How do you fix benign proliferative endometrium?
What is a Proliferative Endometrium?
- Definition. A proliferative endometrium is a normal part of healthy uterine function when it occurs during the first half of the menstrual cycle.
- Disordered Proliferation. ...
- Associated Conditions. ...
- Common Symptoms. ...
- Diagnosis by Ultrasound. ...
- Endometrial Biopsy. ...
- Common Causes. ...
- Treatment Options. ...
- Surgical Treatment. ...
- Self-Help Measures. ...
What causes non secretory endometrium?
Inherent Defect of the Endometrium Causes Implantation Failure in Assisted Reproductive Technique
- Abstract. Introduction: Implantation failure appears to be a significant factor in Assisted reproductive technique (ART) procedures.
- Keywords
- Introduction. ...
- Material and Method. ...
- Ethical Consideration. ...
- Statistical Analysis. ...
- Results. ...
- Discussion. ...
- Conclusion. ...
- Acknowledgements. ...
What is benign endometrium?
Benign neoplasm of endometrium (Concept Id: C0686239) A neoplastic endometrial proliferation that is confined to the endometrium and does not have metastatic potential. Benign neoplasm of endometrium MedGen UID:
What is the meaning of secretory endometrium?
secretory refers to endometrium in the second half of the cycle (shedding phase). so, it basically means you have endometrium that is reacting to estrogen is some fashion. you should probably have a trial of provera 10mg for 10 days to see if you have a withdrawal bleed.

What is the ICD 10 code for secretory endometrium?
Endometrial hyperplasia, unspecified N85. 00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N85. 00 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is secretory endometrium?
After ovulation occurs, the endometrium enters the luteal or secretory phase, which means that the lining has undergone a series of changes which will prepare it for a possible pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, the thickened endometrium will be shed during menstruation.
What does benign endometrium mean?
Overgrowth of cells in the lining of the uterus (endometrium) leads to the formation of uterine polyps, also known as endometrial polyps. These polyps are usually noncancerous (benign), although some can be cancerous or can eventually turn into cancer (precancerous polyps).
What is benign proliferative endometrium?
Proliferative endometrium isn't a symptom or condition. The term describes healthy reproductive cell activity. It refers to the time during your menstrual cycle when a layer of endometrial cells is prepared for attachment of a fertilized egg.
What is secretory phase of the uterus?
The secretory phase of the uterine cycle is the stage in which glycogen is secreted from the endometrium. These substances are secreted by endometrial glands that reside within the endometrium. The endometrium lines the uterus and goes through several changes depending on the state of fertilization.
What does the secretory phase mean?
Definitions of secretory phase. the second half of the menstrual cycle after ovulation; the corpus luteum secretes progesterone which prepares the endometrium for the implantation of an embryo; if fertilization does not occur then menstrual flow begins. synonyms: luteal phase.
What is Dyssynchronous secretory endometrium?
Disordered or dyssynchronous endometrium suggests ovulatory dysfunction. A result of disordered or crowded glands is common with anovulatory cycles due to prolonged estrogen stimulation without postovulatory progesterone exposure.
Can thickened endometrium be benign?
A benign endometrial appearance was defined as an endometrial thickness of less than 4 mm, the presence of a smoothly echogenic mass in the endometrial lumen or a diffusely thickened endometrium of greater than 4 mm.
What is the medical term for benign tumors that grow in the uterine wall?
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths of the uterus that often appear during childbearing years. Also called leiomyomas (lie-o-my-O-muhs) or myomas, uterine fibroids aren't associated with an increased risk of uterine cancer and almost never develop into cancer.
Is proliferative endometrium the same as endometrial hyperplasia?
"Disordered proliferative endometrium" is a somewhat vague term that generally indicates the unusual growth of endometrial cells. The term can refer to a form of simple endometrial hyperplasia — or the abnormal thickening of the endometrial lining — but it can indicate a more serious problem in some cases.
Is proliferative endometrium cancerous?
Background: Proliferative endometrium has been reported in 15% of endometrial biopsies of women aged 50 years and older. Contrary to endometrial hyperplasia, proliferative endometrium has not been associated with the risk of endometrial cancer.
What is inactive endometrium mean?
Atrophic and inactive endometria are defined as those deprived of functionalis and consisting exclusively of thin basalis with a few narrow tubular glands lined by cuboidal indeterminate epithelium showing neither proliferative nor secretary activity (Fig. 1).
