What are C diff toxins?
Oct 01, 2021 · Enterocolitis due to Clostridium difficile, not specified as recurrent. A04.72 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM A04.72 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of A04.72 - other international versions of ICD-10 A04.72 …
What is the diagnosis code for C diff?
A04.71. Enterocolitis due to Clostridium difficile, recurrent. A04.72. Enterocolitis due to Clostridium difficile, not specified as recurrent. View More. The above codes may be potentially relevant when billing for DIFICID and its administration.
When to test for C diff?
Oct 01, 2021 · Enterocolitis due to Clostridium difficile, recurrent. 2018 - New Code 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. A04.71 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM A04.71 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How to collect stool sample for C diff?
Oct 01, 2021 · Enterocolitis due to Clostridium difficile. 2016 2017 2018 - Converted to Parent Code 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code. A04.7 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM A04.7 became effective on October 1, 2021.
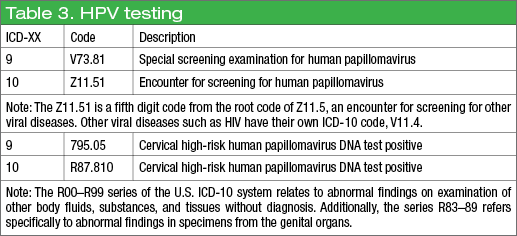
What is the ICD-10-CM code for C. diff?
Enterocolitis due to Clostridium difficile, not specified as recurrent. A04. 72 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Does C. diff have toxin?
C. diff is a spore-forming, Gram-positive anaerobic bacillus that produces two exotoxins: toxin A and toxin B. It is a common cause of antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) and accounts for 15 to 25% of all episodes of AAD.Jul 20, 2021
What is toxin negative C. diff?
A negative test result for the C. difficile toxin gene likely indicates that the person's diarrhea and related symptoms are not due to toxin-producing C. difficile. Negative test results for both the bacteria and the toxin may mean that the diarrhea and other symptoms are being caused by something other than C.Nov 9, 2021
What does C. diff toxin positive mean?
If tests for C. difficile toxin gene and C. difficile toxin are positive, it is likely that the person's diarrhea and related symptoms are due to the presence of toxin-producing C. difficile.
What toxin does C. difficile produce?
difficile strains produce two major toxins, i.e., TcdA and TcdB, generated by the genes tcdA and tcdB within the organism's Pathogenicity loci (PaLoc), while certain C. difficile strains may produce a binary toxin called C. difficile transferase (CDT), closely related to the Clostridium perfringens binary toxin.May 3, 2016
What is C. difficile toxin NAA?
Toxigenic C difficile is a major cause of antibiotic-associated diarrhea and colitis and is the causative agent for virtually all cases of pseudomembranous colitis. Although about 2% of normal healthy adults are colonized with C difficile, many patients acquire this organism through nosocomial infection.
What is the difference between C. diff antigen and toxin?
difficile antigen = this test detects vegetative C. difficile bacteria but does not detect toxin which is the disease causing component of CDI. The CDI antigen has a very high negative predictive value (98-99%) and a negative result rules out CDI. C.
What is C difficile toxin PCR?
Clostridium difficile PCR is designed to amplify 2 different genes that are specific to toxigenic strains of C difficile: tcdB, which encodes for toxin B, and tcdC, which encodes for a toxin regulatory pathway.
What is the toxin test?
This is a test to look at your bowel movement (stool) for harmful substances called toxins produced by Clostridioides (formerly Clostridium) difficile bacteria. Your gastrointestinal (GI) tract is home to many healthy bacteria, and sometimes C.
Which is worse C. diff toxin A or B?
Only toxin-producing C diff strains cause disease and toxins A and B (encoded by the tcdA and tcdB genes) appear to play important roles. The toxins are pro-inflammatory enterotoxins, but toxin B is a more potent cytotoxin.Jun 1, 2011
How is Clostridium difficile diagnosis?
