Can keratosis pilaris be completely cured?
No treatment clears keratosis pilaris completely, but it can improve the condition temporarily. Emollients (moisturisers) can be of benefit. Creams containing salicylic acid, lactic acid and/or urea are more effective than emollients and can be purchased over the counter or obtained on prescription from the doctor.
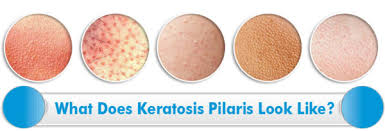
What is keratosis pilaris, and what does it look like?
What Does Keratosis Pilaris Look Like At Close Quarters? Keratosis pilaris under a microscope (a process known as histopathy) reveals a hardening of the outer skin layer and a proliferation of the epidermis cells. Some of the individual hair follicles also show signs of plugging.
Can cocoa butter help in keratosis pilaris?
You can use any body scrub and cocoa butter for that matter, but these are just the things I use. Within one week of doing this, my bumps have noticeably reduced and my skin has felt smoother. I still have “scarring” from the bumps, but I’m hoping the cocoa butter can help reduce the appearance of them.
How does keratosis pilaris affect the body?
Key points
- Keratosis pilaris is a very common and harmless skin condition that occurs when there is too much protein in the hair follicles.
- It is usually inherited from one or both parents.
- Keratosis pilaris causes the skin to appear blotchy and bumpy and can be itchy if it occurs with dry skin.
How do you describe keratosis pilaris?
Keratosis pilaris (ker-uh-TOE-sis pih-LAIR-is) is a common, harmless skin condition that causes dry, rough patches and tiny bumps, often on the upper arms, thighs, cheeks or buttocks. The bumps usually don't hurt or itch. Keratosis pilaris is often considered a variant of normal skin.
What is the ICD-10 code for skin discoloration?
L81. 9 - Disorder of pigmentation, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
What is the code for cyanotic?
ICD-10 code R23. 0 for Cyanosis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is diagnosis code l989?
ICD-10 code: L98. 9 Disorder of skin and subcutaneous tissue, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10 code for keratosis pilaris?
Acquired keratosis [keratoderma] palmaris et plantaris L85. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM L85. 1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for seborrheic keratosis?
ICD-10 code L82 for Seborrheic keratosis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue .
What is the ICD-10 code for code blue?
Cardiac arrest, cause unspecified I46. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I46. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for cyanosis?
ICD-10 code: R23. 0 Cyanosis | gesund.bund.de.
What does the term cyanotic mean?
Definition of cyanotic : marked by or causing a bluish or purplish discoloration (as of the skin and mucous membranes) due to deficient oxygenation of the blood : relating to or affected with cyanosis On arrival at the emergency room, the patient was cyanotic and unconscious with labored respirations at 40/min.—
What is the ICD-10 code for actinic keratosis?
ICD-10 code L57. 0 for Actinic keratosis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue .
What is skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders?
Panniculitis. Panniculitis is a group of conditions that causes inflammation of your subcutaneous fat. Panniculitis causes painful bumps of varying sizes under your skin. There are numerous potential causes including infections, inflammatory diseases, and some types of connective tissue disorders like lupus.
What is the ICD-10 code for folliculitis?
ICD-10-CM Code for Folliculitis decalvans L66. 2.
What should be included in clinical documentation of keratosis?
Clinical documentation of keratosis should include the type of keratosis—actinic or seborrheic—and whether the keratosis is inflamed ( or not otherwise specified). The location of the growths must be noted, as should contributing factors, such as tanning bed exposure.
What is AK in ICd 10?
Keratosis ICD-10 Coding. Actinic keratosis (AK) is a small, rough spot on the skin. It usually occurs in middle-aged and older individuals, and may also be called senile keratosis or solar keratosis. AK is a premalignant lesion, which may develop into skin cancer. Although clinicians generally can diagnose AK by examining the area, ...
Is SK a benign disease?
Seborrheic keratosis (SK) may present as single or multiple elevated plagues and nodules that are often hyper-pigmented (darkened) with an overgrown, greasy surface. This type of SK is benign, of unknown cause, and involves only the top layers of the epidermis.
What is a skin disease?
Clinical Information. A chronic skin disease characterized by small follicular papules, disseminated reddish-brown scaly patches, and often, palmoplantar hyperkeratosis. The papules are about the size of a pin and topped by a horny plug.
What is a papule?
