Acquired clubfoot, unspecified foot. M21.549 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM M21.549 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for clubfoot?
Acquired clubfoot, unspecified foot. M21.549 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM M21.549 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for unspecified foot?
Acquired clubfoot, unspecified foot 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code M21.549 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM M21.549 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICD 10 code for urethral fibrillation?
Q66.89 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM Q66.89 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Q66.89 - other international versions of ICD-10 Q66.89 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for reduction defects of feet?
Q66.89 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM Q66.89 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Q66.89 - other international versions of ICD-10 Q66.89 may differ. reduction defects of feet ( Q72.-)
What is the ICD-10 code for congenital clubfoot?
Q66.0ICD-10-CM Code for Congenital talipes equinovarus Q66. 0.
What is the ICD-10 code for bilateral flat feet?
M21. 4 - Flat foot [pes planus] (acquired) | ICD-10-CM.
What is diagnosis code Z98 890?
ICD-10 code Z98. 890 for Other specified postprocedural states is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the medical term for clubfoot?
Club foot (also called talipes) is where a baby is born with a foot or feet that turn in and under. Early treatment should correct it.
What is Z51 12?
ICD-10 code Z51. 12 for Encounter for antineoplastic immunotherapy is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the ICD-10 code for leg length discrepancy?
769: Unequal limb length (acquired), unspecified tibia and fibula.
Is Z98 890 billable?
Z98. 890 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z98. 890 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for orthopedic aftercare?
Z47.89ICD-10-CM Code for Encounter for other orthopedic aftercare Z47. 89.
What is the ICD-10 code for other specified Postprocedural States?
Z98.890Z98. 890 Other specified postprocedural states - ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes.
How common is bilateral clubfoot?
About one to four of every 1,000 babies are born with clubfoot. The condition affects boys twice as often as it does girls. About 50 percent of children with clubfoot have it in both feet, a condition known as bilateral clubfoot.
Is club foot the same as pigeon toed?
Club foot is different than pigeon toes (also called intoeing). Intoeing is very common and can be caused by a twist in the feet, calves, or hips. Most of the time, intoeing corrects itself without treatment.
Are there different types of clubfoot?
The most common congenital deformity of feet is TEV; however, there are other forms of clubfoot, specifically talipes calcaneovalgus (in which the ankle joint is dorsiflexed and the forefoot deviated outwards), and talipes calcaneovarus (in which the ankle joint is dorsiflexed and the forefoot deviated inwards).
What is the ICD-10 code for Status post cervical fusion?
ICD-10 code M43. 22 for Fusion of spine, cervical region is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Dorsopathies .
What is the ICD-10 code for pain in left ankle?
ICD-10 code M25. 572 for Pain in left ankle and joints of left foot is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Arthropathies .
What is the ICD-10 code for History of craniotomy?
011.
What is the ICD-10 code for hernia?
9 Unspecified abdominal hernia without obstruction or gangrene.
What is a deformed foot?
A deformed foot in which the foot is plantarflexed, inverted and adducted. A deformity of the foot which occurs at birth in which one or both feet are twisted. The most common congenital deformation of the foot, occurring in 1 of 1,000 live births.
When will the ICD-10-CM Q66.0 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q66.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD code for club foot?
The ICD code Q668 is used to code Club foot. Club foot or clubfoot, also called congenital talipes equinovarus (CTEV), is a congenital deformity involving one foot or both. The affected foot appears to have been rotated internally at the ankle.
What is the ICD code for acute care?
Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code Q66.8 is a non-billable code.
What is a deformed foot?
A deformed foot in which the foot is plantarflexed, inverted and adducted. A deformity of the foot which occurs at birth in which one or both feet are twisted. The most common congenital deformation of the foot, occurring in 1 of 1,000 live births.
When will the ICd 10-CM Q66.89 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q66.89 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How many babies have clubfoot?
According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS), approximately one infant in every 1,000 births will have clubfoot, making it one of the more common congenital foot deformities. Boys are twice as likely as girls to have this condition, which can be detected with prenatal ultrasound.
When is clubfoot day?
There is even a World Clubfoot Day celebrated every year on June 3. The Ponseti Method consists of a series of casts, which are placed beginning shortly after birth. The baby’s foot is gently stretched and held in place with a long-leg cast.
Why is Ponseti's method of clubfoot surgery not very good?
Early in his career, Ponseti saw that the outcomes of clubfoot surgical treatments were not very good because patients (like me) had limited movement. Ponseti developed a treatment that makes the most of babies’ flexible ligaments. His method is widely accepted today, all over the world.
