What is the ICD 10 code for adenomatous polyp?
ICD-10-CM Code for Polyp of colon K63. 5.
What are adenomatous polyps?
Adenomatous polyps are a common type. They are gland-like growths that develop on the mucous membrane that lines the large intestine. They are also called adenomas and are most often one of the following: Tubular polyp, which protrudes out in the lumen (open space) of the colon.
What is the ICD 10 code for adenoma?
Benign neoplasm of pituitary gland The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D35. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for familial adenomatous polyposis?
Without colectomy, the risk of colorectal carcinoma is almost 100%. The Tenth and Eleventh edition of the ICD-10-AM, ACHI and ACS have been reviewed. familial adenomatous (M8220/0) (see also Polyposis/colon) D12.
What is adenomatous tissue?
An adenoma is a polyp made up of tissue that looks much like the normal lining of your colon, although it is different in several important ways when it is looked at under the microscope. In some cases, a cancer can start in the adenoma.
What does adenomatous mean?
(A-deh-NOH-muh) A tumor that is not cancer. It starts in gland-like cells of the epithelial tissue (thin layer of tissue that covers organs, glands, and other structures within the body).
Are adenomas always benign?
Adenomas are generally benign or non cancerous but carry the potential to become adenocarcinomas which are malignant or cancerous. As benign growths they can grow in size to press upon the surrounding vital structures and leading to severe consequences.
What is diagnosis code d35 2?
2: Benign neoplasm: Pituitary gland.
What is benign neoplasm of colon unspecified?
Benign neoplasm of colon, rectum, anus and anal canal A non-metastasizing neoplasm arising from the wall of the colon and rectum. A non-metastasizing neoplasm arising from the wall of the colon.
What is the CPT code for familial adenomatous polyposis?
Group 1CodeDescription81203APC (ADENOMATOUS POLYPOSIS COLI) (EG, FAMILIAL ADENOMATOSIS POLYPOSIS [FAP], ATTENUATED FAP) GENE ANALYSIS; DUPLICATION/DELETION VARIANTS81479UNLISTED MOLECULAR PATHOLOGY PROCEDURE2 more rows
What does benign sessile polyp mean?
Sessile polyps are often precancerous , meaning that cancer can develop in them, but they can also be benign or cancerous. Doctors may find them during a colonoscopy and will often remove them to prevent the risk of cancer developing. Polyps can also be peduncled.
What is the ICD-10 code for History of polypectomy?
Z86. 010 - Personal history of colonic polyps | ICD-10-CM.
How serious are adenomatous polyps?
Adenomatous polyps (adenomas) of the colon and rectum are benign (noncancerous) growths, but may be precursor lesions to colorectal cancer. Polyps greater than one centimeter in diameter are associated with a greater risk of cancer. If polyps are not removed, they continue to grow and can become cancerous.
What percent of adenomatous polyps become cancerous?
Doctors generally remove them anyway, just to be safe. Adenomas: Many colon polyps are the precancerous type, called adenomas. It can take seven to 10 or more years for an adenoma to evolve into cancer—if it ever does. Overall, only 5% of adenomas progress to cancer, but your individual risk is hard to predict.
What can cause adenomatous polyps?
Familial adenomatous polyposis is caused by a defect in a gene that's usually inherited from a parent. But some people develop the abnormal gene that causes the condition.
How serious is an adenoma?
These small clumps of cells that form on your colon lining are usually harmless. But some of them can lead to colon cancer. The most common types of colon polyps doctors remove are a type called tubular adenoma. It can become cancerous, and that danger goes up the bigger the polyps get.
What is a malignant neoplasm?
A non-metastasizing neoplasm arising from the wall of the colon and rectum . A non-metastasizing neoplasm arising from the wall of the colon.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as D12.6. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What does type 1 excludes mean?