The papules are about the size of a pin and topped by a horny plug. A rare cutaneous disorder of unknown etiology characterized by the presence of reddish-orange scaly plaques, palmoplantar keratoderma, keratotic follicular papules, and confluent erythematous areas with areas of normal skin between the lesions.
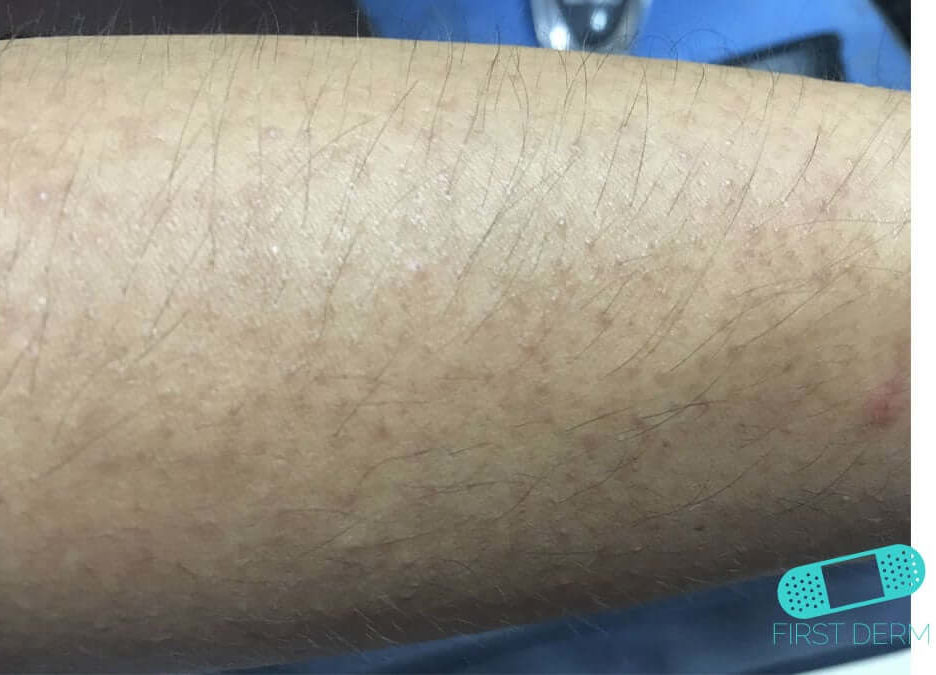
Diagnosis
- Actinic keratosis (AK) is a small, rough spot on the skin. It usually occurs in middle-aged and older individuals, and may also be called senile keratosis or solar keratosis. AK is a premalignant lesion, which may develop into skin cancer. Although clinicians generally can diagnose AK by examining the area, biopsy may be necessary. Clinical documentation of keratosis should include the type …
Treatment
- AK typically develops on fair-skinned individuals, those with excessive sun exposure, or individuals with indoor tanning radiation. Treatment for AK is generally straightforward, and may include cryosurgery (freezing), scraping, and photodynamic therapy.
Symptoms
- Seborrheic keratosis (SK) may present as single or multiple elevated plagues and nodules that are often hyper-pigmented (darkened) with an overgrown, greasy surface. This type of SK is benign, of unknown cause, and involves only the top layers of the epidermis. No treatment is necessary, although there is risk of irritation or infection caused by friction (such as when clothing rubs the …
Categories
- Category L57.0 describes AK, including keratosis not otherwise specified, solar keratosis, and senile keratosis. Subcategory L57.0 requires that you use an additional code to identify the source of the ultraviolet radiation.
Clinical significance
- Subcategory L82 contains codes for SK, and includes dermatosis papulosa nigra and Leser-Trelat disease.
Miscellaneous
- L82 also contains an Excludes II note telling the user that codes for seborrheic dermatitis (L21-) may be cited, in addition to the L82 code, if both are supported in documentation.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for dental pain
- 2. icd 10 code for pseudomembranous colitis
- 3. icd 10 code for right knee traumatic arthritis
- 4. icd 9 code for lumbar spine strain pain
- 5. icd 10 code for fourth middle phalanx fracture
- 6. icd 10 code for osteoarthritis bilat knees
- 7. icd 10 code for gave with bleeding
- 8. icd 10 code for decreased fetal movement
- 9. icd 10 code for packing removal
- 10. icd 9 code for cyclic vomiting syndrome