What is the ICD 10 code for spinal stenosis?
- 2016 (effective 10/1/2015): New code (first year of non-draft ICD-10-CM)
- 2017 (effective 10/1/2016): No change
- 2018 (effective 10/1/2017): Deleted code
- 2018 (effective 10/1/2017): New code
- 2019 (effective 10/1/2018): No change
- 2020 (effective 10/1/2019): No change
- 2021 (effective 10/1/2020): No change
- 2022 (effective 10/1/2021): No change
What is mild to moderate left foraminal stenosis?
Moderate neural foraminal narrowing refers to the gradual constriction of the foramina, which are the nerve passageways in the spinal column that has caused nerve (neural) compression. As we age, these small passageways can slowly close around the nerves they are supposed to protect, resulting in neck and back pain.
What would be appropriate ICD-10-CM code for lumbar stenosis?
M48.061 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Spinal stenosis, lumbar region without neurogenic claud.
What is mild bilateral foraminal stenosos?
Bilateral foraminal stenosis is where both foramina have become narrowed and the nerve roots on both sides of the spine are compressed.
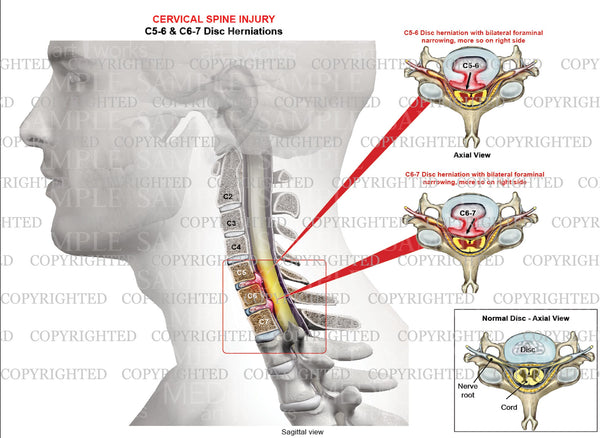
What is the ICD 10 code for foraminal stenosis lumbar?
Osseous and subluxation stenosis of intervertebral foramina of lumbar region. M99. 63 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M99.
Is foraminal stenosis the same as spinal stenosis?
Spinal stenosis and foraminal stenosis describe the narrowing of the canals in your spine. Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the canals through which the spinal cord travels, foraminal stenosis is the narrowing through which the spinal nerves travel before exiting the spine.
What is foraminal stenosis of lumbar region?
Foraminal stenosis is the narrowing or tightening of the openings between the bones in your spine. These small openings are called the foramen. Foraminal stenosis is a specific type of spinal stenosis. Nerves pass though the foramen from your spinal cord out to the rest of your body.
What is bilateral l5 foraminal stenosis?
Bilateral foraminal stenosis details when the spinal nerve root is compressed on both sides due to narrowing of the foramen that may be caused by an enlarged joint, a collapsed disc space or a foraminal herniated disc.
What is the difference between lateral recess stenosis and foraminal stenosis?
Stenosis may occur in the central spinal canal (central stenosis) where the spinal cord or cauda equina are located, in the tract where the nerve root exits the central canal (lateral recess stenosis) or in the lateral foramen (foraminal stenosis) where the individual nerve roots exit out to the body.
Is bilateral foraminal stenosis a disability?
Foraminal Stenosis can be one of the spine disorders that qualify for disability. The symptoms of foraminal stenosis can be severely disabling. The SSA uses a medical guide, which is called the Blue Book, to determine if a claimant medically qualifies for disability benefits.
What is bilateral Foraminotomy?
Intervertebral foramina; Spine surgery - foraminotomy; Back pain - foraminotomy; Stenosis - foraminotomy. Foraminotomy is surgery that widens the opening in your spine where nerve roots leave your spinal canal. You may have a narrowing of the nerve opening (foraminal stenosis).
Is it Neuroforaminal or neural foraminal?
Neuroforaminal stenosis is a narrowing that occurs in the foramina. Foramina are holes that are located on either side of the spinal column; they are smaller than the spinal canal. Spinal nerves exit the foramina after branching off from the spinal cord.
What is foraminal stenosis at L5 S1?
Foraminal Stenosis I5 S1 Condition Another common instance of foraminal stenosis, foraminal stenosis l5 s1, afflicts the L5 and S1 vertebrae in the lower spine. This is where the nerve roots branch away from the spinal cord and down the legs.
What is bilateral L5 S1?
The L5-S1 spinal motion segment, also called the lumbosacral joint, is the transition region between the lumbar spine and sacral spine in the lower back. In this region, the curvature of the spine changes from lumbar lordosis (forward curve) to sacral kyphosis (backward curve).
What are the symptoms of bilateral foraminal stenosis?
Symptoms of Bilateral Foraminal StenosisPain that develops over the course of time (often years)Muscle weakness, tingling, and numbness.Pins and needles sensation.Burning pain in the extremities.Headaches and brain fog (cervical)
What is bilateral foraminal encroachment?
Foraminal encroachment is a term used to describe degeneration of the spinal column which has caused an obstruction of the foramina. The foramina are open spaces on either sides of the vertebra where the spinal nerves pass on their way to other parts of the body.
What causes spinal stenosis?
Diseases such as arthritis and scoliosis can cause spinal stenosis, too. Symptoms might appear gradually or not at all. They include pain in your neck or back, numbness, weakness or pain in your arms or legs, and foot problems.
What causes the spinal canal to narrow?
Narrowing of the spinal canal. Your spine, or backbone, protects your spinal cord and allows you to stand and bend. Spinal stenosis causes narrowing in your spine. The narrowing can occur at the center of your spine, in the canals branching off your spine and/or between the vertebrae, the bones of the spine.
Can narrowing of the spine cause pain?
The narrowing puts pressure on your nerves and spinal cord and can cause pain.spinal stenosis occurs mostly in people older than 50. Younger people with a spine injury or a narrow spinal canal are also at risk. Diseases such as arthritis and scoliosis can cause spinal stenosis, too.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for attention seeking behavior
- 2. icd 10 code for medial meniscus tear
- 3. icd 10 code for rectal recent arterial bleed upper stomach
- 4. icd 10 code for lumbosacral ligament sprain
- 5. icd 10 cm code for underfeeding of newborn
- 6. what is the icd-10 code for liver mass
- 7. icd 10 code for pulmonary granulomas
- 8. icd 10 code for motorcycle driver hit by car
- 9. icd 10 code for initiation of oral contraceptives
- 10. icd 10 code for abnormal myocardial perfusion scan