What is ICD 10 code for severe persistent asthma?
Severe persistent asthma, uncomplicated. J45.50 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J45.50 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for chronic otitis media?
Otitis media, unspecified, unspecified ear
- H66.90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H66.90 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H66.90 - other international versions of ICD-10 H66.90 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for chronic ear infection?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H65.20 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Chronic serous otitis media, unspecified ear. Chronic serous otitis media; Otitis media (middle ear infection), chronic serous; Otitis media, chronic serosanguinous; Serosanguineous chronic otitis media. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H65.20.
How is acute otitis media diagnosed?
What a diagnosis means
- Acute otitis media. The diagnosis of "ear infection" is generally shorthand for acute otitis media. ...
- Otitis media with effusion. If the diagnosis is otitis media with effusion, the doctor has found evidence of fluid in the middle ear, but there are presently no signs or ...
- Chronic suppurative otitis media. ...
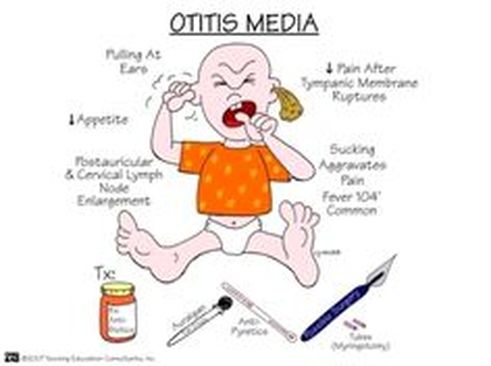
What is the ICD-10 code for bilateral otitis media?
ICD-10 code H66. 93 for Otitis media, unspecified, bilateral is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the ear and mastoid process .
What is otitis externa bilateral?
Otitis externa is a condition that causes inflammation (redness and swelling) of the external ear canal, which is the tube between the outer ear and eardrum. Otitis externa is often referred to as "swimmer's ear" because repeated exposure to water can make the ear canal more vulnerable to inflammation.
Is otitis externa unilateral or bilateral?
Unilateral otitis externa may suggest the presence of an underlying foreign body or neoplasia, although bilateral involvement with these causes is possible, and unilateral involvement can occur with symmetric disorders such as allergic dermatitis and ceruminous gland hyperplasia.
Can you have both otitis media and externa?
Middle ear infections If infected material from behind the eardrum leaks into the ear canal it will tend to cause otitis externa in addition to the otitis media. This condition may need oral antibiotics.
What is the ICD 10 code for otitis externa?
Unspecified otitis externa, unspecified ear H60. 90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H60. 90 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How is otitis externa diagnosis?
Diagnosis. Acute otitis externa is diagnosed clinically based on signs and symptoms of canal inflammation (Table 24 ; Figures 1 and 2). Presentation can range from mild discomfort, itching, and minimal edema to severe pain, complete canal obstruction, and involvement of the pinna and surrounding skin.
How do I document otitis externa?
The key physical finding of OE is pain upon palpation of the tragus (anterior to ear canal) or application of traction to the pinna (the hallmark of OE). Examination reveals erythema, edema, and narrowing of the external auditory canal (EAC), and a purulent or serous discharge may be noted (see the image below).
What is the most common cause of otitis externa?
The most common cause of otitis externa is a bacterial infection, although fungal overgrowth is a principal cause in 10 percent of cases. Otitis externa can also result from any of a broad range of noninfectious dermatologic processes.
What is canine otitis externa?
Otitis externa is an inflammatory disease of the external ear canal, including the ear pinna. Otitis externa may be acute or chronic (persistent or recurrent otitis lasting for 3 months or longer).
How can you tell the difference between otitis externa and otitis media?
The main symptom of otitis is pain, whether it is otitis externa or otitis media. If it is otitis externa, the pain may increase when the earlobe is pulled, which is generally not the case for otitis media. In young children, the pain can be expressed in these different signs, the child: frequently pulls on the ear.
What is the difference between acute otitis media and otitis media with effusion?
The position of the tympanic membrane is a key for differentiating acute otitis media and otitis media with effusion. In acute otitis media, the tympanic membrane is usually bulging. In otitis media with effusion, it is typically retracted or in the neutral position.
Can otitis media cause otitis externa?
Chronic otitis externa is caused by irritation from drainage through a perforated tympanic membrane. The underlying cause is chronic suppurative otitis media.
Popular Posts:
- 1. how do you code a stent for commom illiac artery in icd 10?
- 2. icd 10 code for jumping on a trampoline
- 3. icd-10 code for large volume of stool
- 4. icd 10 code for cyst above knee
- 5. icd 10 code for tick parts
- 6. icd 10 code for gastritis in preg 1st trim
- 7. icd 10 code for peripheral neuralgia
- 8. icd 10 code for post cardiac catheterization
- 9. icd 10 cm code for disease of lumbar
- 10. icd 10 code for subungual hematoma of toe, right