Brittle Diabetes Mellitus Icd 10
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus With Hyperglycemia. E10.65 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a...
- Icd-10 Codes For Diabetes Mellitus Type 1. List of ICD-10cm Codes for Diabetes Mellitus Type 1. You can also checkout...
- Brittle Diabetes (labile Diabetes). Tweet Brittle diabetes mellitus (or labile diabetes) is a...
How to code diabetes correctly?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E10.620 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Type 1 diabetes mellitus with diabetic dermatitis. Dermatitis due to type 1 diabetes mellitus; Diabetes type 1 with diabetic dermatitis; Type 1 diabetes mellitus with diabetic necrobiosis lipoidica. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E10.620.
What is ICD 10 for poorly controlled diabetes?
2016 (effective 10/1/2015): New code (first year of non-draft ICD-10-CM) 2017 (effective 10/1/2016): No change 2018 (effective 10/1/2017): No change 2019 (effective 10/1/2018): No change 2020 (effective 10/1/2019): No change 2021 (effective 10/1/2020): No change 2022 (effective 10/1/2021): No ...
What is considered prediabetes A1C ICD 10?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2016 (effective 10/1/2015): New code (first year of non-draft ICD-10-CM) 2017 (effective 10/1/2016): No change 2018 (effective 10/1/2017): No change 2019 (effective 10/1/2018): No change 2020 (effective 10/1/2019): No change 2021 (effective 10/1/2020): No change 2022 (effective 10/1/2021): No ...
What is ICD 10 code for insulin dependent diabetes?
Oct 12, 2010 · Best answers. 0. Oct 11, 2010. #2. Brittle diabetes is exceptionally difficult to control, marked by alternating episodes of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Frequent adjustments of dietary intake and insulin dosage are required. However, even brittle diabetes can be "controlled" with vigilance on the part of the patient and/or caregivers.
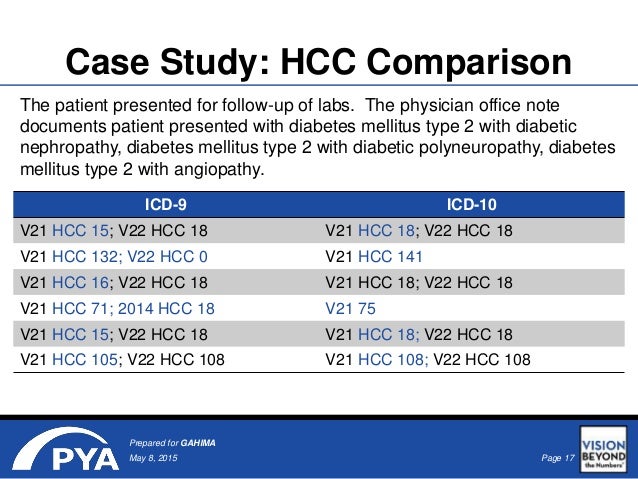
What is the ICD-10 code for brittle type 1?
64.
What is brittle type 1 diabetes?
Brittle diabetes is also known as unstable diabetes or labile diabetes, meaning that blood sugar swings can be severe and frequent. This version is rare and happens mainly to people with Type 1 diabetes. Talk to your healthcare provider about management methods, possibly including special equipment.Mar 26, 2021
What is the ICD-10 code for type 2 diabetes?
ICD-10 Code: E11* – Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
When do you code Z79 4?
ICD-10 Code Z79. 4, Long-term (current) use of insulin should be assigned to indicate that the patient uses insulin for Type 2 diabetes mellitus (Category E11* codes). Z79. 4 should NOT be used for Type 1 diabetes mellitus (Category E10* codes).
Why is it called brittle diabetes?
Brittle diabetes is the name doctors give diabetes that is especially hard to control. It's also called “labile” diabetes. The words brittle and labile can both mean “unstable” or “easily changed.”Jan 27, 2022
Is there such a thing as a brittle diabetic?
Brittle diabetes is a severe form of diabetes. Also called labile diabetes, this condition causes unpredictable swings in blood sugar (glucose) levels. These swings can affect your quality of life and even lead to hospitalization. Thanks to advances in diabetes management, this condition is uncommon.
What is the diagnosis code for diabetes?
E08. 10 Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition... E08.
What is ICD-10 code for insulin dependent diabetes?
Z79. 4 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What type of diabetes are included in Category E11?
TABLE 3.CodeUsed to report type 2 diabetes with:E11.2XWith kidney complicationsE11.21With diabetic nephropathyE11.22With diabetic chronic kidney diseaseE11.29With other diabetic kidney complications47 more rows
When do you code E11 8?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus with unspecified complications 8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11. 8 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for insulin use?
4.
Can you code E11 21 and E11 22 together?
The incorrect portion of the response came as an aside at the end, where it was stated that “it would be redundant to assign codes for both diabetic nephropathy (E11. 21) and diabetic chronic kidney disease (E11. 22), as diabetic chronic kidney disease is a more specific condition.” It is true you wouldn't code both.Nov 18, 2019
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as E10. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition (.