Type 1 Excludes Help. A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here ". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as D13.1.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
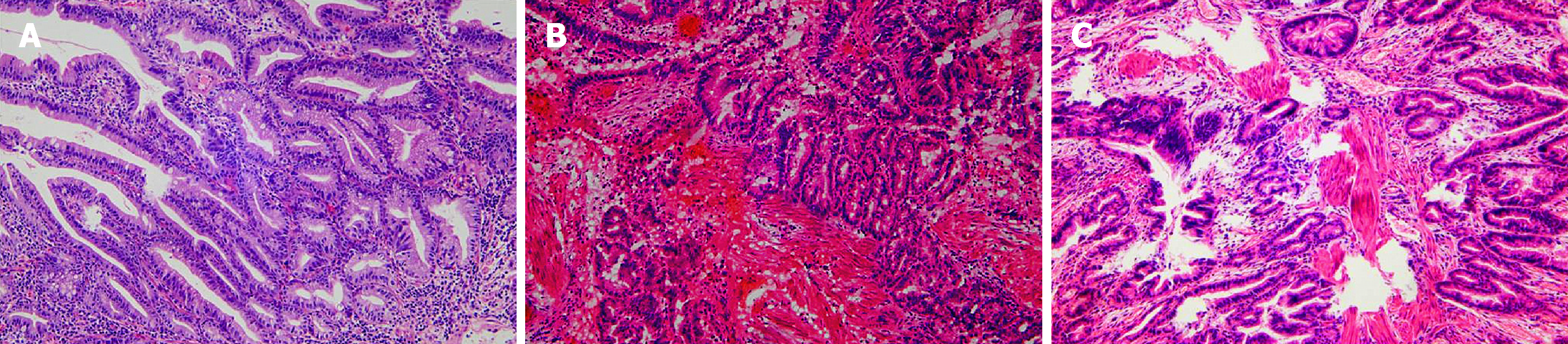
What is an adenomatous colon polyp?
Adenomatous colon polyps are considered to be precursor lesions of colon cancer. An extra piece of tissue that grows in the large intestine, or colon. Discrete tissue masses that protrude into the lumen of the colon. These polyps are connected to the wall of the colon either by a stalk, pedunculus, or by a broad base.
What is a polypoid lesion?
A polypoid lesion that arises from the colon and protrudes into the lumen. This group includes adenomatous polyps, serrated polyps, and hamartomatous polyps. Abnormal growths of tissue in the lining of the bowel. Polyps are a risk factor for colon cancer.
What is a mass of tissue that bulges or projects into the lumen of the colon?
This is a descriptive term referring of a mass of tissue that bulges or projects into the lumen of the colon. The mass is macroscopically visible and may either have a broad base attachment to the colon wall, or be on a pedunculated stalk. These may be benign or malignant.
What does "type 1 excludes note" mean?
A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. adenomatous polyp of colon (.
Can colon polyps cause diarrhea?
most colon polyps do not cause symptoms. If you have symptoms, they may include blood on your underwear or on toilet paper after a bowel movement, blood in your stool, or constipation or diarrhea lasting more than a week. nih: national institute of diabetes and digestive diseases.
Is a polyp of the intestine dangerous?
Polyp colon, hyperplastic. Polyp of intestine. Clinical Information. A polyp is an extra piece of tissue that grows inside your body. Colonic polyps grow in the large intestine, or colon. Most polyps are not dangerous . However, some polyps may turn into cancer or already be cancer.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is a malignant neoplasm?
Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site mentioned, e.g., ectopic pancreatic malignant neoplasms are coded to pancreas, unspecified ( C25.9 ). A benign abnormal growth of the cells that comprise the bladder.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is the ICd 10 code for benign neoplasm of appendix?
Benign neoplasm of appendix 1 D12.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM D12.1 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D12.1 - other international versions of ICD-10 D12.1 may differ.
What is a malignant neoplasm?
A non-metastasizing neoplasm arising from the appendix.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as D12.1. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is functional activity?
Functional activity. All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology]
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for mva driver loss of control
- 2. icd 10 code for acute otitis media left ear
- 3. what is the icd 10 code for amenorrhea
- 4. icd 10 code for robotic port placement
- 5. icd 10 code for chronic uveitis
- 6. icd 10 code for displaced distal phalanx right thumb initial
- 7. icd 9 code for disorientation
- 8. icd 10 code for helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis
- 9. icd 10 code for abdominal pain right side
- 10. icd code for uti symptoms