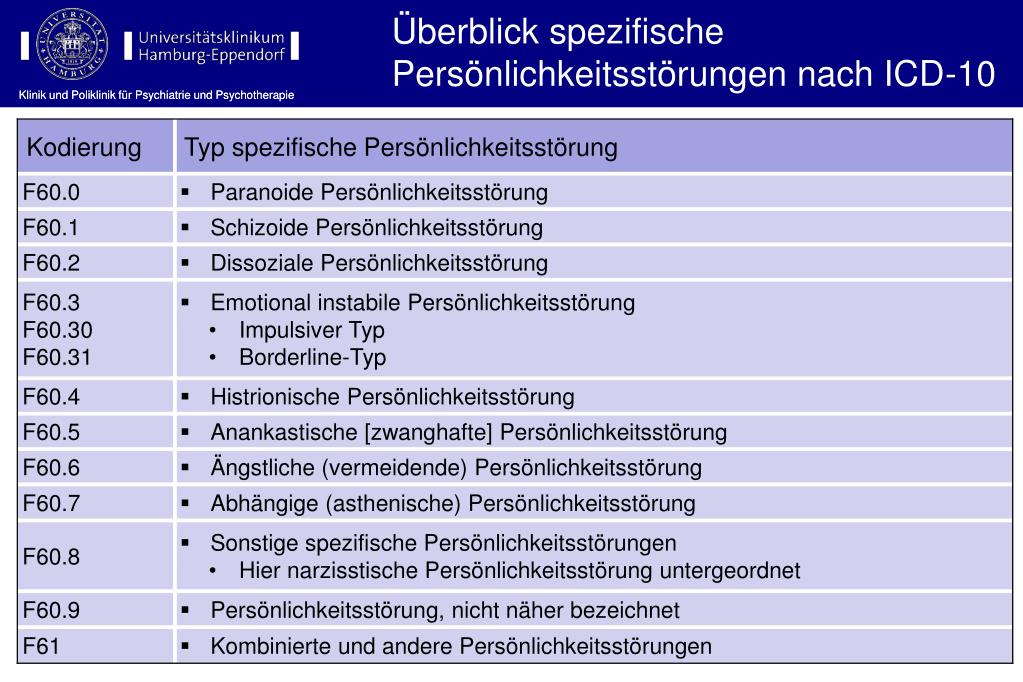
What would the Diagnostic Code be for Barretts esophagus?
Barrett's esophagus with low grade dysplasia. K22.710 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM K22.710 became effective on October 1, 2020.
Does Barretts esophagus ever heal?
With medications called proton pump inhibitors, which reduce acid production in the stomach so there's less acid rising into the esophagus For some people, Barrett's esophagus can heal, per Cedars Sinai, though it's typically a permanent condition.
Does Barretts esophagus go away?
This may occur up to 20% of the time in people with small segments of Barrett’s mucosa. There is still some controversy, as some physicians believe that Barrett’s esophagus can regress, or disappear. However, the above explanation seems much more plausible. The bottom line is that you have Barrett’s esophagus. The most recent biopsies were fine.
How to treat Barrett esophagus?
Treatments for Barrett's Esophagus
- Lifestyle Modifications. Your daily habits can impact your symptoms when you have Barrett's esophagus. ...
- Over-the-Counter Therapies and Prescriptions. Currently, there are no medications that will cure or reverse Barrett's esophagus. ...
- Surgery and Specialist-Driven Procedures. ...

What is the ICD 9 code for Barrett's esophagus?
530.2Barrett's esophagus is a chronic complication associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease. The ICD-9-CM code used for Barrett's esophagus, 530.2, is also used for patients with “ulcer of the esophagus.”
What is the ICD-10 code for Barrett's esophagus with high grade dysplasia?
K22. 711 - Barrett's esophagus with high grade dysplasia | ICD-10-CM.
What is Barrett's oesophagus?
Barrett's oesophagus is a medical condition where some of the cells in your oesophagus grow abnormally. If you have Barrett's oesophagus you are slightly more likely to get oesophageal cancer. But this is not common. It is sometimes called a pre-cancerous condition.
Is Barrett's mucosa the same as Barrett's esophagus?
When the lining of the esophagus changes from its normal lining (squamous cells) to goblet cells and absorptive columnar cells that are usually found in the intestines, we call this Barrett's esophagus or Barrett's mucosa.
What is the correct code for Barrett's esophagus with low grade dysplasia?
K22. 710 - Barrett's esophagus with low grade dysplasia | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for Barrett's esophagus without dysplasia?
ICD-10 code K22. 70 for Barrett's esophagus without dysplasia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is Barrett's disease caused from?