What does it mean when your blood sugar is too high?
diabetes means your blood glucose, or blood sugar, is too high. With type 1 diabetes, your pancreas does not make insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get into your cells to give them energy. Without insulin, too much glucose stays in your blood.
What is the ICd 10 code for diabetes mellitus?
E10.65 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E10.65 - other international versions of ICD-10 E10.65 may differ. Approximate Synonyms Diabetes type 1 with hyperglycemia Hyperglycemia due to type 1 diabetes mellitus ICD-10-CM E10.65 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v35.0): Code History 2016 (effective 10/1/2015): New code (first year of non-draft ICD-10-CM) 2017 (effective 10/1/2016): No change 2018 (effective 10/1/2017): No change Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015 require the use of ICD-10-CM codes. Continue reading >>
Why is my blood glucose level unstable?
Other causes of unstable blood glucose levels include emotional stress, eating disorders, drug or alcohol use, malabsorption, gastroparesis, and celiac disease.
What is the disease of diabetes mellitus?
A subtype of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by insulin deficiency. It is manifested by the sudden onset of severe hyperglycemia, rapid progression to diabetic ketoacidosis, and death unless treated with insulin. The disease may occur at any age, but is most common in childhood or adolescence. diabetes means your blood glucose, or blood sugar, is too high. With type 1 diabetes, your pancreas does not make insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get into your cells to give them energy. Without insulin, too much glucose stays in your blood. Over time, high blood glucose can lead to serious problems with your heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves, and gums and teeth. Type 1 diabetes happens most often in children and young adults but can appear at any age. Symptoms may include being very thirsty urinating often feeling very hungry or tired losing weight without trying having sores that heal slowly having dry, itchy skin losing the feeling in your feet or having tingling in your feet having blurry eyesight a blood test can show if you have diabetes. If you do, you will need to take insulin for the rest of your life. Diabetes mellitus characterized by insulin deficiency, sudden onset, severe hyperglycemia, rapid progression to ketoacidosis, and death unless treated with insulin. The disease may occur at any age, but is most common in childhood or adolescence. Subtype of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by insulin deficiency; it is manifested by the sudden onset of severe hyperglycemia, rapid progression to diabetic ketoacidosis, and death unless treated with insulin; the disease may occur at any age, but is most common in childhood or adolescence. Continue reading >>
What is brittle diabetes?
Brittle diabetes is a term that is sometimes used to describe hard-to-control diabetes (also called labile diabetes). It is characterized by wide variations or “swings” in blood glucose (sugar) in which blood glucose levels can quickly move from too high (hyperglycemia) to too low (hypoglycemia). These episodes are hard to predict and can disrupt quality of life. They can require frequent or lengthy hospitalizations and can be fatal. People with type 1 diabetes are at greatest risk. While many people with type 1 diabetes experience hypoglycemia, only a small proportion of people with type 1 diabetes experience the frequent blood glucose swings described as “brittle.” People with long-standing type 2 diabetes may also have difficulty controlling blood glucose, but few have these frequent swings. People of any age with diabetes can be affected with these frequent ups and downs in blood glucose levels. Some research suggests that women may be affected more often than men. Frequent episodes of hypoglycemia can lead to hypoglycemic unawareness and make the condition worse. Keeping diabetes under good control for at least several weeks can restore hypoglycemic awareness. New technologies such as continuous glucose monitors and insulin pumps may help improve control.In diabetes, many factors can trigger frequent changes in blood glucose levels. For example, people who don’t test blood glucose or take diabetes medications as prescribed often experience significant fluctuations in blood glucose levels. Other causes of unstable blood glucose levels include emotional stress, eating disorders, drug or alcohol use, malabsorption, gastroparesis, and celiac disease. The development of new treatments for diabetes has made it easier for most people to control their blood gluco Continue reading >>
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 Excludes note is a pure excludes. It means 'NOT CODED HERE!' An Excludes1 note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as the code above the Excludes1 note. An Excludes1 is used when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. A type 2 Excludes note represents 'Not included here'. An Excludes2 note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When an Excludes2 note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code together. A code also note instructs that 2 codes may be required to fully describe a condition but the sequencing of the two codes is discretionary, depending on the severity of the conditions and the reason for the encounter. Certain conditions have both an underlying etiology and multiple body system manifestations due to the underlying etiology. For such conditions the ICD-10-CM has a coding convention that requires the underlying condition be sequenced first followed by the manifestation. Wherever such a combination exists there is a 'use additional code' note at the etiology code, and a 'code first' note at the manifestation code. These instructional notes indicate the proper sequencing order of the codes, etiology followed by manifestation. In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, 'in diseases classified elsewhere.' Codes with this title area component of the etiology / manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code. 'In disease Continue reading >>

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for renal agenesis
- 2. icd 10 code for snow skiing accident
- 3. icd code for sprain of right wrist
- 4. icd 10 code for kidney cyst pain
- 5. icd 10 code for erectile dysfunction after prostatectomy
- 6. 2017 icd 10 code for fetal demise
- 7. icd 10 code for classical hodgkin lymphoma
- 8. icd 10 code for hip tenderness
- 9. icd 10 code for nause
- 10. icd 10 code for superficial thrombosis left cephalic vein