What does brain edema mean?
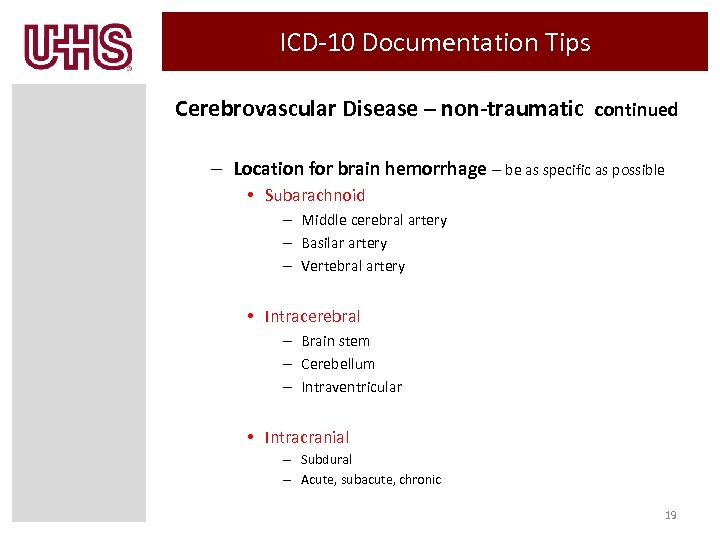
· Diagnosis Index entries containing back-references to G93.6: Edema, edematous (infectious) (pitting) (toxic) R60.9 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R60.9 Edema, unspecified 2016 2017 2018... Effusion cerebrospinal - see also Meningitis vessel G93.6 brain G93.6 (serous) cerebral G93.6 intracranial G93.6 ...
What is the ICD 10 code for edema?
Type 1 Excludes cerebral edema due to birth injury P11.0 traumatic cerebral edema S06.1
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S06.1X7A. Traumatic cerebral edema with loss of consciousness of any duration with death due to brain injury prior to regaining consciousness, initial encounter. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S06.2. Diffuse traumatic brain injury.
What is the diagnosis code for brain tumor?
ICD-10 code G93.6 for Cerebral edema is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash. Request a Demo 14 Day Free Trial Buy Now Official Long Descriptor Cerebral edema Excludes1: cerebral edema due to birth injury ( P11.0)
What is G93 89 diagnosis?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G93. 89: Other specified disorders of brain.
What is an edema in the brain?
Introduction. The most basic definition of cerebral edema is swelling of the brain. It is a relatively common phenomenon with numerous etiologies. Cerebral edema categorizes into either vasogenic, cellular, osmotic, and interstitial causes.
Is cerebral edema a brain tumor?
Cerebral edema associated with brain tumors is extremely common and can occur in both primary and metastatic tumors. The edema surrounding brain tumors results from leakage of plasma across the vessel wall into the parenchyma secondary to disruption of the blood-brain barrier.
What are the 3 types of cerebral edema?
Cerebral edema occurs due to an increase in brain fluid content and can be divided into three forms: cytotoxic, vasogenic and interstitial, or a combination (Table II).
What are the two types of cerebral edema?
Cerebral edema has been traditional classified into two major sub-types: cytotoxic and vasogenic cerebral edema.
What is the difference between cerebral edema and hydrocephalus?
Cerebral oedema can be classified as the tangible swelling produced by expansion of the interstitial fluid volume. Hydrocephalus can be succinctly described as the abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the brain which ultimately leads to oedema within specific sites of parenchymal tissue.
What is the difference between cerebral edema and increased intracranial pressure?
Cerebral edema contributes to an increase in intracranial volume. Global cerebral edema primarily results in a global rise in ICP, while focal cerebral edema can result in cerebral herniation syndromes with or without ICP elevation.
Is cerebral edema a traumatic brain injury?
Cerebral edema (CE) and resultant intracranial hypertension are associated with unfavorable prognosis in traumatic brain injury (TBI). CE is a leading cause of in-hospital mortality, occurring in >60% of patients with mass lesions, and ∼15% of those with normal initial computed tomography scans.
How is brain edema treated?
What are the treatment options?Medication. Depending on the severity of your condition and the underlying cause, doctors may prescribe you medication to help reduce swelling and prevent blood clots.Osmotherapy. When your brain swells, it accumulates excess fluid. ... Hyperventilation. ... Hypothermia. ... Ventriculostomy. ... Surgery.
Is mass effect the same as cerebral edema?
Intracranial pathological processes, such as masses and haemorrhage, can cause mass effect. Surrounding cerebral oedema often worsens mass effect, and in the case of infarcts, which are not in themselves 'space-occupying', the mass effect is solely due to oedema.
What does brain edema look like on CT?
In vasogenic edema, CT shows hypodense frond-like regions located within the white matter. This edema surrounds the underlying pathological lesion. The edema may be quite extensive in relation to the size of the lesion.
Is vasogenic edema the same as cerebral edema?