The development of Barrett's esophagus is most often attributed to long-standing GERD , which may include these signs and symptoms: Frequent heartburn and regurgitation of stomach contents. Difficulty swallowing food.
How is Barrett's esophagus diagnosed?
How do doctors diagnose Barrett's esophagus? Doctors diagnose Barrett's esophagus with an upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy and a biopsy. Doctors may diagnose Barrett's esophagus while performing tests to find the cause of a patient's gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) symptoms.
What are the symptoms of Barrett's oesophagus?
The main symptom of Barrett's Oesophagus is reflux, which can cause heartburn, regurgitation of food (bringing food back up), nausea and pain in the upper abdomen.
Is an irregular Z line the same as Barrett's esophagus?
Background & aims: Many patients with a < 1 cm segment of columnar metaplasia in the distal esophagus, also called an irregular Z line, are encountered. These patients, often referred to as patients with Barrett's esophagus (BE), are enrolled in surveillance programs.
What are the stages of Barrett's esophagus?
The stages of Barrett's esophagus are:non-dysplastic (no cancerous tissue present)low-grade dysplasia (minor cell changes found)high-grade dysplasia (extensive cell changes found, but not yet cancer)noninvasive cancer.invasive cancer.
Where is Barrett's esophagus located?
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the lining of the esophagus changes, becoming more like the lining of the small intestine rather than the esophagus. This occurs in the area where the esophagus is joined to the stomach. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD).
Is Barrett's esophagus a serious condition?
Barrett's esophagus is a potentially serious complication of GERD, which stands for gastroesophageal reflux disease. In Barrett's esophagus, normal tissue lining the esophagus -- the tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach -- changes to tissue that resembles the lining of the intestine.
Can Barrett's esophagus be cured?
There is no cure for Barrett's esophagus. Your care plan will try to stop any more damage by keeping acid reflux out of your esophagus.
What foods should you avoid if you have Barrett's esophagus?
Here are some common foods to limit or avoid if you have acid reflux or Barrett's esophagus:alcohol.coffee.tea.milk and dairy.chocolate.peppermint.tomatoes, tomato sauce, and ketchup.french fries.More items...
What is the best treatment for Barrett's esophagus?
Preferred treatments include: Endoscopic resection, which uses an endoscope to remove damaged cells to aid in the detection of dysplasia and cancer. Radiofrequency ablation, which uses heat to remove abnormal esophagus tissue. Radiofrequency ablation may be recommended after endoscopic resection.
What is Barrett's columnar epithelium?
Barrett's columnar epithelium is a marker for severe reflux and precursor to adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Esophageal lesion lined with columnar metaplastic epithelium which is flat or villiform. Barrett epithelium is characterized by two different types of cells: goblet cells and columnar cells. The symptomatology of barrett esophagus is that ...
What is the term for a condition where the lining of the lower esophagus is damaged?
A condition with damage to the lining of the lower esophagus resulting from chronic acid reflux (esophagitis, reflux). Through the process of metaplasia, the squamous cells are replaced by a columnar epithelium with cells resembling those of the intestine or the salmon-pink mucosa of the stomach.
What is the name of the condition where the cells in the lower part of the esophagus have changed
malignant neoplasm of esophagus ( C15.-) A condition in which the cells lining the lower part of the esophagus have changed or been replaced with abnormal cells that could lead to cancer of the esophagus. The backing up of stomach contents (reflux) may irritate the esophagus and, over time, cause barrett's esophagus.
What is a varices esophageal?
esophageal varices ( I85.-) malignant neoplasm of esophagus ( C15.-) A condition in which the cells lining the lower part of the esophagus have changed or been replaced with abnormal cells that could lead to cancer of the esophagus.
What is hiatus hernia?
hiatus hernia ( K44.-) esophageal varices ( I85.-) malignant neoplasm of esophagus ( C15.-) A condition in which the cells lining the lower part of the esophagus have changed or been replaced with abnormal cells that could lead to cancer of the esophagus.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for undiagnosed attention deficit disorder
- 2. icd 10 code for anaphylaxis to fire ants
- 3. icd 10 cm code for uncontrolled diabetes with diabetic cataracts
- 4. icd 10 code for sacroiliac joint dysfunction of right side
- 5. icd 10 code for cesarean scar ectopic pregnancy
- 6. icd 10 code for cutaneous hypersensitivity
- 7. icd 10 cm code for chronic back pain, lumbosacral region
- 8. icd 9 code for acetabular fracture
- 9. icd-10 code for intracranial hemorrage
- 10. icd 10 code for lymphedema ble