The simplest way to detect C. difficile is through a stool test, in which you provide a sample in a sterile container given to you at your doctor's office or a lab. A pathologist, a doctor who studies diseases in a laboratory, determines whether the sample has signs of C. difficile.
What is C difficile toxins A and B EIA?
C difficile can produce two toxins, designated A and B, that have pathogenic effects in humans. Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis has been shown to result from the action of these two toxins.
What is C diff?
Clostridium Difficile Enterocolitis (C. diff) is a diagnosis that coders see a lot these days. This is a bacteria that causes inflammation in the large intestine (colitis) and may cause watery diarrhea, fever, nausea and abdominal pain. C. diff causes antibiotic-associated colitis by colonizing the intestine after the normal gut flora is altered by ...
Where do bacteria get infected?
The bacteria is shed in feces and people may become infected if they touch a surface that has been contaminated ( e.g., commode, bathtub) and then touch their mouth or mucous membranes.
What are the two toxins in C difficile?
C difficile can produce two toxins, designated A and B , that have pathogenic effects in humans. Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis has been shown to result from the action of these two toxins. This disease has been associated with clindamycin use but it is now recognized that pseudomembranous colitis can follow administration of virtually any antibiotic. More than 70% of the cases in a large series were associated with cephalosporin therapy. 1 The clinical spectrum of antibiotic-induced syndromes caused by C difficile includes patients with symptoms of acute abdomen with little or no diarrhea, as well as cases with fulminant life-threatening diarrhea. Nosocomial transmission and reinfection with different strains occurs as do spontaneous cases without prior antimicrobial therapy. In cases where cessation of antibiotic therapy does not produce a response, specific therapy with oral vancomycin, metronidazole, or oral bacitracin may be effective. Detection of the toxins produced by C difficile (rather than culture of the organism) is important in the determining therapy of this potentially fatal disease. The routine use of culture does not seem appropriate because of the costs and the high rate of recovery of strains which do not produce toxin.
How long should a specimen be refrigerated?
Specimen should be kept refrigerated and transported to the laboratory within 24 hours of collection. If a longer period is required, the specimen should be frozen at -70°C on dry ice.
Is there a preservative in a sterile screw cap?
Sterile screw-cap container or stool transport (Para-Pak® white clean vial), no preservative. “Cool Whip” containers, denture cups, or other similar containers often leak or even explode during transport and may be rejected by the laboratory.
Includes
If the GDH Antigen is detected and the Toxin A and B are not detected or the GDH Antigen is not detected and the Toxin A and B are detected, Clostridium difficile Toxin B, Qualitative, Real-Time PCR will be performed at an additional charge (CPT code (s): 87493).
Collection Instructions
Collect fresh stool in sterile, leak-proof container without media, preservative, or metal ion. For patients requiring the use of diapers, first line the diaper with clean plastic to prevent absorption. Then transfer 5 grams or 5 mL of the stool specimen from the plastic lined diaper to the sterile container.#N#Do not submit the diaper itself.
Reject Criteria
Formed stool • Stool submitted in transport media or swab • Rectal swab • Unfrozen stool >72 hours old • Received room temperature
Setup Schedule
Collect fresh stool in sterile, leak-proof container without media, preservative, or metal ion. For patients requiring the use of diapers, first line the diaper with clean plastic to prevent absorption. Then transfer 5 grams or 5 mL of the stool specimen from the plastic lined diaper to the sterile container.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for acne eruption nose
- 2. 2016 icd 10 code for hallux valgus
- 3. icd 10 code for elevated wbcs
- 4. icd 10 code for personal history of non hodgkin's lymphoma
- 5. icd 10 code for genital lesions
- 6. icd 10 code for polymyositis
- 7. icd 10 code for hepatomegally
- 8. icd-10 code for heavy metal toxicity
- 9. icd 1 0 code for vaginal ca
- 10. icd 10 code for work stress