Vasogenic cerebral edema refers to a type of cerebral edema in which the blood brain barrier (BBB) is disrupted (cf. cytotoxic cerebral edema, where the blood-brain barrier remains intact). It is an extracellular edema which mainly affects the white matter via leakage of fluid from capillaries.
What is brain edema?
BRAIN EDEMA-. increased intracellular or extracellular fluid in brain tissue. cytotoxic brain edema swelling due to increased intracellular fluid is indicative of a disturbance in cell metabolism and is commonly associated with hypoxic or ischemic injuries see hypoxia brain. an increase in extracellular fluid may be caused by increased brain capillary permeability vasogenic edema an osmotic gradient local blockages in interstitial fluid pathways or by obstruction of csf flow e.g. obstructive hydrocephalus. from childs nerv syst 1992 sep; 86:301 6
When was the ICd 10 code implemented?
FY 2016 - New Code, effective from 10/1/2015 through 9/30/2016 (First year ICD-10-CM implemented into the HIPAA code set)
How to correct brain damage?
In some cases, damage is permanent. In other cases, treatments such as surgery, medicines, or physical therapy can correct the source of the problem or improve symptoms.
What is the G93.6 code?
G93.6 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of cerebral edema. The code G93.6 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is the synonym for brain lesion?
Approximate Synonyms. Brain lesion. Brain mass. Lesion of brain. Clinical Information. A non-neoplastic or neoplastic disorder that affects the brain. Pathologic conditions affecting the brain, which is composed of the intracranial components of the central nervous system. Pathologic conditions affecting the brain, ...
What are the pathologic conditions of the brain?
Pathologic conditions affecting the brain, which is composed of the intracranial components of the central nervous system. This includes (but is not limited to) the cerebral cortex; intracranial white matter; basal ganglia; thalamus; hypothalamus; brain stem; and cerebellum. The brain is the control center of the body.
When will the ICD-10 G93.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G93.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the code for cerebral edema?
Non-traumatic conditions, which are accompanied by cerebral edema, get the code G93.6, from the Diseases of the nervous system section. G93.6 has two principal diagnosis MCC exclusions – itself and G93.82, Brain death.
Is there an uptick in clinical validation denials for cerebral edema?
You may be noticing an uptick in clinical validation denials for cerebral edema. Here’s my take on this.
Can cerebral edema be woven into notes?
Have cerebral edema be woven into the notes repeatedly, not just once in a single note. They should link the treatment and monitoring with the condition (e.g., “will start on Decadron for the cerebral edema and get repeat MRI in two weeks.”). It should also be present in the discharge summary.
Should cerebral edema be picked up?
But should it always be picked up? This depends on whether the provider considers it clinically significant, and whether it meets the criteria for a valid secondary diagnosis. The provider will often not distinguish between the contribution of the underlying condition and the resultant cerebral edema or brain compression. The patient is undergoing an urgent decompressive surgery – and maybe it wouldn’t have been as urgent if the cerebral edema hadn’t been present. It is easier to identify when the treatment is Decadron or mannitol, because those are specifically targeted for edema.
Can a patient have non-traumatic cerebral edema?
It often magnifies or complicates the clinical features of the primary underlying condition. The only Excludes 1 instructions are that a patient can’t have non- traumatic and traumatic cerebral edema concomitantly.
Is cerebral edema a component of brain tumor?
However, the development of cerebral edema isn’t invariable; for instance, not all brain tumors have surrounding vasogenic edema. It is an additional facet or component, and therefore, it is eligible for additional coding. It often magnifies or complicates the clinical features of the primary underlying condition.
Does cerebral edema happen randomly?
Cerebral edema doesn’t develop randomly, or out of the blue. Conditions that cause cerebral edema include traumatic brain injuries, ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, brain tumors, infection, altitude sickness, electrolyte derangements, and toxins. However, the development of cerebral edema isn’t invariable; for instance, ...
Why did the coder not assign a code for cerebral edema?
Audit Considerations & Strategies. The coder originally did not assign a code for the cerebral edema because it was not treated ( e.g. high-dose steroids (Decadron), diuretics (Mannitol), intubation, transfer to the ICU, etc.)
Is cerebral edema treated?
Even though the cerebral edema was not treated, it was evaluated and could have contributed to the decision for comfort care only
Is cerebral edema mild or moderate?
If cerebral edema is noted as “mild” or “without mass effect”, we recommend either querying to clarify the clinical relevance or not coding the condition at all. If cerebral edema is present with “mass effect” or when there is “midline-shift” potentially causing “brain compression (MCC)” or “brain herniation” ...

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for contact bleeding cervix
- 2. icd 10 diagnosis code for bilateral shoulder pain
- 3. icd 10 code for history subarachnoid hemorrhage
- 4. icd 10 cm code for splenic artery aneurysm
- 5. icd 9 code for atypical lobular hyperplasia
- 6. icd 10 code for diabetes mellitus complicated by peripheral neuropathy
- 7. icd 9 code for chest wall hematoma
- 8. icd 10 code for yeast infection groin area
- 9. icd 10 code for behavioral disorder
- 10. icd 10 cm code for mouth sores