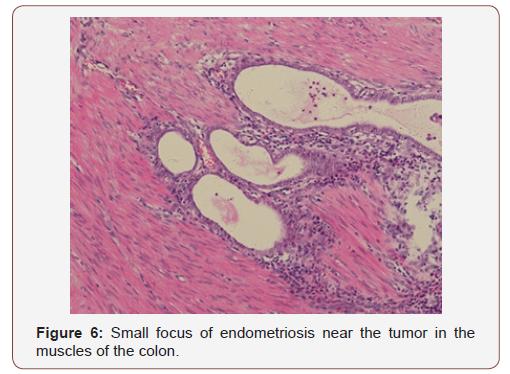
What is a benign condition in which tissue that looks like endometrial tissue grows in abnormal places in the abdomen
A benign condition in which tissue that looks like endometrial tissue grows in abnormal places in the abdomen. A condition in which functional endometrial tissue is present outside the uterus. It is often confined to the pelvis involving the ovary, the ligaments, cul-de-sac, and the uterovesical peritoneum.
Where does endometriosis grow?
It can grow on the ovaries, behind the uterus or on the bowels or bladder. Rarely, it grows in other parts of the body. This "misplaced" tissue can cause pain, infertility, and very heavy periods.
What is benign proliferation of the endometrium in the uterus?
Benign proliferation of the endometrium in the uterus. Endometrial hyperplasia is classified by its cytology and glandular tissue. There are simple, complex (adenomatous without atypia), and atypical hyperplasia representing also the ascending risk of becoming malignant.
How many types of endometrial hyperplasia are there?
There are four types of endometrial hyperplasia: simple endometrial hyperplasia, complex endometrial hyperplasia, simple endometrial hyperplasia with atypia, and complex endometrial hyperplasia with atypia. These differ in terms of how abnormal the cells are and how likely it is that the condition will become cancer.
What is the ICd 10 code for benign endometrial hyperplasia?
N85.01 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Benign endometrial hyperplasia . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also: Hyperplasia, hyperplastic.
The ICD code N850 is used to code Endometrial hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition of excessive proliferation of the cells of the endometrium, or inner lining of the uterus.
Coding Notes for N85.01 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #742-743 - Uterine and adnexa procedure for non-malignancy with CC or MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'N85.01 - Benign endometrial hyperplasia'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code N85.01. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
What is secretory endometrium?
Quick facts: Secretory endometrium means that the cells on the inside of the uterus are producing substances necessary to support implantation of an egg should conception occur. Secretory endometrium is a normal part of the menstrual cycle.
What does it mean when a pathologist sees secretory endometrium?
The diagnosis of secretory endometrium means that your pathologist saw specific features including an increased amount of tissue, twisted glands, and secretions when your tissue sample was examined under the microscope.
What is the term for the period when the endometrium grows?
This is also known as proliferative endometrium.
What are the layers of the uterus?
The walls of the uterus are made up of three layers: Endometrium – The endometrium forms the inner lining of the uterus. The endometrium is made up of endometrial glands lined by one layer of columnar epithelium and surrounded by endometrial stroma. Myometrium – The myometrium is the middle layer and is made up of smooth muscle which allows ...
What happens to the endometrium after ovulation?
After ovulation, the endometrium grows under the influence of progesterone. During this phase, the endometrial glands become long and twisted, and the secretion starts. Pathologists call this phase the secretory endometrium.
What is the upper part of the uterus?
The upper part of the uterus, the fundus, is attached to the fallopian tubes while the lower part is connected to the vagina through the uterine cervix. Functions of the uterus include nurturing the baby, and holding it until the baby is mature enough for birth.
Which layer of the uterus is made up of smooth muscle?
Myometrium – The myometrium is the middle layer and is made up of smooth muscle which allows the uterus to change size and contract. Perimetrium– The perimetrium is a thin layer of tissue that surrounds the outside of the uterus.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for thigh mass
- 2. icd 10 code for weight check in infant
- 3. icd 10 code for insect bite left knee
- 4. icd 10 code for gastroitrologist
- 5. what is the icd 10 code for peripheral artery disease of the superficial femoral artery
- 6. icd 10 code for alzheimer's unspecified
- 7. icd 10 code for bilateral hand
- 8. icd-10 code for carotid stenosis
- 9. icd 10 code for stomal scar
- 10. icd 10 code for severe persistent asthma with acute exacerbation