is Hill-Sachs or Bankart more common?
Bankart lesions are up to 11x more common in patients with a Hill-Sachs lesion, with increasing incidence with increasing size 8.
What is the difference between Hill-Sachs and Bankart lesion?
Anterior dislocation causes a typical impression fracture on the posterior humeral head, known as a Hill–Sachs lesion. The labrum or the glenoid itself may also be damaged; these injuries are known as Bankart lesions.
What is the difference between a Bankart lesion and a SLAP tear?
A SLAP (Superior Labrum Anterior to Posterior) tear, a specific type of labral tear, involves the attachment site of the biceps tendon located at the top of the shoulder joint. A Bankart tear describes a torn labrum where the humeral head shifts toward the front of the body, as an anterior labral tear.
What is a reverse Bankart lesion?
Reverse Bankart lesion is defined as the detachment of posteroinferior labrum with avulsion of posterior capsular periosteum. This leads to laxity of the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament with posterior displacement of the humeral head.
What is the CPT code for Bankart repair?
CPT, Current Procedural Terminology. CPT 29806 corresponded to arthroscopic stabilization; CPT 23455 to open Bankart repair; and CPT 23460, 23462 to bone block procedure.
What is posterior Bankart repair?
The posterior Bankart procedure is one where the orthopaedic surgeon repairs the torn posterior capsule by re-at- taching it to the glenoid rim. Postoperatively, the patient must be cautious with over aggressive ROM and stretching activities.
Where is a Bankart repair?
A Bankart repair is a surgical procedure to prevent recurring anterior shoulder dislocations due to instability in the back of the shoulder. The most common form of shoulder ligament injury is the Bankart lesion, where the ligaments are torn from the front of the socket.
What is Bankart lesion?
The Bankart Lesion is the tearing away of the anterior glenoid labrum and capsular tissues from the anterior boney rim/margin of the glenoid of the humerus.
What is Hill Sachs lesion?
The Hill-Sachs Lesion is an impaction/articular fracture of the humeral head, located on the back side (posterior aspect) of the humeral head; an indentation resulting from the back of the humeral head being caught, damaged by the anterior boney margin of the glenoid resulting from the dislocation. Since these are indentations, they are not usually ...
Abstract
The glenoid labrum is a densely fibrous tissue that is located along the periphery of the glenoid portion of the scapula. It functions to provide increased stability, while still allowing great range of motion. In addition, it serves as an attachment point for tendons and ligaments. Tears can occur in all regions of the labrum.
Definition
The glenoid labrum is a densely fibrous tissue that is located along the periphery of the glenoid portion of the scapula ( Fig. 15.1 ). As the outer labrum transitions from the periphery to its articulation with the glenoid, the histology changes from fibrous to a small fibrocartilaginous zone at the junction with the glenoid articular cartilage.
Superior Labral Anterior-Posterior Tear
A patient with a SLAP tear will most commonly present with symptoms of deep-seated pain, which can be sharp or dull. It is usually located deep within the center of the shoulder and can be made worse with overhead activities, pushing heavy objects, lifting, or reaching behind the back.
Bankart Lesion
Symptoms of anterior instability are usually obvious, as the patient states that there has been a dislocation and continues to complain of pain or instability in that shoulder. Sometimes there is not a history of overt dislocation, but instead the patient has multiple episodes of instability without a complete dislocation.
Superior Labral Anterior-Posterior Tear
Several clinical tests are designed to assist the clinician in making the SLAP tear diagnosis. These tests aim to do one of two things: to pinch the torn labrum between the humeral head and the glenoid, causing pain or mechanical symptoms, or to place traction on the biceps tendon ( Table 15.1 ).
Bankart Lesion
Evaluation for anterior instability may include a number of tests ( Table 15.2 ). After reduction of a dislocation, a thorough neurovascular examination should be performed to rule out major vessel or brachial plexus injury.
Abstract
Shoulder instability is a common problem that involves excessive translation of the humerus over the glenoid surface, which is normally prevented by both static and dynamic stabilizers. Significant trauma or external rotation with abduction, such as in overhead throwing athletes, can cause instability, subluxation, or dislocation.
Physical Examination
The physical examination should include inspection for any swelling or malformations, palpation for tenderness and regions of anesthesia in the axillary nerve distribution, active and passive range of motion, strength, and neurovascular testing, as well as specific tests to assess for instability.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for difficulty speaking
- 2. icd 10 code for uncontrolled malignant hypertension
- 3. icd-10 code for nail bed tumor
- 4. icd 10 cpt code for clearing obstuction in brain
- 5. icd 10 code for infection to incision
- 6. icd 10 code for lumbar microdiscectomy
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for alcohol intoxication
- 8. icd 10 code for congestive heart fiulure
- 9. icd 10 code for bacterial skin eruption right lower extremity
- 10. icd 9 code for falling while roller blading?