What is bracing after a tenotomy?
Bracing is required after the casting or tenotomy. The child is placed in shoes that are twisted outwards, with a bar in the middle. The bracing is very difficult for many parents to follow, and when not followed properly can result in the child requiring more surgery.
What are the codes for HCPCS level 2?
For the bracing, the following HCPCS Level II supply codes may be used, as prescribed by the physician:#N#L1960 Ankle foot orthosis, posterior solid ankle, plastic, custom fabricated#N#L2280 Addition to lower extremity, molded inner boot#N#L2300 Addition to lower extremity, abduction bar (bilateral hip involvement), jointed, adjustable#N#L2768 Orthotic side bar disconnect device, per bar#N#Bil ling these codes depends on your facility’s DME status, and if you are billing for the orthotic providers that create the boots and ankle-foot orthosis (AFOs), also known as foot-drop braces. As the child grows, new AFOs and bigger bars will be required and may be billed, accordingly.
Is clubfoot a congenital disease?
Clubfoot (talipes equinovarus) is a common congenital disorder, and one that has affected me personally. To help you better understand clubfoot, I’d like to share my experience and research, and some educational information about the condition.
Is clubfoot reversible?
If your providers treat clubfoot regularly, educate them to document “talipes equinovarus” only if that is truly the case, or make sure they select the correct code in the electronic health record. With proper treatment, many clubfoot cases are completely reversible.
What is the most common congenital deformity of the foot?
The most common congenital deformity of feet is TEV; however, there are other forms of clubfoot, specifically talipes calcaneovalgus (in which the ankle joint is dorsiflexed and the forefoot deviated outwards), and talipes calcaneovarus (in which the ankle joint is dorsiflexed and the forefoot deviated inwards).
Is clubfoot a postnatal condition?
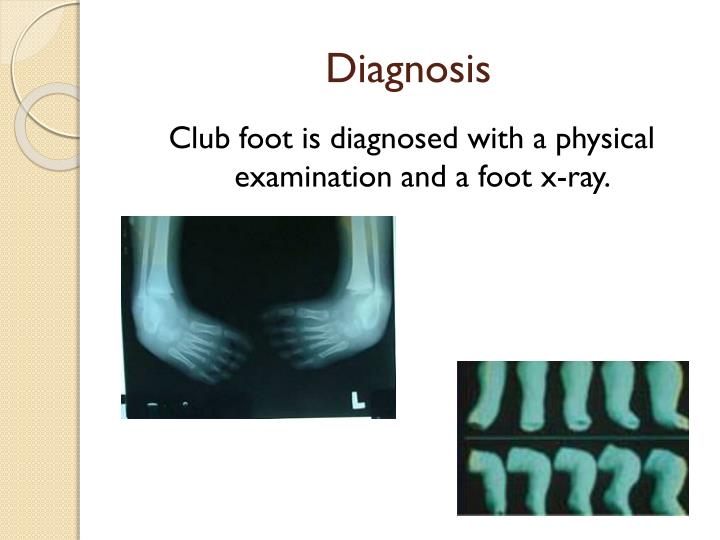
Postnatal. Clubfoot is readily diagnosed in the newborn examination. Cases should be followed and evaluated sequentially to assess the degree of severity and whether treatment other than manipulation is necessary. Sometimes other birth defects of the foot or leg might mimic clubfoot. For example, a deficiency of the tibial bone in the leg might look like a talipes. Imaging studies (typically, radiographs) might provide supplemental information to aid in diagnosis.
Can clubfoot be detected on ultrasound?
Prenatal. Clubfoot can be identified or suspected on prenatal ultrasound. However, it should not be included in birth defects surveillance data without postnatal confirmation. The primary utility of prenatal diagnosis of clubfoot is in its indication for additional evaluations for the genetic conditions and structural anomalies that are commonly associated with TEV.
Is TEV bilateral or unilateral?
TEV is bilateral in about 60% of cases, and when unilateral, TEV is slightly more common on the right side. Especially in the severe forms (fixed or rigid TEV), the calf muscles on the affected side are hypotrophic (smaller).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for fertility preservation
- 2. icd 10 code for muscle aches
- 3. icd 10 code for hemispheric cystic lesion
- 4. icd 9 code for skin tag removal
- 5. icd 10 code for compound nevus
- 6. icd 9 code for fracture of distal radius
- 7. icd 10 code for cut by chainsaw
- 8. icd 10 code for stenosis of right carotid artery
- 9. icd 10 code for ileum polyp
- 10. icd 10 code for acute thrombus left radial vein