What is the ICD 10 code for obstruction of the bladder?
2018/2019 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N32.0. Bladder-neck obstruction. 2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. N32.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for neuromuscular dysfunction of bladder?
Neuromuscular dysfunction of bladder, unspecified. 2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. N31.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM N31.9 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for urinary incontinence?
Other specified disorders of bladder. N32.89 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for urinary tract infection?
N32.89 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM N32.89 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N32.89 - other international versions of ICD-10 N32.89 may differ. Bleeding originating from the urinary bladder wall.
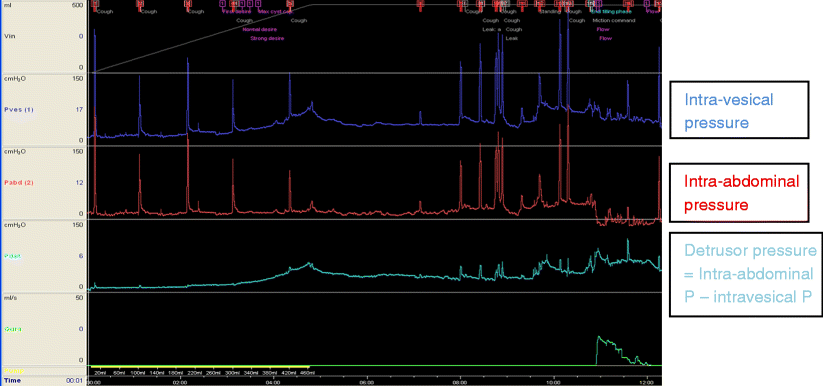
What is diagnosis code N39 41?
ICD-10 code N39. 41 for Urge incontinence is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What is neuromuscular dysfunction of bladder unspecified?
What is Neurogenic Bladder? Neurogenic Bladder, also known as Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction, is when a person lacks bladder control due to brain, spinal cord or nerve problems. Several muscles and nerves must work together for your bladder to hold urine until you are ready to empty.
Is bladder outlet obstruction the same as bladder neck obstruction?
Bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) is when the neck at the very bottom of your bladder gets blocked. The neck is where your bladder connects to your urethra, which carries urine (pee) out of your body. A blockage stops or slows down the flow of pee.
What is the ICD-10 code for voiding dysfunction?
Other difficulties with micturition The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R39. 19 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of R39.
What muscle contracts the bladder?
the detrusor muscleThe primary function of the detrusor muscle is to contract during urination to push the urine out of the bladder and into the urethra. The detrusor muscle will relax to allow the storage of urine in the urinary bladder.
What measures the contraction of urinary muscles?
Electromyography uses sensors to measure the electrical activity of the muscles and nerves in and around the bladder and the sphincters. The test uses electrode patches placed near the urethra and rectum to record electrical currents when muscles in the pelvic floor contract.
What is bladder contracture?
Bladder Neck: Contracture of the Bladder Neck. Contracture of the bladder neck is a rare condition that can occur in men after prostate surgery. Treatment could consist of dilation, which uses tubes to widen the urethra and its opening.
What is the ICD 10 code for bladder outlet obstruction?
ICD-10 code N32. 0 for Bladder-neck obstruction is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What is a chronic bladder outlet obstruction?
Bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) is a blockage at the base of the bladder. It reduces or stops the flow of urine into the urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries urine out of the body. The male and female urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
What is oliguria and anuria?
Oliguria is defined as having only 100 mL to 400 mL (3.3 to 13.5 oz) of urine per day and anuria (the most extreme of all of these) is defined as urine production of zero to 100 mL (0 to 3.3 oz) per day.
What is dysfunctional voiding?
Dysfunctional Voiding. With this type of dysfunction, the muscles that control the flow of urine out of the body don't relax completely, and the bladder never fully empties.
What is difficulty in voiding?
Voiding dysfunction can manifest as a wide range of symptoms which can include difficulty in emptying bladder, urinary hesitancy, slow or weak urine stream, urinary urgency, urinary frequency or dribbling of urine. Voiding dysfunction can be due to nerve dysfunction, non-relaxing pelvic floor muscles or both.
What is the term for inflammation of the bladder?
cystitis - inflammation of the bladder, often from an infection. urinary incontinence - loss of bladder control. interstitial cystitis - a chronic problem that causes bladder pain and frequent, urgent urination. bladder cancer.
How do doctors diagnose bladder problems?
doctors diagnose bladder diseases using different tests. These include urine tests, x-rays, and an examination of the bladder wall with a scope called a cystoscope. Treatment depends on the cause of the problem. It may include medicines and, in severe cases, surgery.
What is a neoplastic bladder?
A representative example of neoplastic bladder disorder is bladder carcinoma. Disease or disorder of the urinary bladder, the musculomembranous sac in the anterior of the pelvic cavity that serves as a reservoir for urine, which it receives through the ureters and discharges through the urethra.
What is urinary incontinence?
Urinary incontinence (UI) is defined by the International Continence Society as the complaint of any involuntary leakage of urine.3 One component of the ICS standardization divides pelvic floor muscle dysfunction symptoms into five groups: lower urinary tract symptoms, bowel symptoms, sexual function, prolapse, and pain.4 It is of note that many of these symptoms occur simultaneously and are relevant to each other. In this report, we will focus on lower urinary tract symptoms: urinary incontinence, urgency and frequency, slow or intermittent urine stream and straining, and feeling of incomplete emptying.
What is the best medication for urgency urinary incontinence?
Common medications to treat urgency or urgency urinary incontinence have historically included anticholinergics/antimuscarinic agents: oxybutynin, tolterodine, solifenacin, hyoscyamine, fesoterodine and darifenacin. These drugs are sold under the names of: Ditropan, Detrol, Vesicare, Enablex, Levbid, Cytospaz, Toviaz and Oxytrol. Anticholinergic/antispasmodic drugs are one of the first choices for OAB, as they have been proven to be the most effective agents in suppressing premature detrusor contractions, enhancing bladder storage, and relieving symptoms.9,10 Anticholinergic and antispasmodic agents act by antagonizing cholinergic muscarinic receptors, through which different parasympathetic nerve impulses evoke detrusor contraction Side effects of these medications can be bothersome and include dry mouth, headache, constipation, blurred vision, and confusion.1 Many patients do not continue medications beyond 9 months due to these bothersome side effects.11 A newer class of drugs, beta-3 adrenergic agonists, are mostly currently being used if anticholinergic agents are not effective. One medication, called mirabegron, sold under the name Myrbetriq, works differently than the anticholinergics, as it relaxes the bladder’s smooth muscle while it fills with urine, thereby increasing the bladder’s capacity to hold/store urine.12

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for on lovenox
- 2. icd 9 code for dyshidrosis
- 3. icd 10 code for left ankel pain
- 4. icd 10 code for rightelbow pain
- 5. icd 10 cm code for rib fractures
- 6. icd 10 code for history of amputation of finger on left hand
- 7. what icd 10 code would be used for exotropia
- 8. icd 10 code for history of klebsiella pneumoniae
- 9. icd 10 code for left foot hallux valgus
- 10. icd 10 code for history of cocaine abuse